2. 中国地质大学北京地球科学与资源学院, 北京 100083;
3. 国土资源部矿产勘查技术指导中心, 北京 100120;
4. 南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室, 地质流体研究所, 地球科学与工程学院, 江苏 南京 210093
2. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
3. Technical Guidance Center for Mineral Resources Exploration, Ministry of Land and Resources, Beijing 100120, China;
4. State Key Laboratory for Mineral Deposits Research, Institute of Geo-fluids, School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
浙江平水铜矿是浙江省最大的铜矿床,为典型的火山成因块状硫化物矿床(VMS),其位于钦杭成矿带北东段浙西北地区[1]。钦杭成矿带大致自西南端的广西钦州湾、经湘东和赣中延伸到东北端浙江杭州湾,整体呈北东向反S 状弧形展布,全长近2000 km,宽100~150 km。钦杭结合带不仅是一条巨型的构造-岩浆活动带,而且也是有利的成矿作用带。在这条长约2000 km 的古板块结合带上,已探明的大、中型矿床达400 余处,其中包括德兴、银山、金山、永平、东乡、芙蓉、黄沙坪、柿竹园、芙蓉、锡矿山、水口山、黄沙坪、东坡、佛子冲等大型—超大型金属矿床(田)[2, 3, 4]。浙西北地区也位于成矿地质条件优越的钦杭成矿带北东段,但是,区内目前仅发现了中型的平水铜矿、小型的建德铜矿和小型的璜山金矿等;浙西北地区矿化异常和矿化点非常发育,具有进一步寻找大型矿床的潜力。平水铜矿已连续开采了30 余年,前人对平水铜矿在地质特征、成矿流体、矿床成因及成岩成矿年代学等方面已经进行了大量、详细的研究[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12],但主要集中在矿床成因和成矿模式等方面;而在某些方面研究依旧薄弱,制约区域找矿,如:与成矿关系密切的细碧角斑岩的成岩时代以及成矿构造背景等方面仍没有最终确定。因此,本文选择浙西北地区的平水铜矿,对其细碧角斑岩采用精确的LA-MC-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 法进行年代学制约,揭示浙西北地区平水组细碧角斑岩的成岩时代和产出构造背景,为找矿勘查提供依据。
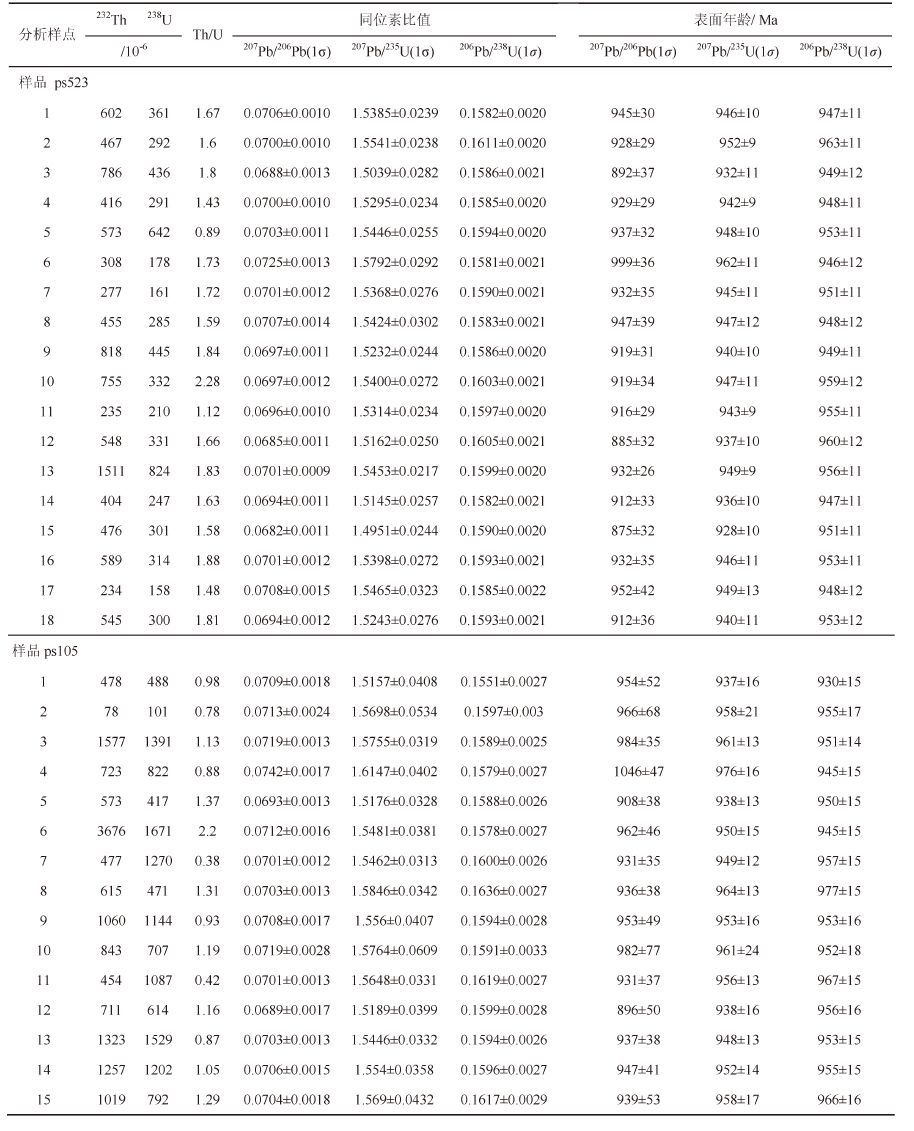
1 地质概况研究区位于钦杭成矿带北东段的绍兴平水地区(图1-a)。出露地层主要为中新元古界双溪坞群平水组,主要岩性为细碧角斑岩系,局部夹晶屑凝灰岩、泥质硅质岩、砂岩等。区域内出露的主要侵入岩为新元古代早期中酸性的西裘岩体(原称平水岩体)和桃红岩体。Ye et al.[13]对桃红和西裘2 个岩体的SHRIMP年代学和地球化学研究表明,桃红岩体((913±15) Ma)与西裘岩体((905±14) Ma)的形成时代基本一致,且均形成于活动大陆边缘环境,为同期幔源岩浆分异形成的典型Ⅰ 型花岗岩。本地区褶皱构造不发育,主要是由平水组构成的倾向北西的单斜构造;断裂较多,主要呈北东走向,如矿区内的F1断层(图1-b)。
|
图1 平水铜矿构造位置及地质简图(据文献[11, 12]修改)a—构造背景示意图; b—平水铜矿矿床地质简图; c—剖面图 Fig.1 Tectonic background schematic map and geological sketch map of the Pingshui copper deposit(modified after references [11, 12])a-Tectonic background schematic map; b-Geological sketch map of the Pingshui copper deposit; c-Geological section |
平水铜矿矿体产于平水组火山旋回第一旋回和第二旋回的间隙期内,位于第一旋回上部的火山岩中,直接容矿岩石是一套细碧角斑岩组合。矿床由19 条铜矿体及1 条硫矿体组成。一号铜矿体是区内最大的矿体,长1000 余米,矿体平均厚8.81 m,倾斜延伸在750 m以上,矿体产状较陡,走向北东40°~60°,沿走向和倾斜均呈舒缓状弯曲。矿体形态简单,呈层状、似层状、透镜状,除三号矿体与顶板细碧质碎屑熔岩呈低角度喷发不整合外,其余矿体和顶底板围岩整合并与围岩同步褶皱,具层控特征(图1-c)。矿石片理亦和围岩片理一致。矿石构造主要为块状、条带状、浸染状,矿石结构主要为细粒他形-半自形结构、破碎结构,矿石矿物主要是黄铁矿、黄铜矿、少量闪锌矿、磁铁矿,脉石矿物主要为石英、方解石、绿泥石、石膏和重晶石等。
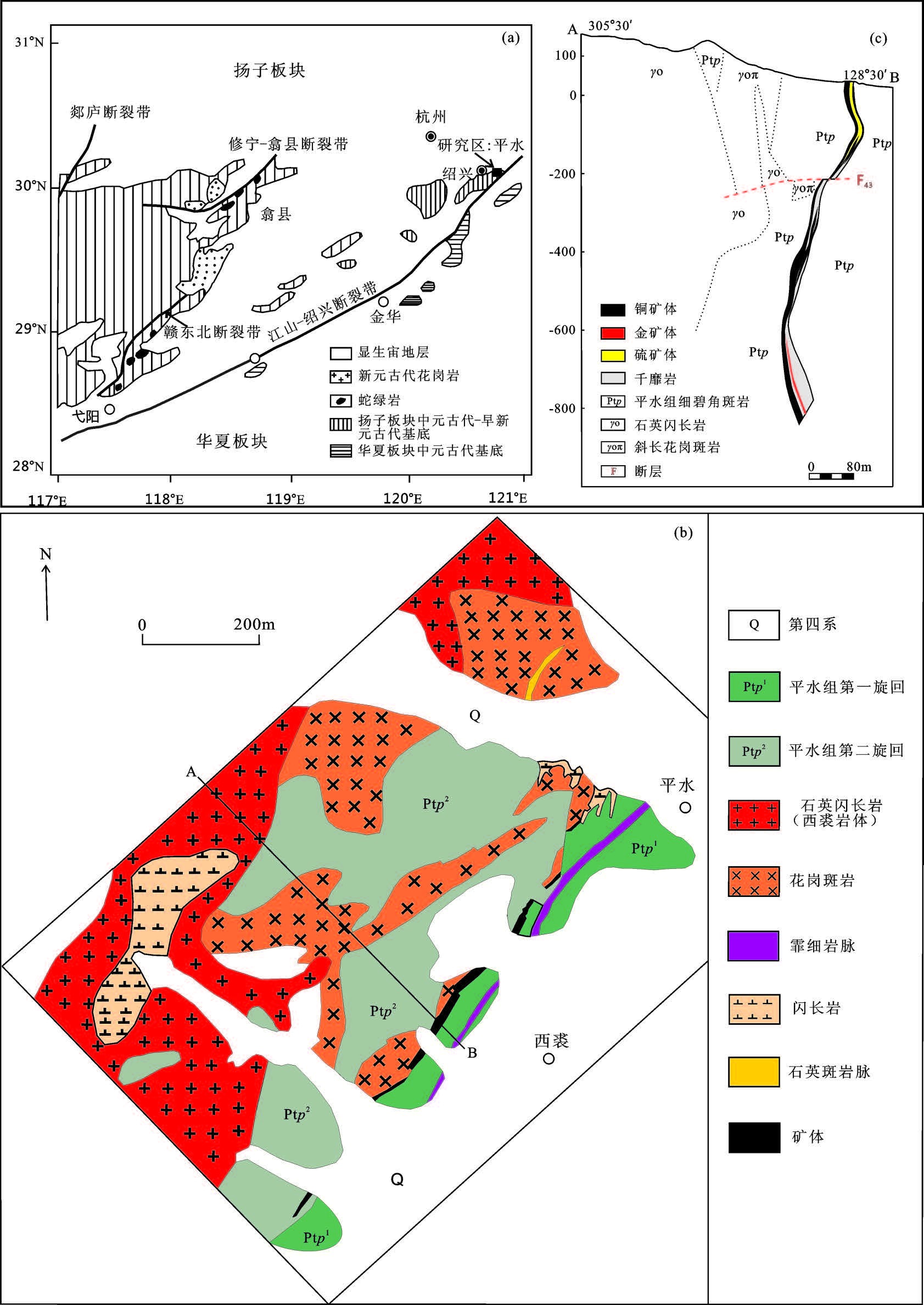
2 样品采集和测试方法 2.1 样品采集和描述本文选择矿体直接顶底板的平水组细碧岩和角斑岩作为研究对象;细碧岩样品采自矿区-505 中段1 线矿体底板位置;角斑岩样品采自剖面露头,地理坐标29°53′27″N、120°36′43″E。细碧岩:主要呈斑状结构,矿物成分主要是钠更长石(70%~80%)和辉石(10%~15%)为主,可见少量铁矿和蚀变矿物,斑晶成分主要为辉石,镜下未见橄榄石及其蚀变假象,绿帘石、绿泥石和辉石常充填于由长柱状钠更长石组成的格架空隙中。细碧岩样品普遍发生了绢云母化和绿泥石化(图2-a、c、d)。角斑岩:多呈灰绿色,斑状结构,基质霏细结构或显微花岗结构;斑晶含量占15%~25%,多以石英与斜长石为主,铁镁质矿物含量较少,未见钾长石。斑晶石英多呈熔蚀或淬冷特征,一些颗粒具波状消光,斑晶斜长石(0.5~1.3 mm)多为宽板状(长宽比1∶3 左右),镜下聚片双晶发育,部分受到蚀变影响。基质主要由长石和石英组成,含少量钛铁矿,粒度0.01~0.1 mm。所有样品均发育不同程度的片理化构造,同时受到后期轻微的绿泥石化、绿帘石化以及碳酸盐化改造(图2-b、e、f)。
|
图2 平水组细碧角斑岩手标本及镜下照片Aug—辉石;Ab—钠长石;Pl—斜长石;Qtz—石英;Chl—绿泥石;Ser—绢云母 Fig.2 Samples and microscopic photos of Pingshui spillite-keratophyreAug-Pyroxene;Ab-Albite;Pl-Plagioclase;Qtz-Quartz;Chl-Chlorite;Ser-Sericite |
样品经人工破碎后,按常规的重力和磁选方法分选出锆石,最后在双目显微镜下挑选。将待测样品锆石颗粒置于环氧树脂中制靶,然后磨至一半,用于阴极发光CL 图像和LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 同位素分析。在显微镜观察的基础上,选择合适的样品进行了阴极发光研究,特别避开锆石内部的包裹物以及锆石内部裂隙,以进行下一步的激光原位剥蚀测试。
阴极发光CL图像在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成,锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 分析在在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制国家重点实验室完成。采用仪器为Agilent 7500a ICP-MS。其工作参数为:等离子气体Ar 16 L/min,辅助气体Ar 1L/min,剥蚀物质载气He 0.9~1.2 L/min。激光剥蚀系统波长213 nm,激光脉冲频率5 Hz,宽度5 ns,剥蚀孔径40 μm,剥蚀时间80 s,背景测量时间40 s,脉冲能量为10~20 J/cm2,206Pb、207Pb、208Pb、232Th 和238U的停留时间依次为15、30、10、10 和15 ms。应用锆石标样GJ-1 进行同位素分馏校正,均一的GEMOC/GJ-1GJ-1 锆石标样的测试值为(601±12)Ma [14];此外,在分析中加入“未知”标样Mud Tank(分析值(735±12) Ma) [15],用于监控测试的重现性和仪器的稳定性,实验室对GJ-1 和Mud Tank 锆石标样的测试结果与其他实验室的测试结果一致。质谱的分析数据通过即时分析软件GLITTER 计算获得相应的同位素比值、年龄以及误差,上述数据采用Andersen 的方法进行普通铅校正[16],校正后的最终结果应用Isoplot 程序完成年龄计算和谐和图的绘制。
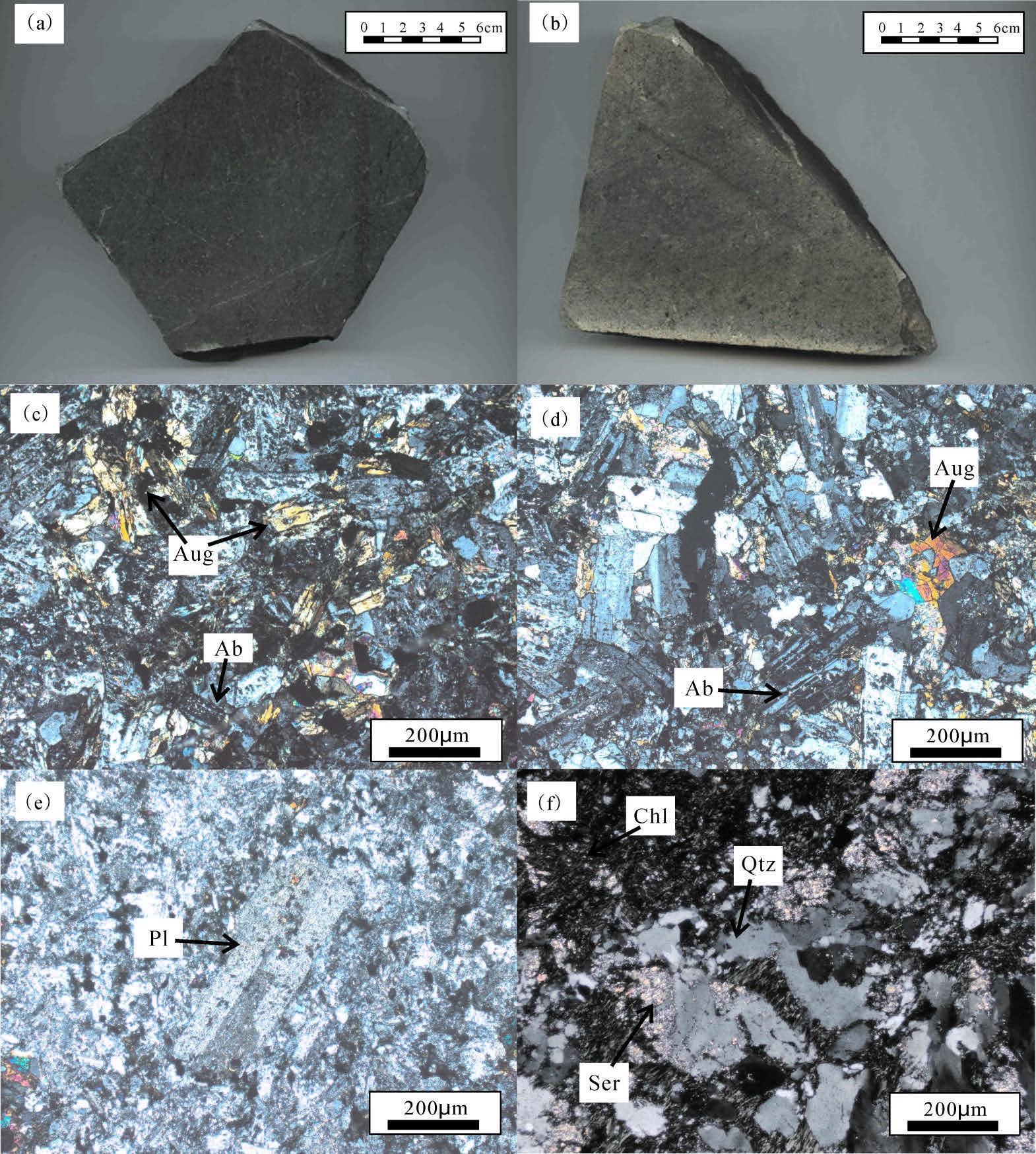
2.3 测定结果LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 定年的样品为细碧岩和角斑岩。锆石定年结果见表1 和图3。锆石阴极发光图像(CL)显示,锆石颗粒长度为100~150 μm,具有典型的岩浆锆石震荡环带。锆石具有U含量101×10-6~1529×10-6,Th 含量78×10-6~3676 ×10-6,Th/U 比值为0.42~2.28 (表1)。Th/U 比值与典型的岩浆锆石一致,明显高于Th/U 比值小于0.1 的变质成因的锆石。CL图像也表现出典型的岩浆生长韵律环带结构(图3)。利用Ludwig Isoplot V.206 进行了谐和曲线和加权平均年龄的投影和计算,几乎所有的锆石颗粒样品都投影在谐和曲线上及其附近,表明这些锆石颗粒形成后U-Pb 同位素体系是封闭的,基本上没有U或Pb的丢失或加入。
| 表1 平水组细碧角斑岩的LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Th-Pb 分析结果 Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb isotope dating results of Pingshui spillite-keratophyre |
大多数U-Pb 定年结果集中在谐和线附近。细碧岩206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为(952±5)Ma (n=18,MSWD=0.19),角斑岩年龄加权平均值为(954±8)Ma (n=15,MSWD=0.51) (图3)。结合锆石自形、发育岩浆环带等特点,该年龄被解释成平水组细碧角斑岩的形成年龄。
|
图3 平水组细碧角斑岩锆石CL图和ICP-MS U-Pb谐和线图 Fig.3 Zircon CL images and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb concordia diagram of Pingshui spillite-keratophyre |
浙西北双溪坞群主要出露于绍兴市平水、富阳章村以及诸暨陈蔡地区西北部。双溪坞群自下而上划分为平水组、北坞组、岩山组和章村组。根据岩石组合差异,可以把双溪坞群火山-沉积岩系划分为早晚2 个火山-沉积旋回。早期旋回以绍兴平水组为代表,以细碧-角斑岩为特征。晚期旋回以富阳章村为代表,以英安质凝灰岩、熔结凝灰岩为主,为中酸性陆相火山岩[17, 18]。
双溪坞群的年代学研究随着同位素定年技术的提高在不断进步,已获得的数据有:绍兴平水组有890~970 Ma[19](Sm-Nd 法)、(978±44) Ma[18](Sm-Nd 法)、1012 Ma[20](Sm-Nd 法)、(906±10) Ma[10](锆石U-Pb 法);北坞组有(926±15) Ma[21](锆石U-Pb 法);富阳章村组有875~904 Ma [17](TIMS 单颗粒锆石UPb法)、(1154±122) Ma[22] (全岩Sm-Nd 等时线法)、(891±12) Ma[21](锆石U-Pb 法)。考虑到定年方法的适用性和可靠性,目前普遍认为北坞组的年龄为926 Ma,章村组的年龄为891 Ma。平水组的年龄仍存在争议,20 世纪90 年代以前发表的测年数据跨度太大,可能因测试方法陈旧等原因而精度不够;而Chen et al.(2009)[10]得到的角斑岩的成岩年龄为906Ma,但是其206Pb/238U U-Pb年龄不谐和,范围跨度较大,为878~999 Ma;而且906 Ma的年龄比上覆北坞组的年龄还年轻,也比侵入其中的桃红岩体和西裘岩体(结晶年龄905~913 Ma)[13]年轻,这与地质事实不符。本文通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 定年法得到细碧岩的结晶年龄为(952±5) Ma,角斑岩的结晶年龄为(954±8) Ma,U-Pb 年龄均很谐和,定年方法可靠;而且,大约950 Ma的成岩年龄与地质事实相符。因此,通过本文详细的锆石年代学研究,确定双溪坞群平水组细碧角斑岩的成岩年龄为950 Ma左右。
3.2 构造背景近年来的地质学、岩石学和年代学研究表明,扬子地块和华夏地块在新元古代时期发生俯冲和碰撞作用,形成了一个联合的统一大陆,其碰撞拼贴带在东北端就为江—绍断裂带[21],但其碰撞时间仍存在争议,主要有2 种观点:一种观点认为是从中元古代到新元古代(1.1~0.9 Ga)[13, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28];另一种观点认为是在新元古代中期(0.86~0.8 Ga)[29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36]。前人研究表明双溪坞群火山岩和平水地区同造山的花岗闪长岩(西裘岩体和桃红岩体)是典型的岛弧岩浆活动[13],本文得到的双溪坞群最老的成岩年龄为952~954 Ma,结合区域上川南回箐沟同构造花岗片麻岩的成岩年龄为1007 Ma和约1.0 Ga的赣东北蛇绿岩及伴生的约970 Ma的埃达克质花岗岩指示当时属于俯冲环境[37]。因此,本文研究结果表明江南造山运动发生的上、下限虽还没有最终限定,但它东端的造山运动很可能发生于1.0~0.9 Ga。
3.3 区域找矿意义火山成因块状硫化物矿床是硫化物以层状形式形成的矿物聚集体,它主要沉淀于海底或者近海底,在空间上、时间上和成因上与同时代的火山作用密切相关[38];矿体常与围岩地层整合产出,围岩成岩年龄常代表其成矿年龄;因此平水组细碧角斑岩的成岩年龄可以对平水铜矿成矿年龄进行了一个很好的限定,其成矿年龄应该是在新元古代(950 Ma左右)。江西弋阳(铁砂街)铜矿同样位于钦杭成矿带北东段,前人研究表明弋阳铜矿是典型的火山成因块状硫化物矿床,其围岩同样为细碧角斑岩,成岩成矿年龄也是新元古代[39]。并且,平水铜矿和弋阳铜矿均是形成于岛弧环境[39]。同时,从全球范围看,火山成因块状硫化物矿床空间上常呈带(区)成群分布,形成总体储量可观的矿田、矿带[38]。因此,平水铜矿成岩年龄的最终确定,为区域找矿,特别是为在钦杭成矿带北东段寻找同类矿床提供了重要依据。
致谢:野外工作得到浙江平水铜矿领导以及中国冶金地质总局第一地质勘查院衢州分院的领导及相关人员的热情帮助,南京大学武兵老师在测试期间提供了技术保障,论文修改过程中审稿专家和编辑部李亚萍老师提出了宝贵修改意见,在此表示衷心的感谢!
| [1] | Chen H, Ni P, Wang R C, et al. A combined fluid inclusion and SPb isotope study of the Neoproterozoic Pingshui volcanogenic massive sulfide Cu-Zn deposit, Southeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66: 388-402.( 1) 1) |
| [2] | 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 等. 华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(5): 636-658. Mao Jingwen, Chen Maohong, Yuan Shunda, et al. Geological characteristics of Qinhang (or Shihang) metollogenic belt in south China and spatical-temporal distribution regularity of mineral deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinaca, 2011, 85(5): 636-658 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [3] | 杨明桂, 黄水保, 楼法生, 等. 中国东南陆区岩石圈结构与大规模成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 528-543. Yang Minggui, Huang Shuibao, Lou Fasheng, et al. Lithospheric structure and large-scale metallogenic process in southeast China continental area[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(3): 528-543 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [4] | 杨明桂, 梅勇文. 钦-杭古板块结合带与成矿带的主要特征[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 1997, 3: 52-59. Yang Minggui, Mei Yongwen. Characteristics of geology and metallization in the Qinzhou-Hangzhou paleoplate juncture[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 1997, 3: 52-59 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [5] | 黄有年. 浙江西裘含铜块状硫化物矿床特征及成矿模式[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1992, 7(3): 22-34. Huang Younian. Characteristics of Xiqiu copper massive sulfide deposit, Zhejiang and the metallogenic model[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1992, 7(3): 22-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [6] | 王执均, 赵筱富. 西裘铜矿矿床特征及其成因探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 1980, 2: 19-24. Wang Zhijun, Zhao Xiaofu. Geology and genesis of the Xiqiu copper deposit[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1980, 2: 19-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [7] | 浙江省地质矿产局. 浙江省区域地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1989: 1-688. Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Zhejiang Province. Regional Geology of Zhejiang Province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1989: 1-688 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [8] | 徐跃通, 尚树川, 张邦花. 浙江西裘铜块状硫化物矿床火山-热泉沉积成矿的地质地球化学证据[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29 (1): 14-20. Xu Yuetong, Shang Shuchuan, Zhang Banghua. Evidence for metallogenic geochemistry of volcano-hot spring deposition in Xiqiu copper massive sulfide deposit, Zhejiang Province [J]. Geochemica, 2000, 29 (1): 14-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [9] | Chen Z H, Guo K Y, Dong Y G, et al. Possible early Neoproterozoic magmatism associated with slab window in the Pingshui segment of the Jiangshan-Shaoxing suture zone: Evidence from zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2009, 52(7): 925-939.( 1) 1) |
| [10] | Chen Z H, Xing G F, Guo K Y, et al. Petrogenesis of keratophyes in the Pingshui Group, Zhejiang: Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(9): 1570-1578( 1) 1) |
| [11] | 李春海, 邢光福, 姜耀辉, 等. 浙江平水铜矿含硫化物石英脉锆石U-Pb 定年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(2): 477-487. Li Chunhai, Xing Guangfu, Jiang Yaohui, et al. LA-ICP-MS UPb dating of zircons from sulfide-bearing quartz veins in the Pingshui copper deposit, Zhejiang Province, and its geological implications[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(2): 477-487 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  3) 3) |
| [12] | 陈辉, 倪培, 刘家润, 等. 浙江省绍兴市平水铜矿流体包裹体研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1352-1360. Chen Hui, Ni Pei, Liu Jiarun, et al. Fluid inclusion study on the Pingshui copper deposit in Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(5): 1352-1360 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  3) 3) |
| [13] | Ye M F, Li X H, Li W X, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronological and whole-rock geochemical evidence from early Neoproterozic Sibaoan magmatic arc along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Gondwanwa Research, 2007, 12: 144-156.( 4) 4) |
| [14] | Xu X, Griffin W L, Ma X, et al. The Taihua Group on the southern margin of the North China craton: Further insights from U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009, 97: 43-59.( 1) 1) |
| [15] | Black L, Gulson B. The age of the mud tank carbonatite, Strangways range, northern territory[J]. BMR Journal of Australian Geology and Geophysics, 1978, 3: 227-232.( 1) 1) |
| [16] | Anderson T. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002: 192: 59-79.( 1) 1) |
| [17] | 程海. 浙西北晚元古代岛弧火山岩的地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 1993, 1: 18-27. Cheng Hai. Geochemistry of Proterozoic island-arc volcanic rocks in Northwest Zhejiang[J]. Geochimica, 1993, 22: 18-27 (in Chinese with English Abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [18] | 章邦桐, 凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 等. 浙江绍兴西裘双溪坞群细碧-角斑岩的Sm-Nd 等时线年龄[J]. 南京大学学报(地球科学), 1990, 2: 9-14. Zhang Bangtong, Ling Hongfei, Shen Weizou, et al. Sm-Nd isochronic age of spilite-keratophyre of Shuangxiwu Group in 第43卷第2 期陈辉等:浙西北平水铜矿细碧角斑岩成岩年龄及其地质意义417 Xiqiu, Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Earth Science), 1990, 2: 9-14 (in Chinese with English Abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [19] | 浙江省地质矿产厅. 区域地质调查报告(平水幅) [M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 1-225. Regional Geological Survey Report (Pingshui Sheet)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990:1-225 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [20] | 沈渭洲, 朱金初, 刘昌实, 等. 华南基底变质岩的Sm-Nd 同位素及其对花岗岩类物质来源的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(2): 115-124. Shen Weizhou, Zhu Jinchu, Liu Changshi, et al. Sm-Nd isotopic study of basement metamorphic rocks in south China and its constraint on material sources of grantoids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(2): 115-124 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [21] | Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174(1): 117-128.( 3) 3) |
| [22] | 徐步台, 邱郁双. 章村-楼塔一带双溪坞群Sm-Nd 和40Ar/39Ar 年龄及地质年代意义[J]. 浙江地质, 1996, 12(1): 46-53. Xu Butai, Qiu Yushuang. Sm-Nd and 40Ar/39Ar ages of Shuangxiwu Group and their geological significance[J]. Geology of Zhejiang, 1996, 12(1): 46-53 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [23] | Li W X, Li, X H, Li Z X, et al. Obduction-type granites within the NE Jiangxi ophiolite: implications for the final amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 13: 288-301.( 1) 1) |
| [24] | Li X H, Li Z X, Sinclair J A, et al. Revisiting the"Yanbian Terrane": implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of thewestern Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006,151: 14-30.( 1) 1) |
| [25] | Li Z X. Zhang L H, McApowell C. South China in Rodinia: part of the missing link between Australia-East Antarctica and Laurentia?[J]. Geology, 1995, 23: 407-410.( 1) 1) |
| [26] | Li Z X, Li X H, Zhou H W, et al. Grenvillian continental collision in south China: New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon results and implications for the configuration of Rodinia[J]. Geology, 2002, 30: 163-166.( 1) 1) |
| [27] | Li Z X, Wartho J A, Occhipinti S, et al. Early history of the eastern Sibao Orogen (South China) during the assembly of Rodinia: New mica 40Ar/39Ar dating and SHRIMP U-Pb detrital zircon provenance constraints[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159: 79-94.( 1) 1) |
| [28] | Li Z X, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, et al. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia: A synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160: 179-210.( 1) 1) |
| [29] | Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. Geochemistry of the Mesoto Neoproterozoic basic-acid rocks from Hunan Province, South China: Implications for the evolution of the western Jiangnan orogen[J]. Precambrian Research , 2004, 135: 79-103.( 1) 1) |
| [30] | Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research , 2006, 145: 111-130.( 1) 1) |
| [31] | Wang X L, Zhou J C, Griffin W L, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen: Dating the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159: 117-131.( 1) 1) |
| [32] | Wang X L, Zhao G, Zhou J C, et al. Geochronology and Hf isotopes of zircon from volcanic rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, South China: Implications for the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Jiangnan orogen[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 14: 355-367.( 1) 1) |
| [33] | Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96: 127-150.( 1) 1) |
| [34] | Zhou M F, Yan D P, Kennedy A K, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. , 2002, 196: 51-67.( 1) 1) |
| [35] | 徐先兵, 汤帅, 李源, 等. 江南造山带东段新元古代至早中生代多期造山作用特征[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1): 33-50. Xu Xianbing, Tang Shuai, Li Yuan, et al. Characteristics of Neoproterozoic-Early Mesozoic multiphase orogenic activities of eastern Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(1): 33-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [36] | 张恒, 李廷栋, 高林志, 等. 江南造山带东段赣东北广丰地区翁家岭组凝灰岩SHRIMP 锆石U-Pb 年龄及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1): 96-104. Zhang Heng, Li Tingdong, Gao Linzhi, et al. Zircon SHRIMP UTh-Pb dating of the Wengjialing Formation in the eastern segment of the Jiangnan orogenic belt in northeast Jiangxi Province and its geological implications[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(1): 96-104 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [37] | Chen J, Foland K A, Xing F, et al. Magmatism along the southeastern margin of the Yangtze block: Precambrian collision of the Yangtze and Cathysia blocks of China[J]. Geology, 1991, 19: 815-818.( 1) 1) |
| [38] | Franklin J, Gibson H, Jonasson I, et al. Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits[J]. Economic Geology 100th anniversary, 2005, 98: 523-560.( 2) 2) |
| [39] | 程海, 胡世玲, 唐朝辉. 赣东北铁砂街变质混杂岩块的同位素年代[J]. 中国区域地质, 1991, 10(2): 151-154. Cheng Hai, Hu Shiling, Tang Zhaohui. New recognition on the isotopic geochronology of the"Tieshajie Group"in the southern part of northeastern Jiangxi[J]. Regional geology of China, 1991, 10(2): 151-154 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |