2. 中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心, 陕西 西安 710054;
3. 国土资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710054;
4. 青海煤炭地质一〇五勘探队, 青海 西宁 810007
2. Xi'an Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Xi'an 710054, Shaanxi, China;
3. Key Laboratory for the Study of Focused Magmatism and Giant Ore Deposits, MLR, Xi'an 710054, Shaanxi, China;
4. No. 105 Exploration Party, Qinghai Coal Geology Bureau, Xining 810007, Qinghai, China
世界石油工业正进入常规油气稳定增产、非常规油气快速发展阶段,随着北美页岩气的勘探开发在北美获得巨大成功,全球正在掀起以页岩气为首的能源革命热潮。但随着勘探的深入和地质理论的发展,人们发现在页岩气的勘探开发过程中常常伴随着页岩油的产生[1, 2, 3, 4],二者并没有截然的界限。例如美国Fort Worth 盆地的Barnett 组页岩,在页岩气产出的同时也产出大量的油[3]。
页岩油是以游离(含凝析态)、吸附及溶解态(可溶解于天然气、干酪根和残余水等)等多种方式赋存于有效生烃泥页岩地层层系中并具有勘探开发意义的非气态烃类[5]。页岩油的概念有狭义和广义之分,广义页岩油含义与广义致密油一致,还包括油页岩资源[6]。中国主要含油气盆地在常规油气勘探开发过程中也发现了大量赋存在泥页岩中的非常规石油资源。目前国内不但南方海相层系页岩气勘探获得了突破,在东部的泌阳凹陷、济阳坳陷等中新生代陆相泥页岩层系中也获得了工业性油气流[7, 8],展现了我国中新生代陆相地层页岩油气资源良好的勘探前景[9]。充分研究页岩油的形成条件、成藏机理,对于我国今后的油气勘探开发和能源接替具有重要的意义。
柴达木盆地是中国西部典型的叠合含油气盆地,经过50 多年的勘探开发,发现了一批重要的油气田,柴达木盆地北缘已被证实存在中、下侏罗统两套较好烃源岩[10, 11,12,13]。但由于构造复杂,勘探难度大,常规油气资源的总体探明率不高[14, 15]。而页岩油气由于其自生自储的特性,并且在生成后受后期构造改造、保存条件等因素影响相对较小,因此具备一定的资源潜力。近几年,中国地质调查局联合青海油田、青海煤炭地质局等对柴北缘的页岩气发育情况进行了调查,总体上页岩气发育的主要的参数条件较好,但侏罗系暗色泥页岩有机质成熟度(Ro)较低是柴北缘存在的一个现实问题。本文正是在这样的基础上开展对柴北缘大煤沟地区页岩油的形成、发育条件研究,并以此为窗口,初步评价柴北缘的页岩油发育条件及资源潜力,本研究将为柴北缘非常规油气勘探和今后油气接替的重要工作。
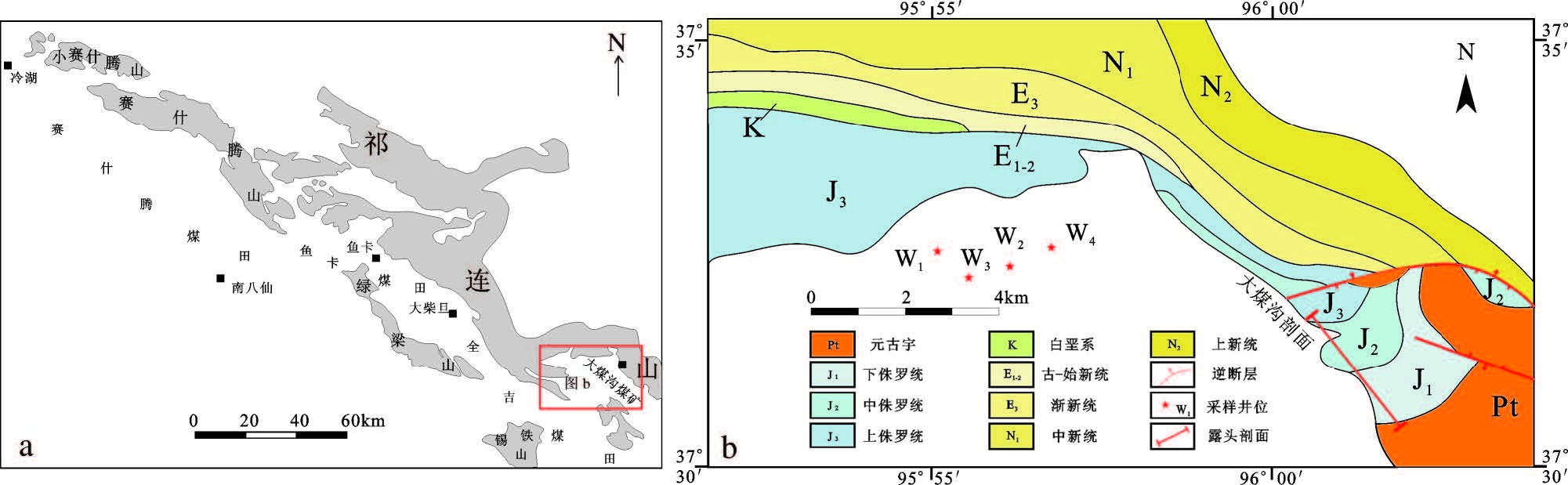
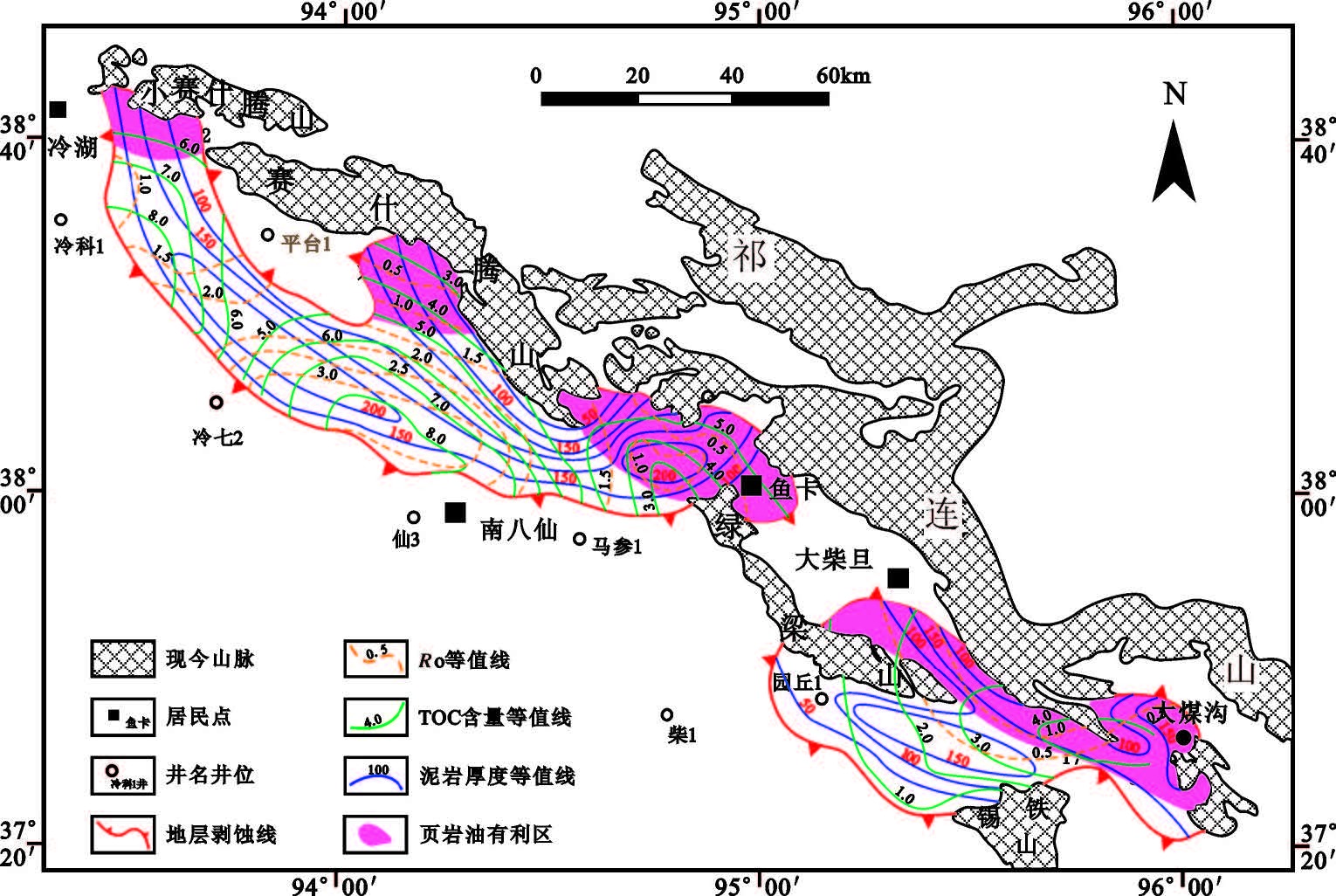
1 区域地质概况柴达木盆地是中国西北三大含油气盆地之一,柴北缘位于柴达木盆地的东北部,属盆地的一级构造单元。柴北缘中、生代以来经历了多期构造运动改造,形成了复杂的构造背景和多变的沉积特征[15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]。早侏罗世时期,柴北缘主要发育断陷型盆地,沉积相以半深湖—深湖亚相为主,沉积中心主要位于柴北缘西段,中段仅在大煤沟煤矿一带见下侏罗统局限分布。中侏罗世时期,柴北缘以断-坳陷型盆地为主,早期地层仅在大煤沟地区沉积,到中后期,随着水体范围的不断扩大,柴北缘中段的赛什腾、鱼卡等地区也发展成为当时的沉积中心之一,沉积了一套全区分布的滨浅湖-半深湖亚相暗色泥岩,也是柴北缘中段主要的烃源岩发育层段。之后柴北缘进入构造改造阶段,在经历了晚侏罗世—早白垩世、古近纪—新近纪大的构造运动后,盆地面貌最终定型。因此,柴北缘中段主要发育中侏罗统以上地层,中侏罗统烃源岩在赛什腾、鱼卡、大煤沟地区普遍发育,为一套中等—好的烃源岩[10, 12, 13]。
大煤沟地区位于柴北缘大柴旦至德令哈的中间区域(图1),是柴达木盆地中、下侏罗统沉积最完整的地区之一,其中,大煤沟剖面是柴北缘侏罗系的建组剖面。通过对大煤沟剖面以及附近煤炭钻孔调查认为,研究区暗色泥页岩主要发育层段有两段,分别是中侏罗统大煤沟组七段(以下简称“煤七段”)和下侏罗统大煤沟组一段(以下简称“煤一段”)。煤七段以灰黑色、黑色页岩为主,富含有机质,页理发育,风化后常呈片状,局部发育油页岩,暗色泥岩厚度为50~80 m。该套暗色泥页岩在柴北缘地区普遍发育,大部分煤炭钻孔都有钻遇,是柴北缘主力页岩油气层位之一。煤一段岩性组合与煤七段相似,中间加砂岩薄层及煤线,厚度为20~50m。该套暗色泥页岩分布局限,仅在大煤沟地区以及柴北缘西段地区部分钻井中见及。因此,本文着重通过对露头及钻井内采集的煤七段样品进行实验测试后分析煤七段的页岩油潜力。
|
图1 研究区位置及采样点示意图 Fig.1 Map showing location of the study area and sampling site |
有机质丰度反映烃源岩有机质的数量特征,是形成油气的物质基础,是决定岩石生烃潜力的主要因素[21]。目前常用于评价烃源岩有机质丰度的指标主要有烃源岩中的总有机碳含量(TOC)、总烃含量(HC)和热解生烃潜量(S1+S2)等。
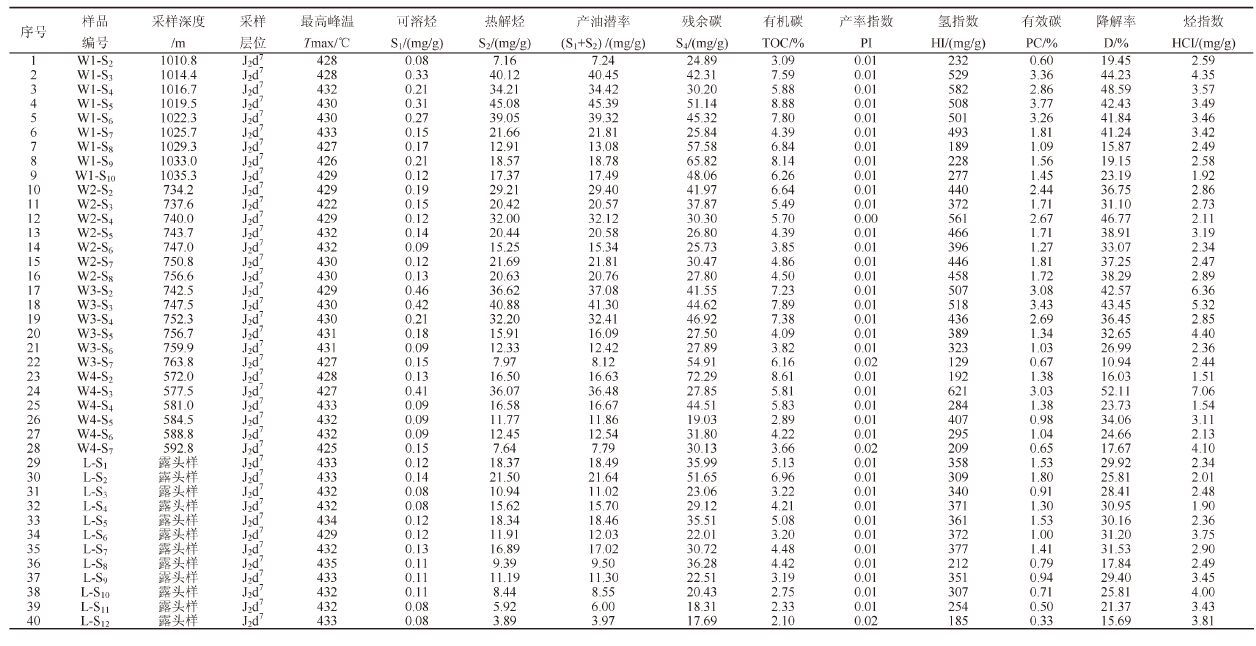
表1 是煤七段40 件样品的热解结果,从表中可以看出,研究区泥页岩样品的TOC 含量范围在2.10%~8.88%,平均值为5.22%,其中,28 件钻井样品的TOC 含量范围在2.89%~8.88%,平均值为5.78%,12 件地面露头样品由于受风化作用的影响,其TOC含量范围在2.10%~6.96%,平均值为3.92%,低于钻井样品。热解产油潜率(S1+S2)也有类似规律,总体(S1+S2)含量范围在3.97~45.39 mg/g,平均为20.04 mg/g;钻井样品(S1+S2)含量范围在7.24~45.39mg/g,平均为23.14 mg/g;露头样品(S1+S2)值低于钻井新鲜样品,含量范围在3.97~21.64 mg/g,平均为12.81 mg/g。无论从烃源岩还是页岩气的有机质丰度评价标准看,都达到了非常好的标准。
| 表1 柴北缘大煤沟组七段泥页岩样品热解结果 Table 1 The pyrolysis results of shales from the 7th member of Dameigou |
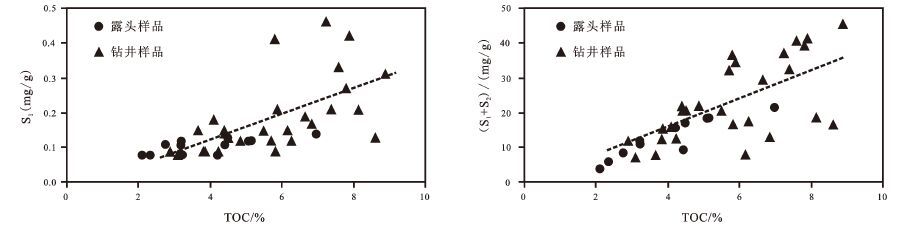
从图2 可以看出,无论是S1或者(S1+S2)与TOC之间都有较好的线性关系,当TOC小于6%时,二者之间的线性关系更为明显,当TOC大于6%以后,投点出现发散现象,同时斜率也变大,说明随着TOC的增大,S1、(S1+S2)的增加更快。
|
图2 柴北缘大煤沟组七段泥页岩S1、(S1+S2)与TOC相关关系 Fig.2 The correlation between S1, (S1+S2) with TOC of shale from the 7th member of Dameigou Formation on the northern margin of Qaidam Basin |
有机质类型是决定泥页岩在成熟阶段生烃倾油、倾气性的重要因素[9]。图3 是研究区干酪根H/C与O/C原子比关系图,从图中可以看出:样品的干酪根类型为Ⅰ- Ⅱ 型,其中大煤沟露头剖面样品主要位于Ⅱ1- Ⅱ2型干酪根,钻井样品Ⅰ- Ⅱ 型都有分布,主要为Ⅰ- Ⅱ1型干酪根。整个研究区样品都以腐泥型为主,具备了页岩油气生成的良好条件。
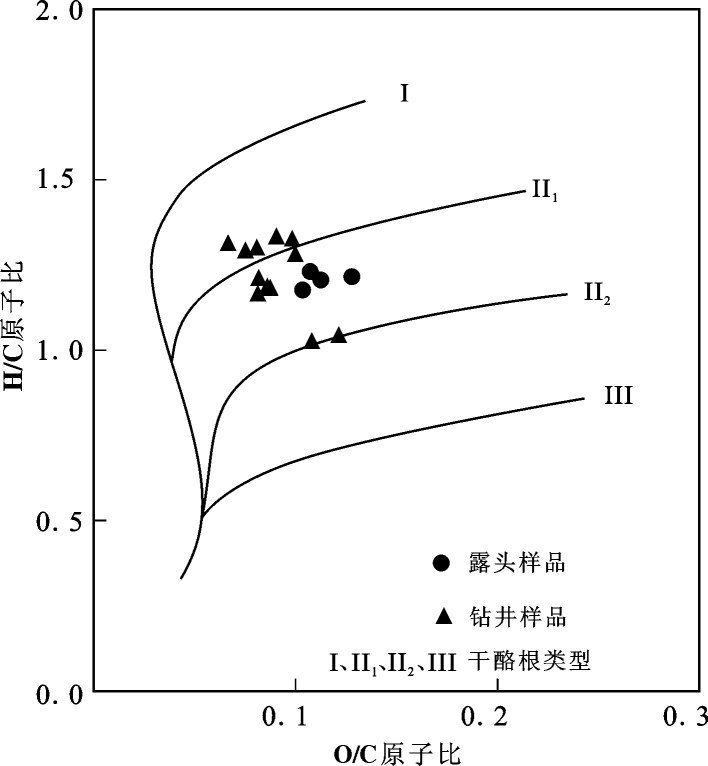
|
图3 研究区泥页岩样品干酪根类型特征 Fig.3 The kerogen type of shale in the study area |
镜质体反射率(Ro)是“经典”的成熟度指标,是衡量有机质成熟度的标尺。通常以0.5、0.7、1.3 和 2.0 作为划分未成熟、低成熟、成熟、高成熟等各成熟阶段的临界值[22]。
图4 为研究区泥页岩样品成熟度分布特征,从图中可以看出样品的成熟度范围为0.340~0.674,平均值为0.518,主要落入未成熟—低成熟区间,在采样深度相差不大的情况下,成熟度增加不明显,同时,露头样品由于受风化作用的影响,成熟度要高于一般钻井样品。
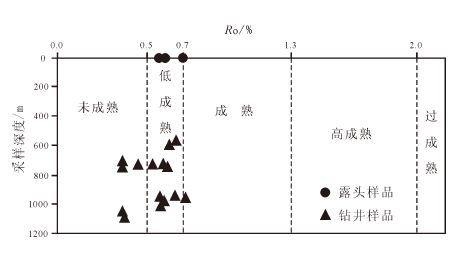
|
图4 研究区泥页岩样品成熟度分布特征 Fig.4 The distribution characteristics of shale maturity in the study area |
大煤沟地区暗色泥页岩矿物组成主要可以分为3 类,以石英、长石为主的脆性矿物、黏土矿物以及菱铁矿、黄铁矿等其他成分。从图5 中可以看出,研究区的矿物组成以黏土矿物和脆性矿物为主,其中,黏土矿物含量在52%~56%,钻井样品和露头样品的差别不大。脆性矿物含量在41%~44%,无论对于页岩气还是页岩油来说,较大的脆性矿物含量是后期压裂的有利条件。从样品的黏土矿物分析中可以看出(图6),研究区的主要黏土矿物成分为蒙脱石、伊蒙混层、伊利石、高岭石和绿泥石,其中伊蒙混层和高岭石的平均含量分别超过30%和40%,是主要的黏土矿物成分,而蒙脱石主要存在于露头剖面的样品中,可能是因为受构造或风化作用的影响,埋藏较浅,还未向伊蒙混层转化所致。另外,根据前人研究,一方面黏土矿物成分具有较大的比表面积,可以较大程度的吸附初期形成的页岩油气,但另一方面,黏土矿物也存在着很大的遇水膨胀性能,也有可能阻塞孔、喉,对后期的开发造成一定影响[23],但总体上,由于泥岩的致密性,孔隙则是重要的方面。
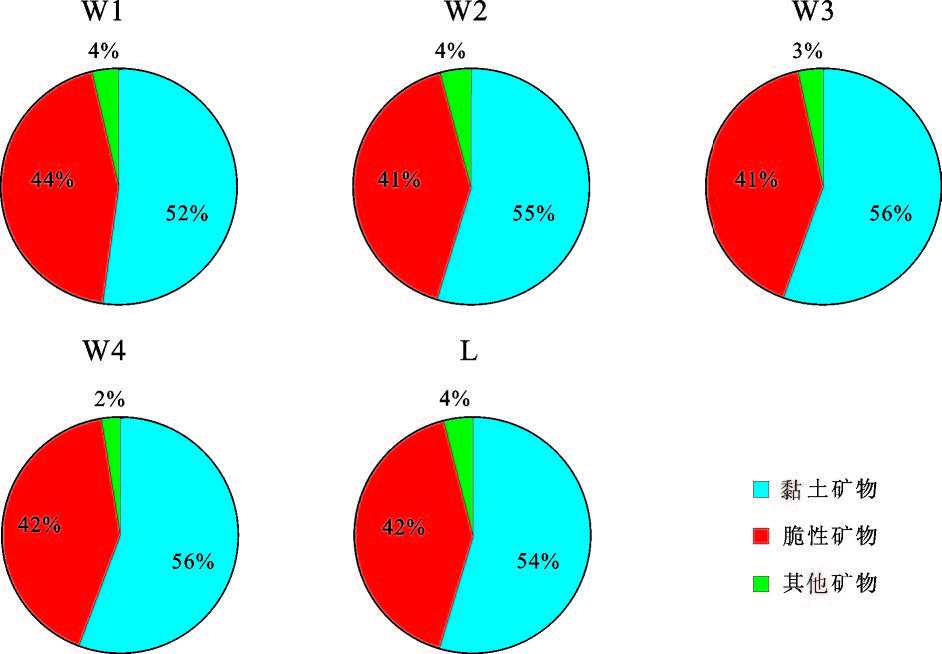
|
图5 研究区泥页岩样品矿物组成特征 Fig.5 The mineral composition characteristics of shale in the study area |
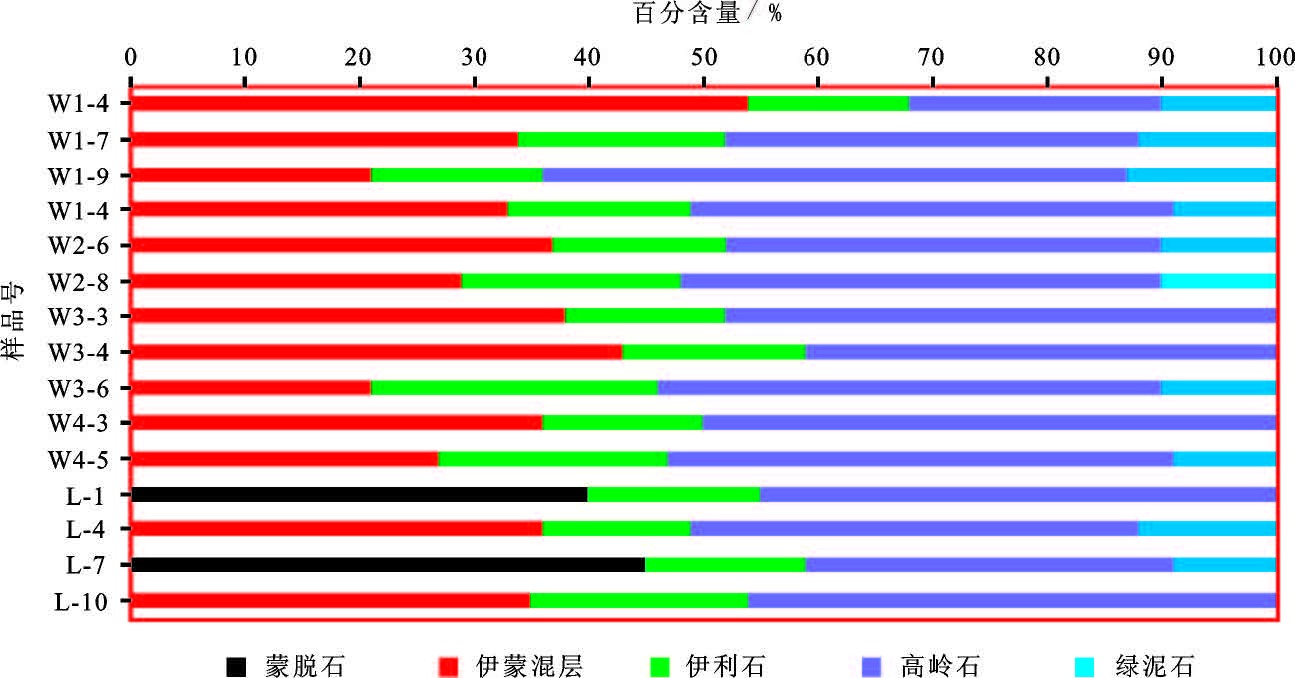
|
图6 研究区泥页岩样品黏土矿物组成特征 Fig.6 The clay mineral composition characteristics of shale in the study area |
扫描电镜下研究区样品的孔隙结构和类型图(图7)显示:研究区泥页岩样品孔隙类型多样,既有残溶蚀孔隙,也有层间孔隙,同时,微裂隙和黏土矿物晶体之间的孔隙也是研究区孔隙组成的重要部分。
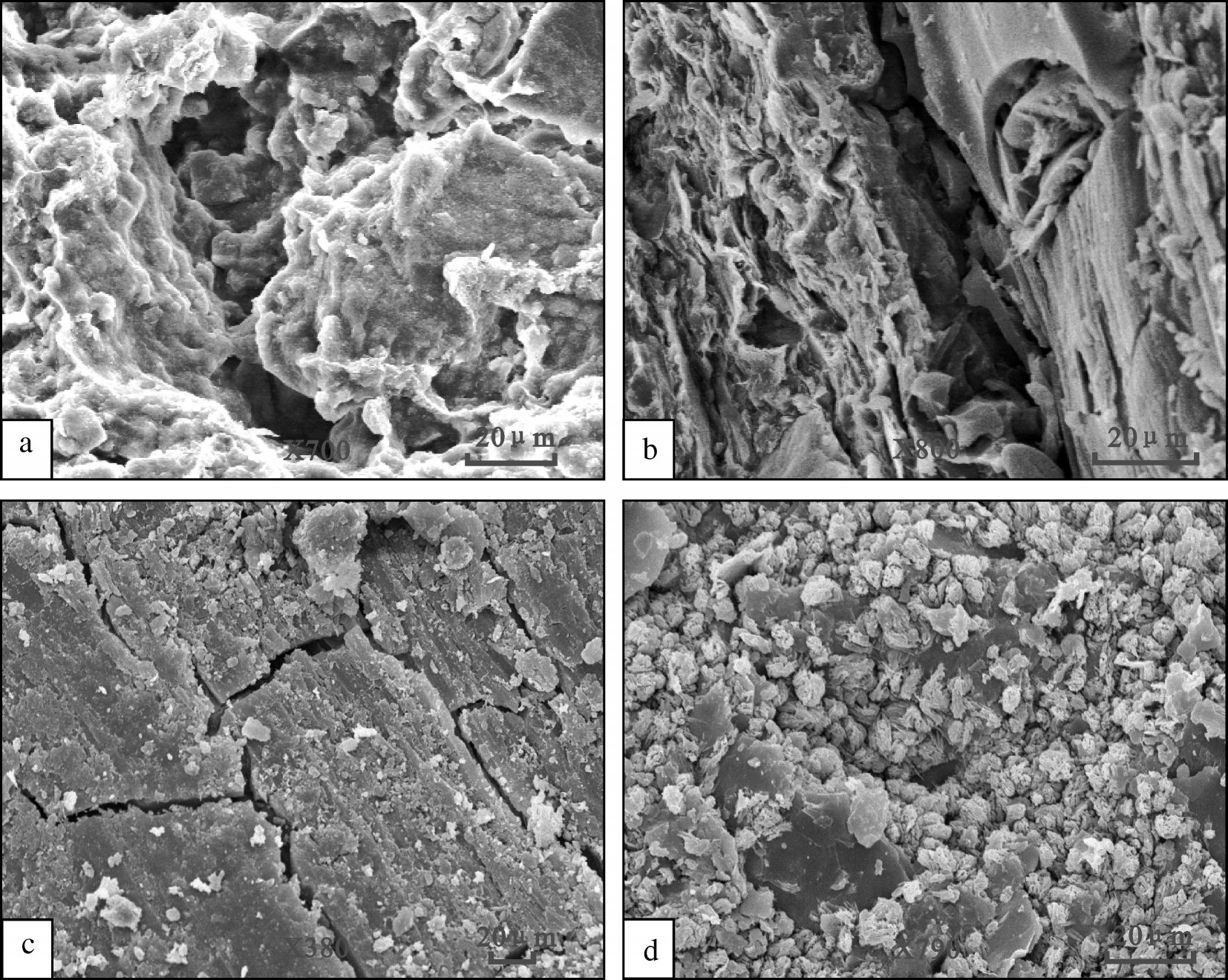
|
图7 a—粒间溶蚀孔,扫描电镜;b—页岩层间孔,扫描电镜;c—微裂缝,扫描电镜; d—黏土矿物晶间孔,扫描电镜 Fig.7 a-Intergranular dissolved pore (SEM); b-The pore between the shale layers (SEM); |
泥页岩一般具有低孔低渗的性质。煤七段泥页岩孔隙度主要分布在1.4%~15.4%,平均为7.4%。渗透率基本都小于0.1×10-3 μm2,属于极低渗透率。从孔隙度、渗透率相关关系图(图8)可以看出,总体上渗透率随着孔隙度的增大变化不大,主要是由于有机质生烃后留下的孔隙、溶蚀孔、晶间孔等都是相对独立,缺乏有效的喉道连通,而造成渗透率不随孔隙度的增大而增大。只有当微裂缝、层间缝等发育时,可以有效连通各孔隙,形成孔隙度增大渗透率也随之增大。总体上,煤七段泥页岩储油空间类型多样,低孔低渗的孔渗条件有利于页岩油生成后的原地保存。
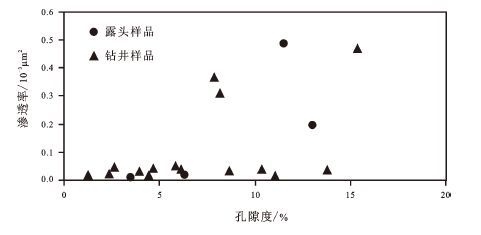
|
图8 研究区泥页岩孔隙度、渗透率相关关系 Fig.8 The relationship between porosity and permeability of shale in the study area |
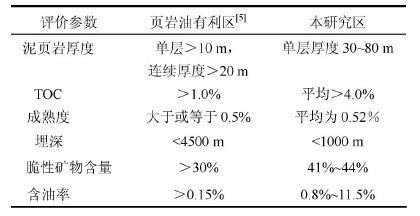
张金川等[5]根据中国页岩油基本地质条件和地球化学特征等,提出了中国页岩油的综合选取参考标准。将研究区获得的各类参数与已有的评价标准对比(表2)可以看出,研究区的各项指标都达到或超过了已有的评价标准。结合已有的其他分析,说明研究区具备了页岩油的生成条件。另外,更为重要的是,对煤七段泥页岩进行荧光照射,可观察到大部分富含有机质泥页岩样品其新鲜断面在荧光下呈亮黄色,泥页岩页理面在荧光下也显示亮黄色(图9)。充分说明研究区暗色泥页岩曾经或正在发生油气生成或运移,为页岩油的存在提供了直接证据。
| 表2 页岩油有利区主要评价参数对比 Table 2 The comparison of main evaluation parameters in favorable area of shale oil |
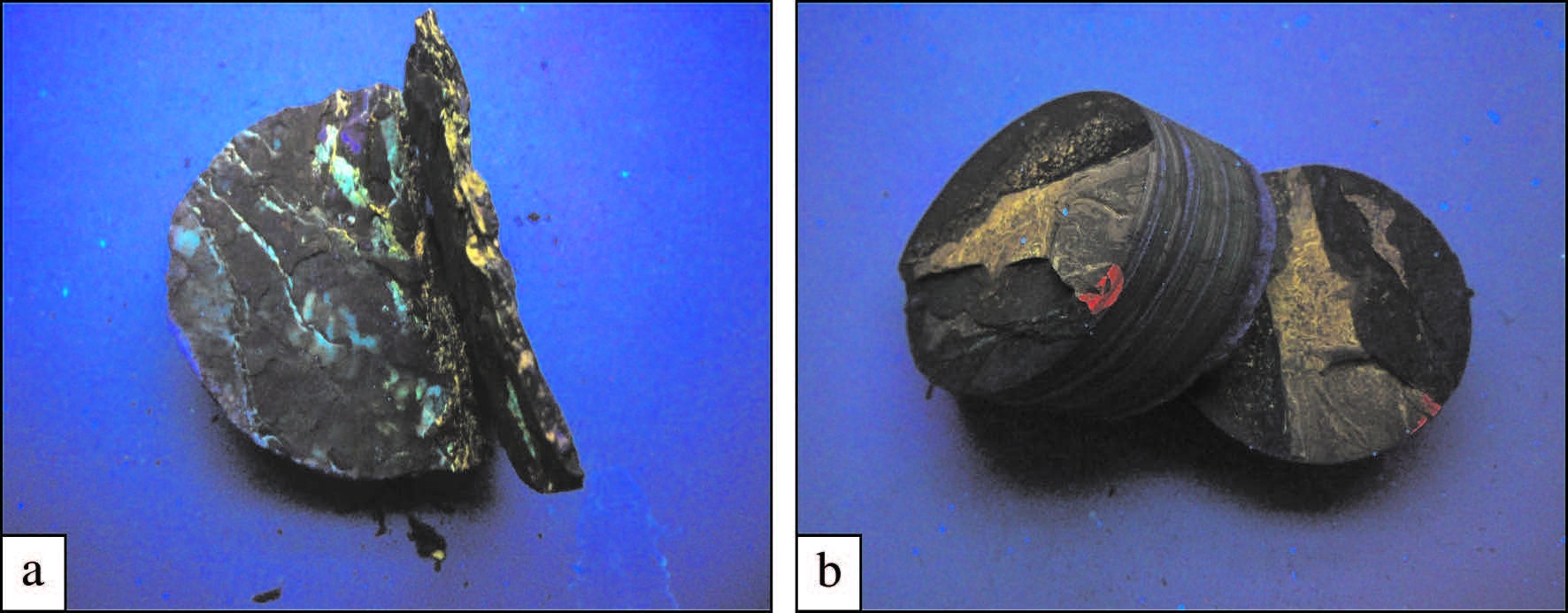
|
图9 a—泥页岩断面荧光特征,W1井,870.5 m;b—泥页岩层面荧光特征,W3井,225.3 m Fig.9 a-The fluorescence characteristics in the fracture surface of shale from W1 Well at 870.5 m; b-The fluorescence characteristics in the shale layers from W3 Well at 225.3 m |
煤七段页岩不仅主要分布在大煤沟地区,而且广泛分布在柴北缘山前凹陷带[24],并且其厚度在鱼卡、赛什腾凹陷具有加厚的趋势,因此,结合本研究在大煤沟地区的分析,同时,也有研究表明柴北缘其他地区的页岩油气发育条件也相当优越[25],通过对柴北缘大煤沟地区煤七段页岩油关键指标的分析,依据研究区地质条件特点,结合已有资料成果,综合确定的有利区评价参数标准包括泥页岩有效厚度超过30 m、TOC含量大于2.0%、有机质成熟度大于0.5%等,采用综合信息叠合法对煤七段页岩油发育有利区进行初步预测。最终在柴北缘初步划分出4 个页岩油发育有利区,分别位于冷湖地区、赛什腾凹陷靠近山前地区、鱼卡凹陷、大柴旦—红山凹陷地区(图10)。这与中侏罗统时期主要的沉积中心分布基本一致。
|
图10 柴北缘大煤沟组七段页岩油有利发育区预测 Fig.10 The favorable areas of shale oil from the 7th member of Dameigou Formation on the northern margin of Qaidam Basin |
(1)柴北缘大煤沟组七段富有机质泥页岩发育集中,单层厚度大,平面上横向分布稳定,在柴北缘中侏罗统的凹陷内都稳定分布,是研究区页岩油气发育的最有利层段。
(2)对研究区40 件样品进行实验测试分析,统计结果显示,样品的总有机碳含量平均值为5.22%,干酪根类型中大煤沟露头剖面样品主要位于Ⅱ1—Ⅱ2型干酪根,钻井样品以Ⅰ— Ⅱ1型为主。样品的有机质成熟度平均值为0.518%,主要为未成熟—低成熟。样品的储集空间类型多样、微裂缝发育,为页岩油的吸附、存储提供了有利场所。样品的矿物组成以黏土矿物和脆性矿物为主,其中,脆性矿物含量在41%~44%,有利于后期的生产压裂。
(3)柴北缘煤七段多个参数显示了该层段具备页岩油形成的地质条件,是中侏罗统页岩油勘探的最有利层段,结合前人研究成果,初步预测冷湖、赛什腾、鱼卡凹陷、大柴旦—大煤沟地区为该层段的页岩油勘探有利区。
致谢:感谢青海煤炭地质一〇五队在煤炭钻孔岩心样品采集、整理方面提供的支持与帮助。
| [1] | 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. Zou Caineng, Yang Zhi, Cui Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1):14-26(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [2] | 卢炳雄, 郑荣才, 梁西文, 等. 四川盆地东部地区大安寨段页岩气 ( 油) 储层特征[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4): 1387-1398. Lu Bingxiong, Zheng Rongcai, Liang Xiwen, et al. Characteristics analysis of Da'anzhai shale gas (oil) reservoirs in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(4): 1387-1398(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [3] | Javie D M, Pollastro R M, Hill R J. Geochemical characterization of thermogenic gas and oil in the Ft. Worth Basin,Texas[C]. AAPG National Convention: Dallas, Texas, USA, poster presentation, 2004.( 1) 1) |
| [4] | 宋国奇,张林晔,卢双舫, 等. 页岩油资源评价技术方法及其应用[J]. 地学前缘,2013, 20(4): 221-228. Song Guoqi, Zhang Linye, Lu Shuangfang, et al. Resource evaluation method for shale oil and its application[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):221-228(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [5] | 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等. 页岩油分类与评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 322-331. Zhang Jinchuan, Lin Lamei, Li Yuxi, et al. Classification and evaluation of shale oil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 322-331(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [6] | 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等. 致密油与页岩油内涵、特征、潜力及挑战[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 3-17. Zou Caineng, Zhu Rukai, Bai Bin, et al. Significance, geologic characteristics, resources potential and future challenges of tight oil and shale oil[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1):3-17(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [7] | 董冬, 杨申镳, 项希勇, 等. 济阳坳陷的泥质岩类油气藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1993, 20(6): 15-22. Dong Dong, Yang Shenbiao, Xiang Xiyong, et al. Muddy hydrocarbon reservoirs in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1993, 20(6): 15-22(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [8] | 陈祥, 王敏, 严永新, 等. 泌阳凹陷陆相页岩油气成藏条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(4): 568-576. Chen Xiang, Wang Min, Yan Yongxin, et al. Accumulation conditions for continental shale oil and gas in the Biyang Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(4): 568-576(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [9] | 付小东, 邱楠生, 饶丹, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系页岩油气成藏条件地质地球化学分析[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 43(5): 437-452. Fu Xiaodong, Qiu Nansheng, Rao Dan, et al. Geological and geochemical analysis on accumulation conditions of shale oil and gas in the Jurassic strata of the north margin of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2014, 43(5): 437-452(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [10] | 刘云田, 杨少勇, 胡凯, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘中侏罗统大煤沟组七段烃源岩有机地球化学特征及生烃潜力[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 20(3): 279-284. Liu Yuntian, Yang Shaoyong, Hu Kai, et al. Organic geochemical features of hydrocarbon source rock from 7th member of Middle Jurassic Dameigou Foramtion in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin and its hydrocarbon-generation potential[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 20(3): 279-284(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [11] | 孙德强, 张涛, 梁彬, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘油气成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(5): 652-656. Sun Deqiang, Zhang Tao, Liang Bin, et al. Reservoir-forming features of oil and gas in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(5): 652-656(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [12] | 阎存凤, 袁剑英, 陈启林, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘东段大煤沟组一段优质烃源岩[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1): 49-53. Yan Cunfeng, Yuan Jianying, Chen Qilin, et al. Discovery of the high-quality source rock of the first member of Dameigou Formation in the east part of the northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1):49-53(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [13] | 翟志伟, 张永庶, 杨红梅, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系有效烃源岩特征及油气聚集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2013, 33(9): 36-42. Zhai Zhiwei, Zhang Yongshu, Yang Hongmei, et al. Characteristics of effective source rock and its accumulation patterns from the Jurassic in the northern margin of the QaidamBasin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(9): 36-42(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [14] | 薛光华, 杨永泰. 柴达木盆地北缘油气分布规律研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2002, 24(2): 141-146. Xue Guanghua, Yang Yongtai. Study on the distribution rules of hydrocarbon in the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2002, 24(2): 141-146(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [15] | 金之钧, 张明利, 汤良杰, 等. 柴达木中新生代盆地演化及其控油气作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(6): 603-608. Jin Zhijun, Zhang Mingli, Tang Liangjie, et al. Evolution of Meso-Cenozoic Qaidam Basin and its control on oil and gas [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(6): 603-608(in Chinese with English abstract).(  2) 2) |
| [16] | 汤良杰, 金之钧, 张明利, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘构造演化与油气成藏阶段[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(2): 36-39. Tang Liangjie, Jin Zhijun, Zhang Mingli, et al. Tectonic evolution and oil (gas) pool-forming stage in northern Qaidam Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(2): 36-39(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [17] | 汤良杰, 金之钧, 张明利, 等. 柴达木盆地构造古地理分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(4): 421-429. Tang Liangjie, Jin Zhijun, Zhang Mingli, et al. An analysis on tectono-paleogeography of the Qaidam Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(4): 421-429 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [18] | 杨永泰, 张宝民, 李伟, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系层序地层与沉积相研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(3): 145-151. Yang Yongtai, Zhang Baoming, Li Wei, et al. Study of Jurassic stratigraphic sequence and sedimentary facies in north of Qaidam Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(3):145-151(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [19] | 周建勋, 徐凤银, 胡勇. 柴达木盆地北缘中、新生代构造变形及其对油气成藏的控制[J].石油学报, 2003, 24(1): 19-24. Zhou Jianxun, Xu Fengyin, Hu Yong. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonism and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation in the northern Qaidam Basin of China [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24 (1):19-24(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [20] | 金振奎, 齐聪伟, 薛建勤, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系沉积相[J]. 古地理学报, 2006, 8(2): 199-210. Jin Zhenkui, Qi Congwei, Xue Jianqin, et al. Sedimentary facies of the Jurassic in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2006, 8(2): 199-210(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [21] | 陈建平, 赵长毅, 何忠华. 煤系有机质生烃潜力评价标准探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1997, 24(1): 1-5. Chen Jianping, Zhao Changyi, He Zhonghua. Criteria for evaluating the hydrocarbon generating potential of organic matter in coal measures [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1997, 24(1): 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [22] | 程顶胜. 烃源岩有机质成熟度评价方法综述[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1998, 19(5): 428-432. Cheng Dingsheng. Review of source rock maturity evaluation by organic petrology method [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1998, 19(5):428-432 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [23] | 赵杏媛. 黏土矿物与油气[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2009, 30(4): 533-536. Zhao Xingyuan. The impact of clay minerals on oil-gas reservoir [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2009, 30(4): 533-536 (in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [24] | 邵龙义,李猛,李永红, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系页岩气地质特征及控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 311-322. Shao Longyi, Li Meng, Li Yonghong, et al. Geological characteristics and controlling factors of shale gas in the Jurassic of the northern Qaidam Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 311-322(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |
| [25] | 付小东, 饶丹, 秦建中, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘地区中侏罗统大煤沟组页岩油形成地质条件[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(6): 20-27. Fu Xiaodong, Rao Dan, Qin Jianzhong, et al. Geological conditions for shale oil forming of Middle Jurassic Dameigou Formation in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(6):20-27(in Chinese with English abstract).(  1) 1) |