2. 中国地质调查局发展研究中心, 北京 100037;
3. 中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所, 河北 廊坊 065000;
4. 辽宁招金白云黄金矿业有限公司, 辽宁 丹东 118107;
5. 中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心, 辽宁 沈阳 110034
2. Development and Research Center, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100037, China;
3. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, Hebei, China;
4. Liaoning Zhaojin Baiyun Gold Mining Corporation, Dandong 118107, Liaoning, China;
5. Shenyang Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning, China
[Objective] The Baiyun gold deposit, located in the eastern margin of the North China Craton, is one of the typical gold deposits in the Qingchengzi ore concentration area of Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province. By clarifying the formation age, genesis and tectonic background of the mafic dikes in the mining area, it is beneficial to deepen the understanding of the regional tectonic evolution process and the genesis of the deposit. [Methods] Based on the field geological characteristics of the deposit, the lamprophyres closely related to mineralization, have been studied in terms of petrography, chronology and geochemistry in this paper. [Results] LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data reveals that the lamprophyre formed at (126.81±0.65) Ma, indicating that it developed in the Early Cretaceous. Petrogeochemical characteristics show that the lamprophyres belong to alkali series and potassium hypostatic rocks, which are rich in magnesium (MgO=3.63%-4.07%, Mg# =54-60), potassium (K2O/Na2O=1.26-3.47) and alkali (K2O + Na2O= 4.41%-5.23%). The lamprophyres are enriched in large ion lithophile elements (Rb, Th, U) and light rare earth elements, but depleted in high field strength elements (Nb, Ta, Ti) and heavy rare earth elements, and exhibit typical arc magmatic features associated with subduction. Isotopic geochemical characteristics demonstrate that the lamprophyres have a high concentration of radioactive Pb isotopes. The initial 176Hf/177Hf value of zircon is 0.282117-0.282471, with negative εHf(t) values (-20.80--7.81), suggesting that the magma source is the enriched lithospheric mantle influenced by subducted melt/fluid metasomatism. [Conclusions] Integrated with the regional tectonic setting, the bottom of the lithospheric mantle was eroded by the heat of the asthenosphere mantle during the Cretaceous period due to the extensional environment caused by the subduction and rollback of the Paleo-Pacific plate, which resulted in partial melting and the formation of the Early Cretaceous mafic magma. The lamprophyres with arc characteristics in the Baiyun mining area may have formed along the Tanlu fault zone and its secondary faults. Therefore, the Early Cretaceous mafic magmatism in this region represents a response to the lithosphere thinning in the eastern North China Craton.
煌斑岩具有其独特的矿物组成和化学成分,通常指一些含有大量暗色矿物斑晶的浅成相暗色火成岩,经常以岩脉或岩墙的形式分布于不同时期的各种构造环境中(Rock, 1977, 1987;Rock et al., 1991)。一般认为煌斑岩是幔源岩浆活动的产物,因而成为窥探和了解地幔物质组成和演化、研究壳幔相互作用的重要突破口(姜耀辉等, 2005)。此外,在一些大型—超大型金多金属矿床集中区,煌斑岩常常表现出与金矿化十分密切的时空关系(Rock et al., 1991;宋英昕等,2018),暗示着其可能与金成矿作用密切相关,因此还显示出巨大的矿床学研究意义。
青城子矿集区位于辽宁省东部,是中国重要的金多金属成矿区域之一。区内中生代构造-岩浆活动较为强烈,形成了一系列不同时期的花岗质侵入体,同时煌斑岩等基性岩也十分发育,且多成脉岩群的形式产出(吴福元等, 2005; Yang et al., 2007a; Yu et al., 2009; 段晓侠等, 2012; 宋运红等, 2015; 杨凤超等, 2015)。该区有10多个中—大型铅锌矿床(如榛子沟、喜鹊沟、甸南、新岭等),4个中—大型金矿床(白云、林家三道沟、小佟家堡子、杨树),1个大型银矿床(高家堡子),以及众多小型矿床及矿点,累计探明铅锌储量160余万t,金300余t,银4000余(t王玉往等, 2017; 曾庆栋等, 2019)。白云金矿是青城子矿集区内的代表性的金矿床之一,该矿床自1978年发现以来,经过多年的找矿与勘探工作,累计探明金资源量已超过60 t,Au平均品位3.04×10-6。长期以来,许多学者围绕区内金多金属矿床的地质特征、成矿时代(张朋等, 2016b; Sun et al., 2019)、流体与金属的来源(代军治, 2005; 郝立波等, 2017;赵岩等,2020)、矿床成因及成矿作用(刘国平等, 2001;Liu et al., 2019)以及区域上及矿区范围内地表出露和钻孔揭露的煌斑岩等脉岩开展了年代学、地球化学(张朋等, 2016a, 2016c; 周国超等, 2017)等方面的研究,积累了丰富的研究成果。现有的研究工作表明,时间上,煌斑岩相较于辉长岩、闪长(玢)岩、花岗斑岩和石英斑岩等形成稍晚(李德东等, 2016; 周国超等, 2017),高精度年代学结果显示,青城子矿集区内发育的煌斑岩形成时代在(225.7 ± 1.1)~(227.7±1.3)Ma(张朋等, 2016a, 2016c; Sun et al., 2020),与前人所获得的印支期成矿年龄比较一致(刘国平等, 2000; 张朋等, 2016b);空间上,李德东等(2020)通过对区内典型铅锌矿区发育的煌斑岩进行的研究,认为煌斑岩具有与矿体/矿床一致的线性分布规律,因此对找矿预测有一定的指示意义。但是目前来看,对于白云金矿区探矿坑道内揭露的与金矿化(体)有密切时空关系的煌斑岩研究却较为薄弱。
本文拟通过辽东青城子矿集区白云金矿坑道内与成矿有关的煌斑岩进行详细的锆石U-Pb年代学、全岩主-微量元素地球化学以及Pb-Hf同位素地球化学的研究,并结合前人的研究成果,探讨本区煌斑岩的岩石成因和构造环境,以期为辽东青城子地区早白垩世构造岩浆演化提供新的约束,以及为区域早白垩世地球动力学背景和成矿提供重要依据。
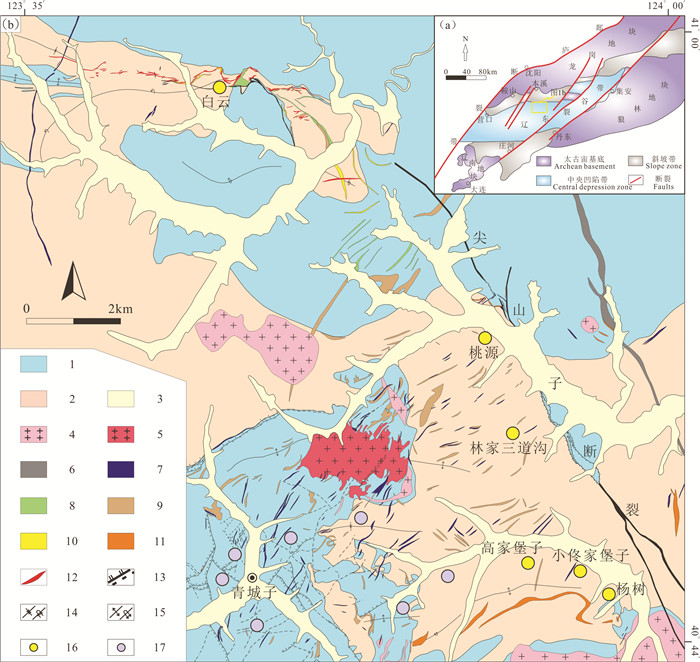
2 区域地质概况白云金矿位于辽东青城子矿集区的西北部,在大地构造位置上位于华北克拉通东缘、郯庐断裂带以东的东西向辽东裂谷带,该裂谷带北接龙岗地块,南邻狼林地块和辽南地块,东临太平洋构造域(图 1a)。区域上广泛出露古元古代辽河群地层,太古宙以及中—新元古代之后的古生代、中生代、新生代第四系等地层仅零星分布。辽河群是一套经历了绿片岩相—低角闪岩相变形变质作用的火山- 沉积变质岩系(Luo et al., 2004),以其特有的变质岩岩石组合、含矿性而独具特色,是区域有色金属、贵金属矿产的重要赋矿层位;按层序自下而上被划分为浪子山组、里尔峪组、高家峪组、大石桥组以及盖县组。受古元古代陆内裂谷作用、裂谷闭合后的碰撞造山过程(王惠初等,2005),以及中生代以来的不同时期、不同性质的构造运动相互叠加影响(王涛等,2007),区内形成了一系列以近东西向为主的复背斜、复向斜,东西向和北东向的深大断裂,以及北北东、北东和北西向的逆冲断裂。区域内岩浆活动强烈,时代集中在古元古代、印支期和燕山期;古元古代主要发育有条痕状角闪二长花岗岩类和斑状花岗岩类(即辽吉花岗岩),印支期发育有花岗岩类、碱性杂岩以及辉长-辉绿岩等,燕山期主要以花岗质和闪长质侵入岩为主、其次为基性—中酸性脉岩等。基性脉岩广泛分布于区域的西北部的甜水、石哈寨、白云—大磨岭一带,呈近东西走向的岩脉状、岩墙状产出。青城子矿集区内的煌斑岩脉、花岗斑岩脉比较密集地分布在新岭岩体、青城子镇以及林家三道沟金矿附近,主要呈北北东—北东向带状侵入到盖县组片岩和大石桥组大理岩中,少数侵入到岩体中(图 1b)。
|
图 1 辽东地区大地构造简图(a)和辽东青城子矿集区地质简图及白云金矿位置(b) (图 1a据骆辉和李俊建, 2002修改; 图 1b据辽宁省有色地质局103队, 2019修改) 1—大石桥组; 2—盖县组; 3—第四系; 4—古元古代花岗岩; 5—三叠纪花岗岩; 6—辉长岩; 7—煌斑岩; 8—闪长岩; 9—花岗斑岩; 10—石英斑岩; 11—伟晶岩; 12—金矿体; 13—断裂; 14—向斜/倒转向斜; 15—背斜/倒转背斜; 16—金(银)矿床; 17—铅锌矿床 Fig. 1 Simplified geotectonic map of eastern Liaoning Province (a), simplified geological map of Qingchengzi ore-concentrated area, showing the location of the Baiyun gold deposit (b) (Fig. 1a is modified from Luo and Li, 2002; Fig. 1b is modified from Liaoning Nonferrous Geology Bureau 103 Liaoning Nonferrous Geology Bureau 103 Team, 2019) 1- Dashiqiao Formation; 2- Gaixian Formation; 3- Quaternary; 4- Paleoproterozoic granite; 5- Triassic granite; 6- Gabbro; 7- Lamprophyre; 8-Diorite; 9-Granite porphyry; 10-Quartz porphyry; 11-Pegmatite; 12-Gold orebody; 13-Fault; 14-Syncline/inverted syncline; 15-Anticline/ inverted anticline; 16-Au(-Ag) deposits; 17-Pb-Zn deposits |
白云金矿矿区内出露的地层主要为古元古界多呈紧闭背(向)斜或倒转、翻卷背(向)斜构造形式辽河群上部层位的大石桥组和盖县组以及第四系出现。断裂构造以近东西向构造带为主体,具多期沉积物;古元古界辽河群变质岩系多呈东西向紧密活动特征,在大石桥组、盖县组地层中顺层产出,为的线型褶皱产出。矿区内构造运动形式复杂,由西主要的控矿构造和赋矿构造;此外,发育北西向尖向东,主体构造以东西向为主,发育一系列的褶皱山子断裂,以及规模较小的北东、北西、南北向的断和韧性、脆性断裂构造。褶皱构造规模大小不等,裂。矿区地表并未见区域上不同时期的较有规模的侵入岩体出露,所见多为各类基性—中酸性岩脉。通过野外调查及手标本观察、室内显微镜下鉴定,识别出辉长岩、煌斑岩、闪长岩、闪长玢岩、花岗斑岩、石英斑岩等岩性的脉岩。其中,辉长岩脉侵位最早,沿近南北向断裂充填;其他脉岩侵位较晚,煌斑岩常沿北东向断裂充填,闪长岩脉、闪长玢岩脉、花岗斑岩脉、石英斑岩脉多沿北西向和近东西向断裂充填。通过井下坑道观察发现,有的脉岩与矿体关系密切,直接构成矿体上下盘围岩。
3 样品采集与分析方法 3.1 样品采集根据野外观察,矿区内发育的煌斑岩脉或分布于矿体上盘围岩中,与矿体无明显穿插关系;或明显切过矿体,可能为成矿期侵位或稍晚于成矿。本文所研究的煌斑岩样品采集于二道沟矿段井下坑道320 m中段,沿着煌斑岩脉连续采样。煌斑岩呈规则脉状穿切1号矿体及含矿石英脉(图 2a),脉宽0.5~ 0.7 m,岩石新鲜部位灰褐色,强烈蚀变部位呈灰绿色-绿色,主要蚀变为硅化、绿泥石化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化及黄铁矿化,对新鲜部位切片通过显微镜下观察并结合手标本,根据长石含量以及暗色矿物种类及含量,将岩性定为闪斜煌斑岩(图 2b)。

|
图 2 白云金矿二道沟矿段320 m中段的煌斑岩穿切矿体(a),煌斑岩手标本(b)以及岩相学(c)特征 Hbl—角闪石; Pl—斜长石; Px—辉石; 红色五角星代表采样点 Fig. 2 Photographs of the lamprophyre crosscutting the orebodies in the elevation of 320 m in the Erdaogou mining section (a), hand specimen (b), and photomicrographs (c) showing some key geological features of the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit Hbl-Hornblende; Pl-Plagioclase; Px-Pyroxene; The red pentacle represents the sampling point |
煌斑岩,岩石呈灰褐色,具有典型的煌斑结构,块状构造,由斑晶和基质两部分组成(图 2c)。斑晶主要为普通角闪石和斜长石,以及少量辉石和黑云母,基质为角闪石、斜长石、碱性长石及少量的磷灰石、锆石和磁铁矿等副矿物。普通角闪石,褐棕色,自形长柱状,粒径多在50~100 μm,常可见六边形横切面,发育绿泥石化或绿帘石化;辉石,自形短柱状或粒状,粒径在50~80 μm,全部蚀变,可见碳酸盐矿物呈辉石的八边形假象;黑云母,浅黄褐色-浅褐色,自形片状,粒径多在50 μm左右;斜长石晶体呈半自形板状分布于角闪石粒间,粒径80~120 μm,发育绢云母化;碱性长石呈板条状,粒径10 μm左右。
3.2 分析方法煌斑岩中锆石颗粒的分选工作在河北省区域地质矿产研究所实验室完成,将岩石破碎,经浮选和电磁选等方法,经淘洗、挑纯出单颗粒锆石。锆石的制靶和照相工作在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成,手工挑出晶型完好、透明度和色泽度好的锆石用环氧树脂固定于样品靶上;样品靶表面经研磨抛光1/3~1/2,直至露出锆石新鲜截面;对靶上的锆石进行镜下透射光、反射光照相后,对锆石进行阴极发光(CL)成像。最后,选择典型的岩浆锆石进行锆石U-Pb测年和Hf同位素分析。
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成。激光剥蚀系统为193 nm ArF准分子激光器(型号为Resonetics-S155),激光束斑直径33 μm,剥蚀频率10 Hz,剥蚀时间30 s,以高纯He气为载气,与Ar气和少量N2气混合后进入电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(型号为iCAP Qc)。测试过程中以标准锆石91500(206Pb/238U年龄为(1065.4±0.6)Ma)为外标校正元素分馏,以标准锆石Plešovice作为盲样监控数据质量。NIST SRM 612作为信号漂移矫正,以标准锆石91500作为外标,以Si为内标测定主量和微量元素含量。测试数据经过ICPMSDataCal软件离线处理完成(Liu et al., 2010a, 2010b),谐和图谱和加权平均年龄计算利用Isoplot软件完成(Ludwig, 2003)。
全岩主、微量元素以及Pb同位素分析测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。所有岩石样品均破碎、磨碎(> 200目)制成分析样品。主量元素采用AxiosmAX型X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)测定;微量元素运用高分辨率电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,型号为Finnigan MAT Element XR)测定,详细的分析流程可参考高剑峰等(2003)。全岩铅同位素利用Phoenix热表面电离质谱仪完成。称取一定量(0.1~0.2 g)待测样品放入聚四氟乙烯坩埚中,加入混合酸(HF+HNO3+HClO4)分解,然后利用树脂交换法将样品分离出Pb,在充分蒸干后利用热表面电离质谱法进行铅同位素测定。质谱分析测量结果使用国际标样(NBS981)进行矫正,测量精度:对1 μg的铅,其204Pb/206Pb比值小于0.05%,208Pb/206Pb比值小于0.005%。
锆石微区原位Hf同位素分析测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所Finnigan Neptune型多接收等离子质谱和Newwave UP 213紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA-MC-ICP-MS)上进行的。Hf同位素分析点与U-Pb分析点上为同一位置,实验过程中使用的激光剥蚀束斑直径为55 μm,采用He气作为剥蚀物质载气,并在与Ar气混合形成混合气后,将剥蚀的样品传送至MC-ICP-MS,测定时使用锆石国际标样GJ1作为参考物质。相关仪器运行条件以及详细的实验流程见侯可军等(2007)。本次分析测试过程中,所测定的锆石标准GJ1的176Hf/177Hf加权平均值为0.282019±28(2SD, n=10),与文献报道值(侯可军等, 2007)在误差范围内保持一致。
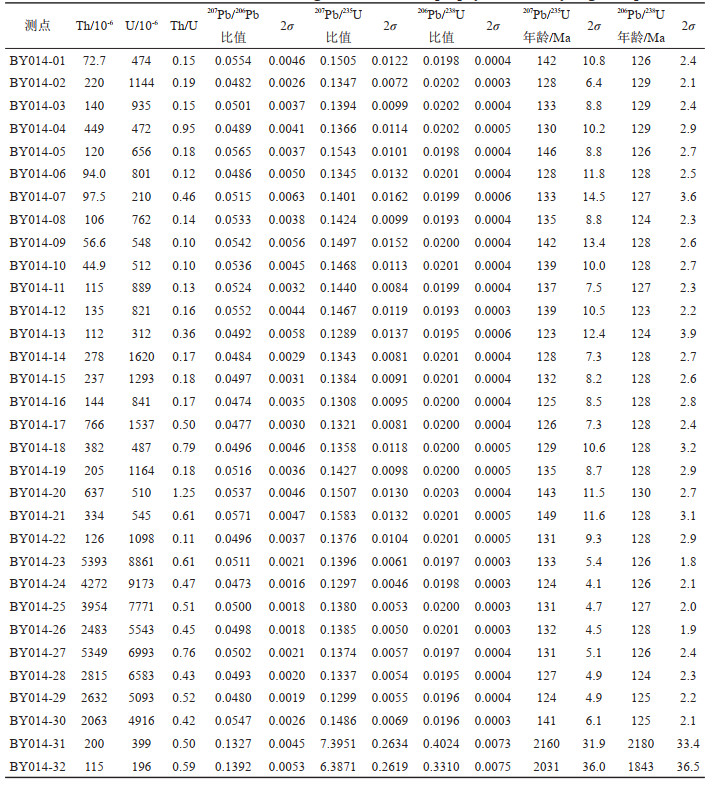
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年代学用于锆石U-Pb定年的煌斑岩样品(BY014)中的锆石多呈自形柱状—短柱状、无色透明。锆石长径在100~260 μm,主要集中在100~180 μm。锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像呈灰白色—灰黑色,内部结构清晰,显示出明显的、规则的振荡环带(图 3),为典型的岩浆成因锆石。32颗锆石的测定结果表明,锆石的Th、U含量较高,分别为44.9×10-6~5393×10-6和196×10-6~ 9173×10-6,Th/U比值为0.10~1.25(平均为0.4),进一步显示为岩浆成因(Hoskin et al., 2003)。

|
图 3 白云金矿煌斑岩的锆石CL图像特征以及U-Pb定年、Hf同位素测试点位 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescence images of zircons of the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit, with their U-Pb age data and corresponding Hf isotope analysis spots |
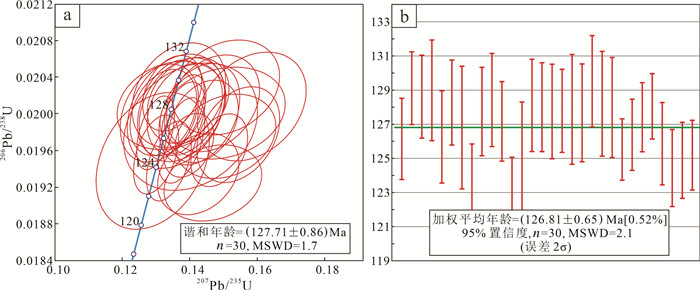
定年结果显示(表 1),除2颗年龄分别为(2160± 32)Ma和(2031±36)Ma较老的继承锆石以外,30颗锆石的年龄变化于(123±2.2)~(130±2.7)Ma,计算出的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(126.81±0.65)Ma(MSWD=2.1,n=30)(图 4b),与206Pb /238U-207Pb/235U谐和年龄(127.71±0.86)Ma(MSWD=1.7)(图 4a)在误差范围内基本一致,该加权平均年龄可解释为煌斑岩的结晶年龄。
|
图 4 白云金矿煌斑岩的锆石U-Pb谐和年龄曲线(a)和加权平均年龄(b) Fig. 4 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb Concordia (a) and weighted average age (b) diagram of the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit |
|
|
表 1 白云金矿煌斑岩的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果 Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit |
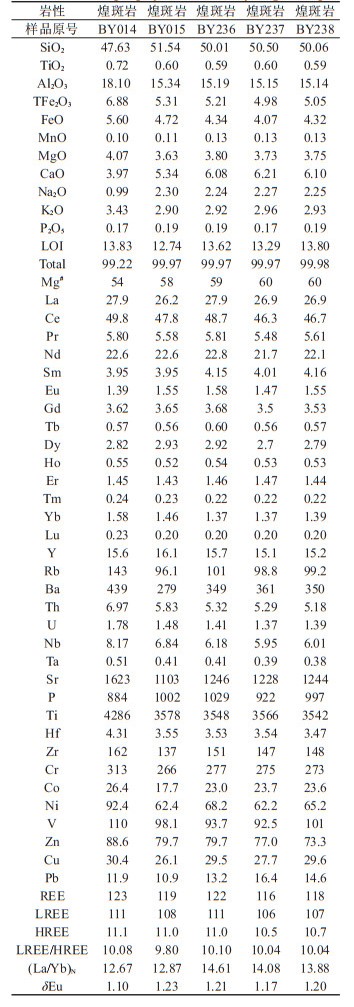
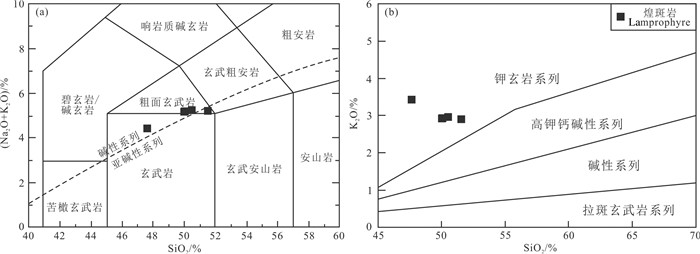
5件煌斑岩样品的全岩主量元素和微量稀土元素分析结果列于表 2。从表中数据可以看出,煌斑岩的烧失量变化较大(LOI=12.74%~13.83%),这可能与煌斑岩类岩石富集挥发分有关(和文言等, 2014),因此,在进行主量元素相关数据投图和分析时,均已扣除烧失量重新换算了百分含量。SiO2含量为47.63%~51.54%,平均为49.95%;MgO含量为3.63%~4.04%,Mg#值为54~60;Al2O3含量为15.14% ~17.96%;K2O含量为2.90% ~3.40%,Na2O含量为0.98%~2.30%,K2O/Na2O介于1.26~3.47,属于高钾系列;全碱(K2O+Na2O)含量为4.41%~5.23%,;在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) 图解中(图 5a),样品点基本落在碱性系列区域;在SiO2-K2O图解中(图 5b),样品点投影于钾玄岩系列区域。因而白云矿区煌斑岩属于碱性、钾玄质煌斑岩。
|
|
表 2 白云金矿煌斑岩的主量元素(%)、稀土和微量元素(10-6)化学分析结果 Table 2 Major (%), rare earth and trace element (10-6) data of the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit |
|
图 5 白云金矿煌斑岩的SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) 图解(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b) (图 5a据Le Bas et al., 1986; 碱性和亚碱性系列的分界线据Irvine and Baragar, 1971; 图 5b据Rock, 1987) Fig. 5 Diagrams of SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) (a) and SiO2-K2O (b) for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (Fig. 5a is after Le Bas et al., 1986, and the dividing line between basic and subbasic series is after Irvine and Baragar, 1971; Fig. 5b is after Rock, 1987) |
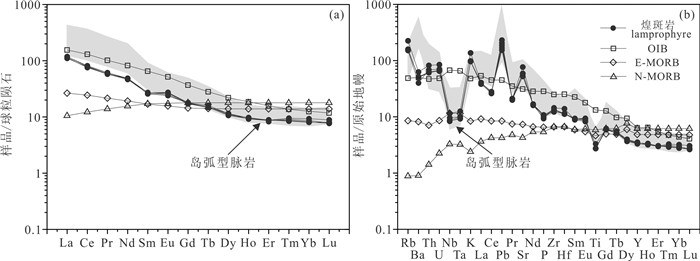
样品的稀土总量介于116×10-6~123×10-6,平均为119 × 10-6;轻稀土元素(LREE)含量介于106 × 10-6~111 × 10-6,平均为109 × 10-6,重稀土元素(HREE)含量介于10.5×10-6~11.1×10-6,平均为10.9× 10-6。LREE/HREE比值介于9.80~10.10,(La/Yb)N比值介于12.67~14.61,整体表现出轻稀土富集、重稀土相对亏损的特征。基本没有Ce异常和Eu负异常。在球粒陨石标准化的稀土配分模式图上(图 6a),所有样品的稀土配分曲线形态基本一致,表现为轻稀土富集、重稀土亏损的右倾平滑曲线。
|
图 6 白云金矿煌斑岩的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数值引自Sun and McDonough, 1989; OIB: 洋岛玄武岩; E-MORB: 富集型洋中脊玄武岩; N-MORB: 正常型洋中脊玄武岩) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized rare earth element (REE) distribution pattern (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (b) for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (Normalizing values are from Sun and McDonough, 1989; OIB: Oceanic island basalt; E-MORB: Enriched mid-oceanic ridge basalt; N-MORB: Normal mid-oceanic ridge basalt) |
从微量元素含量(表 2)和原始地幔标准化的微量元素蛛网图上(图 6b)可以看出,煌斑岩中不相容元素含量明显高于原始地幔,表现为不同程度的富集。一些大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、Sr明显富集,在蛛网图中表现为明显的峰,高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti强烈亏损,在蛛网图中表现为明显的谷。这些地球化学特征与胶东地区形成于早白垩世的岛弧型基性脉岩类似(梁亚运, 2017)
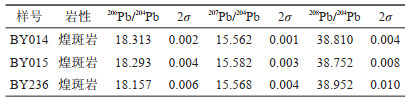
4.4 全岩Pb同位素3件煌斑岩样品的全岩Pb同位素的分析测试结果列于表 3。白云矿区煌斑岩的208Pb/204Pb为38.752~37.952,207Pb/204Pb为15.562~15.582,206Pb/204Pb为18.157~18.313。
|
|
表 3 白云金矿煌斑岩的全岩Pb同位素分析结果 Table 3 Whole rock Pb isotope analysis results of the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit |
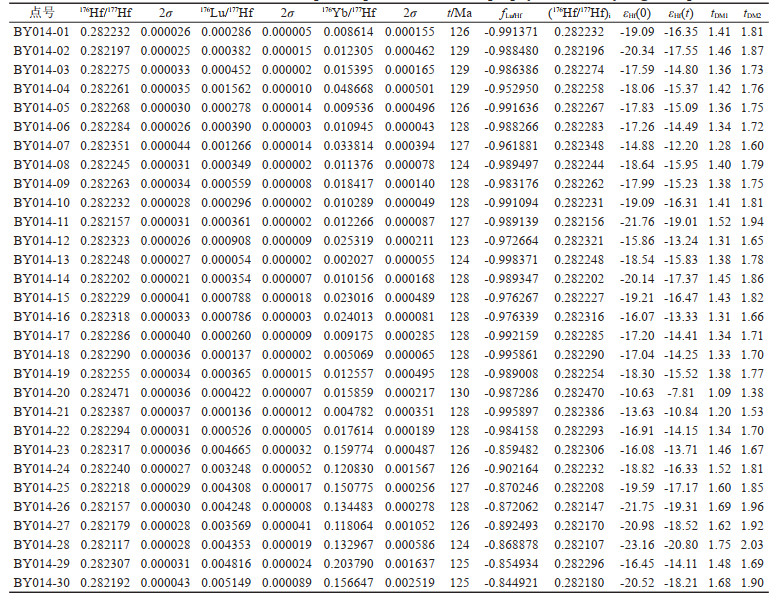
对已经进行U-Pb定年的煌斑岩样品(BY014)的锆石颗粒共进行了30个点的微区原位Hf同位素分析,分析测试及相关计算结果列于表 4,煌斑岩中的锆石εHf(t)值和Hf二阶段模式年龄值的频率直方图见图 7。
|
|
表 4 白云金矿煌斑岩的锆石微区原位Hf同位素分析结果 Table 4 Results of zircon in situ Hf isotopic compositions of the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit |
|
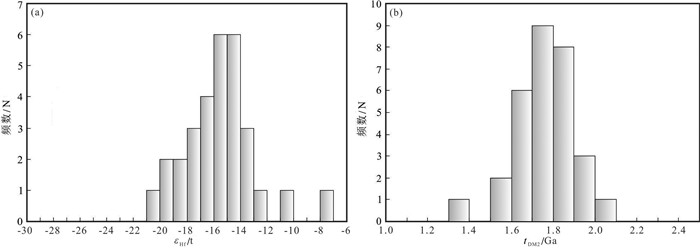
图 7 白云金矿煌斑岩中锆石的εHf(t)值(a)和二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)(b)的频率直方图 Fig. 7 The εHf(t) values (a) and two-stage model ages (tDM2) (b) frequency histograms of the zircons in the lamprophyre in the Baiyun gold deposit |
30个测试点的176Hf/177Hf初始值为0.282117~ 0.282471,比较均一;根据锆石LA-ICP-MS定年的单点原位年龄矫正计算获得的(176Hf/177Hf)i的值为0.282107~0.282470,εHf(t)的变化范围为-20.80~-7.81,平均值为-15.46;tDM2为1.38~2.03 Ga,平均值为1.76 Ga;锆石Hf二阶段模式年龄远大于其结晶年龄。
5 讨论 5.1 岩石成因 5.1.1 富集地幔部分熔融白云金矿煌斑岩的MgO(3.63%~4.04%)含量、Mg#值(54~60)较高,而且相容元素Cr(266×10-6~ 313×10-6)、Co(17.7×10-6~26.4×10-6)、Ni(62.2×10-6~ 92.4×10-6)和V(92.5×10-6~110×10-6)含量较高,显示出岩浆的演化程度较低、具有与起源于地幔的原始岩浆(Cr=200×10-6~500×10-6, Co=25×10-6~80×10-6, Ni=90×10-6~700×10-6; Rock et al., 1991)较相似的特征,表明其来源于镁铁质地幔的部分熔融。此外,白云金矿煌斑岩具有富钾、富碱、富集LILEs(Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、Sr)、相对富集LREE、以及富集放射性Pb同位素的特征,与来源于富集地幔的岩浆特征一致,而明显亏损HFSEs(Nb、Ta、Ti)则暗示富集岩石圈地幔曾经历过俯冲作用的改造。研究显示,镁铁质岩石的这些特征表明其可能来源于俯冲熔体/流体交代改造的富集岩石圈地幔(Tarney and Jones, 1994),或者可能与幔源岩浆上侵过程中遭受地壳物质的同化混染有关(Ma et al., 1998)。
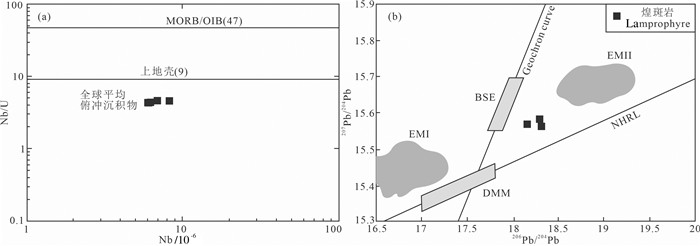
Nb/U比值常作为判别地壳混染的指标(柴凤梅等, 2007; 贾丽琼等, 2013),白云金矿煌斑岩的Nb/U比值(4.3~4.6)远低于MORB和OIB的Nb/U比值(≈ 47)(Hofmann et al., 1986),同时低于上地壳的Nb/U比值(≈9)(Taylor and McLennan, 1985)以及全球平均俯冲沉积物的Nb/U比值(≈5)(Plank and Langmuir, 1998),介于全球平均俯冲沉积物的与俯冲带释放流体的Nb/U比值(≈0.22)(Ayers, 1998)之间(图 8a),表明地幔源区所具有的壳源特征是由于板块俯冲过程中释放的熔体/流体对地幔的交代所致。此外,相对均一的206Pb/204Pb比值也排除了地壳混染的可能性,因为地壳沉积物具有非常大的206Pb/204Pb变化范围(Nelson et al., 1986; 姜耀辉等, 2006)。在207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb图解中(图 8b),样品投影点均落于北半球参考线(NHRL)上方,具有比MORB高很多的207Pb/204Pb和206Pb/204Pb比值,说明其源区是富集的,同时投点趋向于EMII范围附近,EMII地幔端元是与俯冲和地壳物质密切相关的(Hart, 1989),也暗示白云金矿煌斑岩岩浆熔体可能来源于受俯冲熔体/流体交代的富集地幔源区。
|
图 8 白云金矿煌斑岩的Nb-Nb/U图解(a)和206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb图解(b) (图 8a据姜耀辉等, 2006; 图 8b据Zindler and Hart, 1986; DMM—亏损地幔端元; MORB—洋中脊玄武岩; OIB—洋岛玄武岩; EMI—I型富集地幔; EMII—II型富集地幔; BSE—全硅酸盐地球; NHRL—北半球参考线) Fig. 8 Diagrams of Nb-Nb/U (a), and 206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb (b) for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (Fig 8a. is after Jiang et al., 2006; Fig 8b is after Zindler and Hart, 1986; DMM-Depleted mantle end member; MORB-Mid-oceanic ridge basalt; OIB-Oceanic island basalt; EMI-I-type enriched mantle; EMII-II-type enriched mantle; BSE-Bulk silicate earth; NHRL-Northern Hemisphere reference line) |
由于锆石Lu-Hf同位素体系具有很高的封闭温度,即使在麻粒岩相等高级变质作用下,锆石仍可以保持原始的Hf同位素组成,因此锆石Hf同位素组成可以揭示复杂的岩浆形成过程(Griffin et al., 2002)。通常,若锆石εHf(t)为正值,表明岩浆源区为亏损地幔或从亏损地幔中新生的年轻地壳;若锆石εHf(t)为负值,表明岩浆源区为富集地幔或以古老地壳物质为主导(Kinny and Maas, 2003; 吴福元等, 2007)。白云金矿煌斑岩中锆石的强烈的负的εHf(t)值以及εHf(t)值均落在1.6~2.5 Ga的地壳演化线范围内(图 9),显示出地幔来源特征,表明其源自富集岩石圈地幔(Griffin et al., 2000);锆石Hf同位素模式年龄大于其结晶年龄也暗示了煌斑岩来源于富集岩石圈地幔(吴福元等, 2007)。此外,白云金矿煌斑岩的这些岩石地球化学特征与世界范围内的钾镁煌斑岩/钾玄质岩石较为相似,后者被认为是起源于与俯冲作用有关的富集地幔(Nelson, 1992;Nowell et al., 2004;Davies et al., 2006);同时也与辽东地区粗玄质基性脉岩(Yang et al., 2007b)以及胶东地区岛弧型基性脉岩(Yang et al., 2004;Zhao et al., 2012;Ma et al., 2014a, b)的特征相似,表明他们具有一致的源区,即华北克拉通下部富集的岩石圈地幔。因此,笔者认为白云金矿煌斑岩来源于华北克拉通下部被俯冲熔体/流体交代作用改造的富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融。

|
图 9 白云金矿煌斑岩的U-Pb年龄(t)-εHf(t)图解 (DM—亏损地幔; CHUR—球粒陨石均一源储; CC—大陆地壳) Fig. 9 Diagram of U-Pb age(t)-εHf(t) for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (DM-Depleted mantle; CHUR-Chondrite uniform reservoir; CC-Continental crust) |
白云金矿煌斑岩为钾玄质岩石,具有较高的K2O含量(2.90%~3.40%),K2O/Na2O比值(1.26~3.47)高于大陆地壳平均值1.1(Taylor and McLennan, 1985),这表明地幔源区可能存在一个富钾的矿物相,如金云母或角闪石。Furman and Graham(1999)的研究表明,与金云母平衡的熔体具有低的Ba含量和Ba/Rb(< 20)比值,但是与角闪石平衡的熔体具有低的Rb/Sr(< 0.06)比值和高的Ba/Rb比(> 20)比值。白云金矿煌斑岩的Rb/Sr比值为0.08~0.09(大于0.06),Ba/Rb比值为2.90~3.65(小于20),表明其原始岩浆可能形成于含金云母的地幔源区。
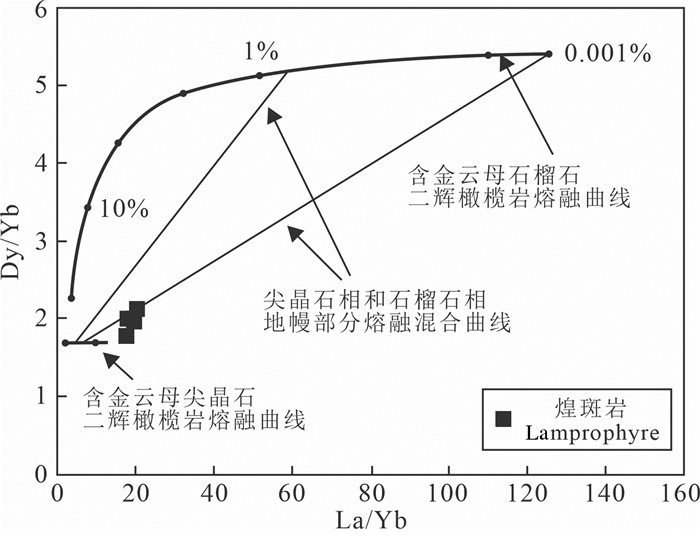
研究表明,地幔橄榄岩部分熔融过程中初始熔体的Yb含量主要受控于源区残留的石榴石(Johnson, 1998)。由石榴石相部分熔融形成的熔体,其La/Yb和Dy/Yb比值变化范围都很大,Dy/Yb比值一般大于2.5;而由尖晶石相地幔部分熔融形成的熔体,其La/Yb比值变化范围很小,Dy/Yb比值几乎恒定,一般都小于1.5(Thirlwall et al., 1994;Miller et al., 1999)。本区煌斑岩的La/Yb比值在17.66~20.36,Dy/Yb比值介于1.78~2.13,La/Yb和Dy/Yb比值变化都很小,在原始岩浆的Dy/Yb-La/ Yb图解中(图 10)可以看出,随着La/Yb比值的变化,Dy/Yb比值变化趋势很小,而且本文研究的白云金矿煌斑岩落在了含金云母的尖晶石二辉橄榄岩部分熔融曲线的范围附近,暗示含金云母的尖晶石相地幔的部分熔融可以形成白云金矿煌斑岩原始镁铁质岩浆,或者说其源区可能位于尖晶石相橄榄岩地幔稳定区。此外,白云金矿煌斑岩稀土配分曲线(图 6a)没有显示出较大的轻重稀土分馏,重稀土配分曲线也相对低而且平坦,这与源于尖晶石相地幔源区的岩浆特征一致,它明显不同于起源于单一的石榴石相地幔源区的岩浆所具有的较陡的重稀土配分曲线特征(Miller et al., 1999)。因此,笔者推断白云金矿煌斑岩的岩浆源区可能是含金云母的尖晶石相二辉橄榄岩地幔。
|
图 10 白云金矿煌斑岩的La/Yb-Dy/Yb图解(据Miller et al., 1999) Fig. 10 Diagram of La/Yb-Dy/Yb for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (after Miller et al., 1999) |
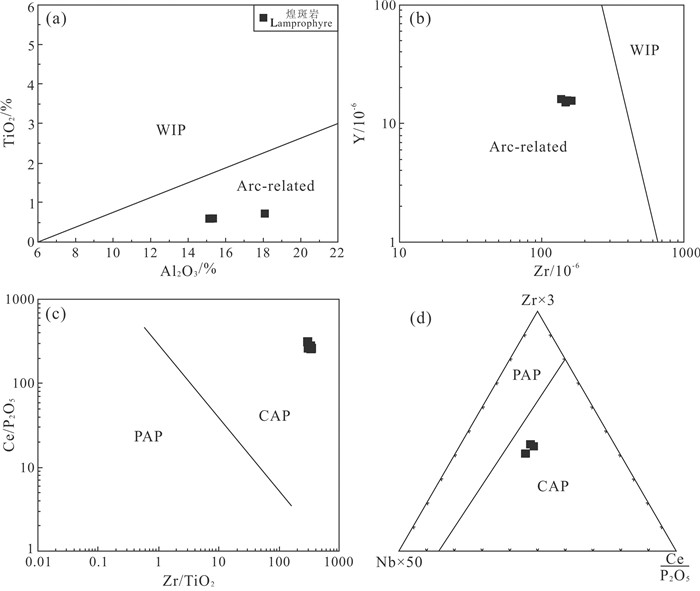
本区煌斑岩富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素、亏损高场强元素和重稀土元素,尤其是在稀土配分图中具有Nb-Ta的槽和Ti的谷,显示出与俯冲相关的弧岩浆岩的特征(Rogers and Hawkesworth, 1989; Stern, 2002);同时,在微量元素蛛网图中,所有煌斑岩样品与岛弧型基性脉岩的曲线特征一致;此外,煌斑岩的岩浆源区为受俯冲熔体/流体交代的富集岩石圈地幔也暗示着其形成环境与板块俯冲-碰撞相关。为了进一步探讨白云金矿煌斑岩形成的构造环境,笔者利用一些不活动元素的协变关系来进行构造环境的判别。在钾玄质岩石的Al2O3-TiO2和Zr-Y图解(图 11a、b)中,白云金矿煌斑岩样品均投点于与岛弧环境相关岩浆岩范围,指示其形成与板块俯冲-碰撞相关。在Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5和Zr×3-Nb×50-Ce/P2O5图解(图 11c、d)中,所有煌斑岩样品均落于大陆弧范围内,暗示其为与俯冲作用有关的形成于活动大陆边缘的陆缘弧岩浆岩。
|
图 11 白云金矿煌斑岩的构造环境判别图解 (底图据Müller et al., 1992修改; WIP—板内环境; Arc-related—岛弧环境; PAP—后碰撞弧; CAP—大陆弧) Fig. 11 Diagrams of tectonic setting discrimination for the lamprophyres in the Baiyun gold deposit (modified after Müller et al., 1992; WIP-Within-plate; Arc-related-island arc related settings; PAP-Post collisional arc; CAP-Continental arc) |
前人研究表明,中生代时期华北克拉通东部岩石圈发生了显著减薄(厚度已经由 > 150 km锐减为60~80 km; Menzies et al., 1993, 2007),同时伴随有强烈的构造-岩浆活动与成矿作用。为了诠释华北克拉通东部岩石圈减薄的地球动力学机制,前人主要提出了两种模型:(1)软流圈地幔热/化学侵蚀模型,认为岩石圈的减薄是受到下伏软流圈地幔衍生熔体产生的热/化学侵蚀所造成的,是一个自下而上的缓慢的均变过程(Xu, 2001);(2)下地壳重力拆沉模型,认为岩石圈的减薄是由于前期造山和加厚使得榴辉岩化的下地壳因重力失稳而连同古老岩石圈地幔拆沉一并进入下伏对流地幔中所致,是一个自上而下的发生在较短时期内的快速过程(Wu et al., 2005a)。然而,随着研究的不断深入,许多学者更倾向于一种板块俯冲改造模型(朱日祥和郑天愉, 2009;吴福元等, 2014;Zhu et al., 2017;郑永飞等, 2018),认为侵蚀和拆沉过程可能只是华北克拉通岩石圈减薄的二级机制,而古太平洋板块的西向俯冲对岩石圈地幔的侧向侵蚀作用可能是华北克拉通岩石圈减薄以及伴随的大规模岩浆作用的一级/主导构造机制(郑永飞和吴福元, 2009;Xu and Zheng, 2017;郑永飞等, 2018)。因此,前人研究普遍认为,处于华北克拉通东部的辽东地区广泛发育的早白垩世构造-岩浆活动主要是受到古太平洋板块俯冲的影响,形成于与古太平洋板块俯冲有关的活动大陆边缘环境。
从区域构造演化历史来看,华北克拉通东部中生代的构造-岩浆活动不是连续的,经历了晚三叠世—早侏罗世(220~178 Ma)的陆内俯冲-碰撞拼贴造山、中—晚侏罗世(170~145 Ma)的古太平洋板块俯冲造成的持续挤压造山、晚侏罗世(144±2 Ma)由挤压向伸展拉张转换、到早白垩世(135~108 Ma)的陆内持续扩张的过程(Jiang et al., 2005b, 2010;Wu et al., 2005a;Yang and Li, 2008;Zhao et al., 2012;Song et al., 2021),并在130~120 Ma期间发生强烈的岩石圈减薄与破坏,伴随有大规模的镁铁质岩浆和长英质岩浆作用(郑永飞等, 2018)。自中侏罗世起,古太平洋板块在东亚大陆之下开始低角度俯冲(Jiang et al., 2006b, 2009),至此,中国大陆东缘成为大陆边缘弧;由于华北克拉通岩石圈地幔受到俯冲流体的交代而弱化甚至板块俯冲的物理侵蚀而发生减薄(郑永飞和吴福元, 2009)。早白垩世(~144 Ma)开始,由于俯冲古太平洋板片发生回卷后撤而与上覆岩石圈地幔发生脱耦,引起弧后拉张作用(姜耀辉和王国昌, 2016; 郑永飞等, 2018),造成下部岩石圈的拆沉,与此同时软流圈地幔开始侧向流动进入残留岩石圈地幔与俯冲板片之间的空隙,岩石圈地幔底部受到软流圈地幔的热侵蚀,从而发生了部分熔融,产生早白垩世镁铁质岩浆,沿着郯庐深大断裂带及其次一级断裂向浅部地壳运移,部分岩浆顺着这些断裂通道上升侵位至地表,最终形成了白云金矿这一时期的具有岛弧特征的煌斑岩。
本文获得的白云金矿煌斑岩的锆石U-Pb加权平均年龄为(126.81±0.65)Ma,形成时代为早白垩世,这为该区构造演化提供了新的年代学证据。结合区域构造演化史以及前述煌斑岩岩石成因及其形成的构造背景,笔者认为白云金矿煌斑岩为早白垩世古太平洋板块俯冲回卷后撤引起的弧后伸展拉张环境中的产物,进一步印证了辽东地区广泛存在的早白垩世镁铁质岩浆活动,是对华北克拉通东部岩石圈减薄的响应。
6 结论(1)白云金矿煌斑岩具有富MgO、富K2O、富碱的地球化学特征,属于碱性系列、钾玄质煌斑岩;富集Rb、Th、U等大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素和重稀土元素,在微量元素蛛网图中显示出明显的Nb、Ta、Ti的谷,表现出与俯冲有关的弧岩浆岩相似的特征。
(2)白云金矿煌斑岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为(126.81±0.65)Ma;锆石εHf(t)= -20.80~-7.81,平均值为-15.46;富集放射性Pb同位素组成;指示岩浆来源于受俯冲熔体/流体交代的富集岩石圈地幔,源区可能为含金云母的尖晶石相地幔橄榄岩。
(3)结合区域构造岩浆演化历史,白云金矿煌斑岩形成于古太平洋板块俯冲后撤所导致的弧后伸展拉张构造环境下;本区早白垩世镁铁质岩浆活动是对这一时期华北克拉通东部岩石圈减薄的响应,为华北克拉通下部富集岩石圈地幔部分熔融的产物。
致谢: 野外工作得到了辽宁招金白云黄金矿业有限公司工程师们的支持和帮助,实验测试工作得到了中国地质大学(武汉)的赵葵东教授、中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所的侯可军研究员、核工业北京地质研究院的刘牧老师的支持和帮助,文章修改过程中得到了两位匿名审稿人及编辑提出的宝贵意见,在此一并表示感谢。
Ayers J. 1998. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the Mantle wedge of subduction zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 132(4): 390-404. |
Chai Fengmei, Parat A, Zhang Zhaochong, Mao Jingwen, Dong Lianhui, Muhtar Z R. 2007. Geochemistry of the lamprophyre dykes in the SW margin of the Tarim Block and their source region[J]. Geological Review, 53(1): 11-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Dai Junzhi. 2005. Characteristics of Ore-forming Fluids and Discussion on the Genesis of Au, Ag Deposits in Qingchengzi region, Liaoning Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
Davies G R, Stolz A J, Mahotkin I L, Nowell G M, Pearson D G. 2006. Trace element and Sr-Pb-Nd-Hf isotope evidence for ancient, fluid-dominated enrichment of the source of Aldan Shield lamproites[J]. Journal of Petrology, 47(6): 1119-1146. |
Duan Xiaoxia, Liu Jianming, Wang Yongbin, Zhou Lingli, Li Yonggui, Li Bin, Zhang Zhuang, Zhang Zuolun. 2012. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological significance of Late Triassic magmatism in Qingchengzi orefield, Liaoning[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2): 595-606 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Furman T, Graham D. 1999. Erosion of lithospheric mantle beneath the East African Rift system: Geochemical evidence from the Kivu volcanic province[J]. Lithos, 48: 237-262. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00031-6 |
Gao Jianfeng, Lu Jianjun, Lai Mingyuan, Lin Yuping, Pu Wei. 2003. Analysis of trace elements in rock samples using HR-ICPMS[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 39(6): 844-850 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, van Achterbergh E, O'Reilly S Y, Shee S R. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle, LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, Pearson N J, O'Reilly S Y, Xu X S, Zhou X M. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 61: 237-269. |
Hao Libo, Zhao Xin, Zhao Yuyan. 2017. Stable isotope characteristics and ore genesis of the Baiyun gold deposit, Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(2): 442-451 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Hart S R. 1989. Heterogeneous mantle domains: Signatures, genesis and mixing chronologies[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90(3): 273-296. |
He Wenyan, Mo Xuanxue, Yu Xuehui, Dong Guochen, He Zhonghua, Huang Xiongfei, Li Xiaowei, Jiang Lili. 2014. Genesis and geodynamic settings of lamprophyres from Beiya, western Yunnan: Constraints from geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3287-3300 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert M, White W M. 1986. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: New constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 79(1/2): 33-45. |
Hoskin P W O, Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62. |
Hou Kejun, Li Yanhe, Zou Tianren, Qu Xiaoming, Shi Yuruo, Xie Guiqing. 2007. Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2595-2604 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523-548. |
Jia Liqiong, Mo Xuanxue, Dong Guochen, Xu Wenyi, Wang Liang, Guo Xiaodong, Wang Zhihua, Wei Shaogang. 2013. Genesis of lamprophyres from Machangqing, western Yunnan: Constraints from geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1247-1260 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Jiang Yaohui, Jiang Shaoyong, Zhao Kuidong, Ni Pei, Ling Hongfei, Liu Dunyi. 2005a. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages of lamprophyres in the Liaodong Peninsula and its restriction on the beginning time of lithospheric thinning in eastern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(19): 2161-2168 (in Chinese). |
Jiang Y H, Ling H F, Jiang S Y, Fan H R, Shen W Z, Ni P. 2005b. Petrogenesis of a Late Jurassic peraluminous volcanic complex and its high-Mg potassic quenched enclaves at Xiangshan, Southeast China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 46(6): 1121-1154. |
Jiang Yaohui, Jiang Shaoyong, Ling Hongfei, Dai Baozhang. 2006a. Petrogenesis of Cu-bearing porphyry associated with continent-continent collisional setting: Evidence from the Yulong porphyry Cu ore-belt, east Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 697-706 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Zhao K D, Ling H F. 2006b. Petrogenesis of Late Jurassic Qianlishan granites and mafic dykes, Southeast China: Implications for a back-arc extension setting[J]. Geological Magazine, 143(4): 457-474. |
Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, Liao S Y, Zhao K D, Ling H F. 2009. Middle to Late Jurassic felsic and mafic magmatism in southern Hunan Province, Southeast China: Implications for a continental arc to rifting[J]. Lithos, 107(3/4): 185-204. |
Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, Ling H F, Ni P. 2010. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Jurassic shoshonitic lamprophyre dikes from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 100(3/4): 127-151. |
Jiang Yaohui, Wang Guochang. 2016. Petrogenesis and geodynamics of Late Mesozoic granitoids in SE China: Tectonic model involving repeated slab-advance-retreat of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(6): 1073-1081 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Johnson K T M. 1998. Experimental determination of partition coefficients for rare earth and high-field-strength elements between clinopyroxene, garnet, and basaltic melt at high pressures[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 133(1/2): 60-68. |
Kinny P D, Maas R. 2003. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 327-341. |
Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B. 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27(3): 745-750. |
Li Dedong, Wang Yuwang, Zhou Guochao, Shi Yu, Xie Hongjing. 2016. Preliminary analysis of the relationship between dikes and gold mineralization in Baiyun gold deposit, Liaoning[J]. Mineral Exploration, 7(1): 113-119 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Liang Yayun. 2017. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Mafic Dikes and Metallogenic Dynamics in Jiaodong Peninsula[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-150 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
Liaoning Nonferrous Geology Bureau 103 Team. 2019. Report of Sub-Projects of Deep Resource Survey in the Baiyun Area, Liaoning Province[R]. 1-166 (in Chinese).
|
Liu Guoping, Ai Yongfu. 2000. Studies on the mineralization age of Baiyun gold deposit in Liaoning[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(4): 627-632 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Liu Guoping, Ai Yongfu, Deng Yanchang, Zhou Guangxue. 2001. Metallogenic environment and prospecting evaluation of gold and silver deposits in Qingchengzi ore field[J]. Geology in China, 28(1): 40-45 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Liu J, Liu F X, Li S H, Lai C K. 2019. Formation of the Baiyun gold deposit, Liaodong gold province, NE China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, fluid inclusion, and C-H-O-Pb-He isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 104: 686-706. |
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, Gao C G, Zong K Q, Wang D B. 2010a. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2): 537-571. |
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, Gao C G, Gao S, Xu J, Chen H H. 2010b. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546. |
Ludwig K R. 2003. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 4: 1-70. |
Luo Hui, Li Junjian. 2002. Geological features of Au, Ag, Pb, Zn, Cu and Co ore deposits and its forming conditions in the eastern region of Liaoning Province, China[J]. Progress in Precambrian Research, 25(3/4): 240-245 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Luo Y, Sun M, Zhao G C, Li S Z, Xu P, Ye K, Xia X P. 2004. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of the Liaohe Group in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton: constraints on the evolution of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt[J]. Precambrian Research, 134(3/4): 349-371. |
Ma C Q, Li Z C, Ehlers C, Yang K G, Wang R J. 1998. A post-collisional magmatic plumbing system: Mesozoic granitoid plutons from the Dabieshan high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone, east-central China[J]. Lithos, 45(1/4): 431-456. |
Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hofman A W, Dai B Z, Hou M L, Zhao K D, Chen L H, Li J W, Jiang Y H. 2014a. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton?[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 124: 250-271. |
Ma L, Jiang S Y, Hou M L, Dai B A, Jiang Y H, Yang T, Zhao K D, Pu W, Zhu Z Y, Xu B. 2014b. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous calc-alkaline lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Implication for lithospheric evolution of the eastern North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 25(2): 859-872. |
Menzies M A, Fan W M, Zhang M. 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 76(1): 71-81. |
Menzies M, Xu Y, Zhang H, Fan W. 2007. Integration of geology, geophysics and geochemistry: A key to understanding the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 96: 1-21. |
Miller C, Schuster R, Klötzli U, Frank W, Purtschellr F. 1999. Post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic magmatism in SW Tibet: geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic constraints for mantle source characteristics and petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 40(90): 1399-1424. |
Müller D, Rock N M S, Groves D I. 1992. Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks in different tectonic settings: a pilot study[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 46: 259-289. |
Nelson D R, McCulloch M, Sun S S. 1986. The origins of ultrapotassic rocks as inferred from Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 50(2): 231-245. |
Nelson D R. 1992. Isotopic characteristics of potassic rocks, evidence for the involvement of subducted sediments in magma genesis[J]. Lithos, 28: 403-420. |
Nowell G M, Pearson D G, Bell D R, Carlson R W, Smith C B, Kempton P D, Noble S R. 2004. Hf isotope systematics of kimberlites and their megacrysts: New constraints on their source regions[J]. Journal of Petrology, 45(8): 1583-1612. |
Plank T, Langmuir C H. 1998. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 145(3/4): 325-394. |
Rock N M S. 1977. The nature and origin of lamprophyres: Some definitions, distinctions, and derivations[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 13(2): 123-169. |
Rock N M S. 1987. The nature and origin of lamprophyres: An overview[J]. In: Fitton JG and Upton BGJ (eds. ). Alkaline Igneous Rocks. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 30(1): 191-226.
|
Rock N M S, Bowes D R, Wright A E. 1991. Lamprophyres[M]. Glasgow: Blackie, 1-285.
|
Rogers G, Hawkesworth C J. 1989. A geochemical traverse across the North Chilean Andes: Evidence for crust generation from the mantle wedge[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 91(3/4): 271-285. |
Song M C, Ding Z J, Zhang J J, Song Y X, Bo J W, Wang Y Q, Liu H B, Li S Y, Li J, Li R X, Wang B, Liu X D, Zhang L L, Dong L L, Li J, He C Y. 2021. Geology and mineralization of the Sanshandao supergiant gold deposit (1200 t) in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A review[J]. China Geology, 4(4): 686-719. |
Song Yunhong, Hao Libo, Yang Fengchao, Zhao Dongfang. 2015. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and geochemistry of the Triassic Dixiongshan rock mass in Liaodong Peninsula: geological significance[J]. Geology and Resources, 24(5): 444-452 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Song Yingxin, Song Mingchun, Sun Weiqing, Ma Xiaodong, Li Dapeng. 2018. Metallogenic epoch and regional crust evolution in the Jiaodong gold deposit, Shandong Province: Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages of mafic dykes[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(5): 908-919 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Stern R J. 2002. Subduction zones[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 40(4): 1-38. |
Sun G T, Zeng Q D, Li T Y, Li A, Wang E Y, Xiang C S, Wang Y B, Chen P W, Yu B. 2019. Ore genesis of the Baiyun gold deposit in Liaoning province, NE China: constraints from fluid inclusions and zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12: 299. |
Sun G T, Zeng Q D, Wang Y B, Li B, Chen P W. 2020. Geochronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic dykes in the Qingchengzi ore field, Liaoning Province, China: Magmatic evolution and implications for ore genesis[J]. Geological Journal, 55(8): 5745-5763. |
Sun S S, McDonough W S. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. |
Tarney J, Jones C E. 1994. Trace element geochemistry of orogenic igneous rocks and crustal growth models[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 151(5): 855-868. |
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1-312.
|
Thirlwall M F, Upton B G J, Jenkins G. 1994. Interaction between continental lithosphere and Iceland plume-Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry of Tertiary basalts, NE Greenland[J]. Journal of Petrology, 35(3): 839-879. |
Wang Huichu, Lu Songnian, Zhao Fengqing, Zhong Changting. 2005. The Paleoproterozoic geological records in North China craton and their tectonic significance[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 28(3): 129-143 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wang Tao, Zheng Yadong, Zhang Jinjiang, Wang Xinshe, Zeng Lingshen, Tong Ying. 2007. Some problems in the study of Mesozoic extensional structure in the North China craton and its significance for the study of lithospheric thinning[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(9): 1154-1166 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wang Yuwang, Xie Hongjing, Li Dedong, Shi Yu, Liu Fuxing, Sun Guoqiang, Sun Qiming, Zhou Guochao. 2017. Prospecting prediction of ore concentration area exemplified by Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Au-Ag ore concentration area, eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 36(1): 1-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wu F Y, Lin J Q, Wilde S A, Zhang X O, Yang J H. 2005a. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1/2): 103-119. |
Wu Fuyuan, Yang Jinhui, Liu Xiaoming. 2005b. Geochronological framework of the Mesozoic granitic magmatism in the Liaodong Peninsula, northeast China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(3): 305-317 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wu Fuyuan, Li Xianhua, Zheng Yongfei, Gao Shan. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wu Fuyuan, Xu Yigang, Zhu Rixiang, Zhang Guowei. 2014. Thinning and destruction of the cratonic lithosphere: A global perspective[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 44: 2358-2372 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Xu Y G. 2001. Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archaean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: evidence, timing and mechanism[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 26: 747-757. |
Xu Z, Zheng Y F. 2017. Continental basalts record the crust-mantle interaction in oceanic subduction channel: A geochemical case study from eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 145: 233-259. |
Yang Fengchao, Song Yunhong, Hao Libo, Chai Peng. 2015. Late Jurassic SHRIMP U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of granite from the Sanjiazi area in Liaodong and their geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(10): 1773-1782 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Yang J H, Chung S L, Zhai M G, Zhou X F. 2004. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of mafic dikes from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: evidence for vein-plus-peridotite melting in the lithospheric mantle[J]. Lithos, 73(3/4): 145-160. |
Yang J H, Sun J F, Chen F K, Wilde S A, Wu F Y. 2007a. Sources and petrogenesis of Late Triassic dolerite dikes in the Liaodong Peninsula: Implications for post-collisional lithosphere thinning of the eastern north China Craton[J]. Journal of Petrology, 48(10): 1973-1997. |
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Wilde S A, Liu X M. 2007b. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic granitoids and their enclaves with implications for post-collisional lithospheric thinning of the Liaodong Peninsula, North China Craton[J]. Chemical Geology, 242(1/2): 155-175. |
Yang W, Li S G. 2008. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Western Liaoning: Implications for lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 102(1/2): 88-117. |
Yu G, Chen J F, Xue C J, Chen Y C, Chen F K, Du X Y. 2009. Geochronological framework and Pb, Sr isotope geochemistry of the Qingchengzi Pb-Zn-Ag-Au orefield, Northeastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(3/4): 367-382. |
Zeng Qingdong, Chen Renyi, Yang Jinhui, Sun Guotao, Yu Bing, Wang Yongbin, Chen Peiwen. 2019. The metallogenic characteristics and exploring ore potential of the gold deposits in eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 5(7): 1939-1963 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhang Peng, Chen Dong, Zhao Yan, Kou Linlin, Yang Hongzhi, Wang Xjin, Sha Deming. 2016a. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemical characteristics and its geological significance of lamprophyres in Zhenzigou Pb-Zn deposit, Liaodong[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 26(3): 636-647 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhang Peng, Li Bin, Li Jie, Chai Peng, Wang Xijin, Sha Deming, Shi Jianmin. 2016b. Re-Os isotopic dating and its geological implication of gold bearing pyrite from the Baiyun gold deposit in Liaodong Rift[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(4): 731-738 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhang Peng, Zhao Yan, Kou Linlin, Yang Hongzhi. 2016c. Zircon U-Pb dating and its geological significance of lamprophyres from Qingchengzi orefield, Liaodong[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 37(7): 1056-1060 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Yan, Yang Hongzhi, Yang Fengchao, Zhang Peng, Gu Yuchao, Xu Jia. 2020. Genesis of the typical gold deposits in Qingchengzi orefield, Liaodong Peninsula: Evidences from S-D-O isotopes[J]. Geology and Resources, 29(1): 21-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Zhang J, Dai L Q, Li Q L, Liu X M. 2012. Syn-exhumation magmatism during continental collision: Evidence from alkaline intrusives of Triassic age in the Sulu orogen[J]. Chemical Geology, 328: 70-88. |
Zheng Yongfei, Wu Fuyuan. 2009. Growth and reworking of cratonic lithosphere[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54: 1945-1949 (in Chinese). |
Zheng Yongfei, Xu Zheng, Zhao Zifu, Dai Liqun. 2018. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in North China: Implications for thinning and destruction of cratonic lithosphere[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 48(4): 379-414 (in Chinese). |
Zhou Guochao, Wang Yuwang, Li Dedong, Shi Yu, Xie Hongjing. 2017. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb dating of dykes from the Baiyun gold deposit in eastern Liaoning[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(4): 620-627 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhu Rixiang, Zheng Tianyu. 2009. Destruction geodynamics of the North China Craton and its Paleoproterozoic plate tectonics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54: 1950-1961 (in Chinese). |
Zhu R X, Zhang H F, Zhu G, Meng Q R, Fan H R, Yang J H, Wu F Y, Zhang Z Y, Zheng T Y. 2017. Craton destruction and related resources[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 106(7): 2233-2257. |
Zindler A, Hart S R. 1986. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 14(1): 493-571. |
柴凤梅, 帕拉提·阿布都卡迪尔, 张招崇, 毛景文, 董连慧, 木合塔尔·扎日. 2007. 塔里木板块西南缘钾质煌斑岩地球化学及源区特征[J]. 地质论评, 53(1): 11-21. |
代军治. 2005. 辽宁青城子地区金、银矿床成矿流体特征及成因探讨[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 1-106.
|
段晓侠, 刘建明, 王永彬, 周伶俐, 李永贵, 李斌, 张壮, 张作伦. 2012. 辽宁青城子铅锌多金属矿田晚三叠世岩浆岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 28(2): 595-606. |
高剑峰, 陆建军, 赖鸣远, 林雨萍, 濮巍. 2003. 岩石样品中微量元素的高分辨率等离子质谱分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 39(6): 844-850. |
和文言, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 董国臣, 和中华, 黄雄飞, 李小伟, 姜丽莉. 2014. 滇西北衙煌斑岩的岩石成因及动力学背景: 年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3287-3300. |
郝立波, 赵昕, 赵玉岩. 2017. 辽宁白云金矿床稳定同位素地球化学特征及矿床成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(2): 442-451. |
侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 曲晓明, 石玉若, 谢桂青. 2007. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2595-2604. |
贾丽琼, 莫宣学, 董国臣, 徐文艺, 王梁, 郭晓东, 王治华, 韦少港. 2013. 滇西马厂箐煌斑岩成因: 地球化学、年代学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 29(4): 1247-1260. |
姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 倪培, 凌洪飞, 刘敦一. 2005. 辽东半岛煌斑岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其对中国东部岩石圈减薄开始时间的制约[J]. 科学通报, 50(19): 2161-2168. |
姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 凌洪飞, 戴宝章. 2006. 陆-陆碰撞造山环境下含铜斑岩岩石成因——以藏东玉龙斑岩铜矿带为例[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 697-706. |
姜耀辉, 王国昌. 2016. 中国东南部晚中生代花岗岩成因与深部动力学机制——古太平洋板块反复俯冲-后退模式[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(6): 1073-1081. |
李德东, 王玉往, 周国超, 石煜, 解洪晶. 2016. 辽宁白云金矿区岩脉与成矿作用浅谈[J]. 矿产勘查, 7(1): 113-119. |
李德东, 王玉往, 王伟, 邱金柱, 李生辉, 张志超, 周国超. 2020. 辽宁青城子地区煌斑岩与找矿预测[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 35(3): 301-313. |
梁亚运. 2017. 胶东早白垩世基性脉岩岩石成因与成矿动力学驱动[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-150.
|
辽宁省有色地质局103队. 2019. 辽宁省白云地区深部资源调查子项目成果报告[R]. 1-166.
|
刘国平, 艾永富. 2000. 辽宁白云金矿床成矿时代探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 16(4): 627-632. |
刘国平, 艾永富, 邓延昌, 周广学. 2001. 青城子矿田金银矿床成矿环境和找矿评价[J]. 中国地质, 28(1): 40-45. |
骆辉, 李俊建. 2002. 辽东裂谷Au、Ag、Pb、Zn、Cu、Co金属矿床地质特征和成矿条件[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 25(3/4): 240-245. |
宋英昕, 宋明春, 孙伟清, 马晓东, 李大鹏. 2018. 胶东金矿成矿时代及区域地壳演化——基性脉岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 37(5): 908-919. |
宋运红, 郝立波, 杨凤超, 赵东芳. 2015. 辽东三叠纪弟兄山岩体SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 24(5): 444-452. |
王惠初, 陆松年, 赵风清, 钟长汀. 2005. 华北克拉通古元古代地质记录及其构造意义[J]. 地质调查与研究, 28(3): 129-143. |
王涛, 郑亚东, 张进江, 王新社, 曾令森, 童英. 2007. 华北克拉通中生代伸展构造研究的几个问题及其在岩石圈减薄研究中的意义[J]. 地质通报, 26(9): 1154-1166. |
王玉往, 解洪晶, 李德东, 石煜, 刘福兴, 孙国强, 孙启明, 周国超. 2017. 矿集区找矿预测研究——以辽东青城子铅锌-金-银矿集区为例[J]. 矿床地质, 36(1): 1-24. |
吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明. 2005. 辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J]. 高校地质学报, 11(3): 305-317. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
吴福元, 徐义刚, 朱日祥, 张国伟. 2014. 克拉通岩石圈减薄与破坏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 44: 2358-2372. |
杨凤超, 宋运红, 郝立波, 柴鹏. 2015. 辽东三家子地区晚侏罗世花岗岩SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 89(10): 1773-1782. |
曾庆栋, 陈仁义, 杨进辉, 孙国涛, 俞炳, 王永彬, 陈沛文. 2019. 辽东地区金矿床类型、成矿特征及找矿潜力[J]. 岩石学报, 35(7): 1939-1963. |
张朋, 陈冬, 赵岩, 寇林林, 杨宏智, 王希今, 沙德铭. 2016a. 辽东榛子沟铅锌矿煌斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 26(3): 636-647. |
张朋, 李斌, 李杰, 柴鹏, 王希今, 沙德铭, 时建民. 2016b. 辽东裂谷白云金矿载金黄铁矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(4): 731-738. |
张朋, 赵岩, 寇林林, 杨宏智. 2016c. 辽东青城子矿田煌斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 37(7): 1056-1060. |
赵岩, 杨宏智, 杨凤超, 张朋, 顾玉超, 胥嘉. 2020. 辽东半岛青城子矿田典型金矿成因: 来自硫、氢、氧同位素的证据[J]. 地质与资源, 29(1): 21-28. |
郑永飞, 吴福元. 2009. 克拉通岩石圈的生长和再造[J]. 科学通报, 54: 1945-1949. |
郑永飞, 徐峥, 赵子福, 戴立群. 2018. 华北中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与克拉通减薄和破坏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(4): 379-414. |
周国超, 王玉往, 李德东, 石煜, 解洪晶. 2017. 辽东白云金矿区脉岩锆石的U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(4): 620-627. |
朱日祥, 郑天愉. 2009. 华北克拉通破坏机制与古元古代板块构造体系[J]. 科学通报, 54: 1950-1961. |