A study of nitrate background level of shollow groundwater in the Liujiang Basin
-
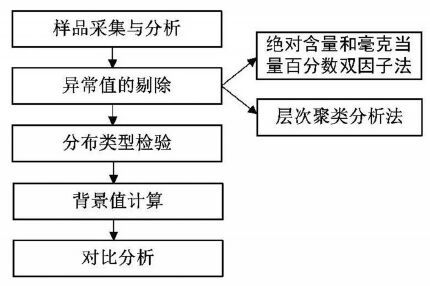
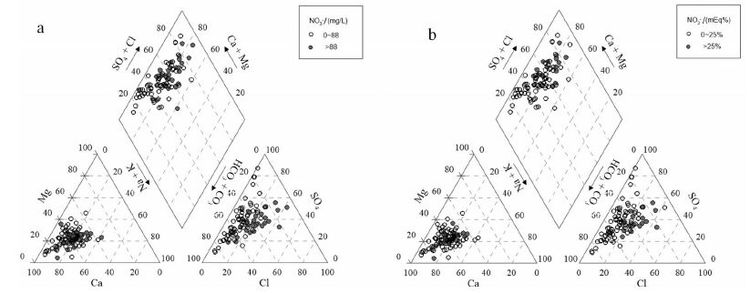
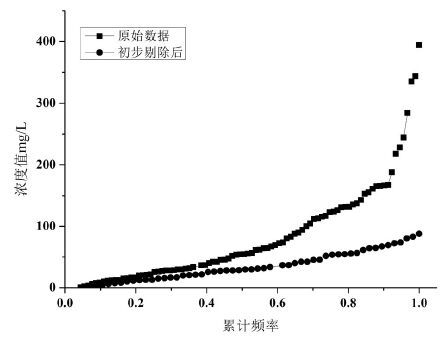
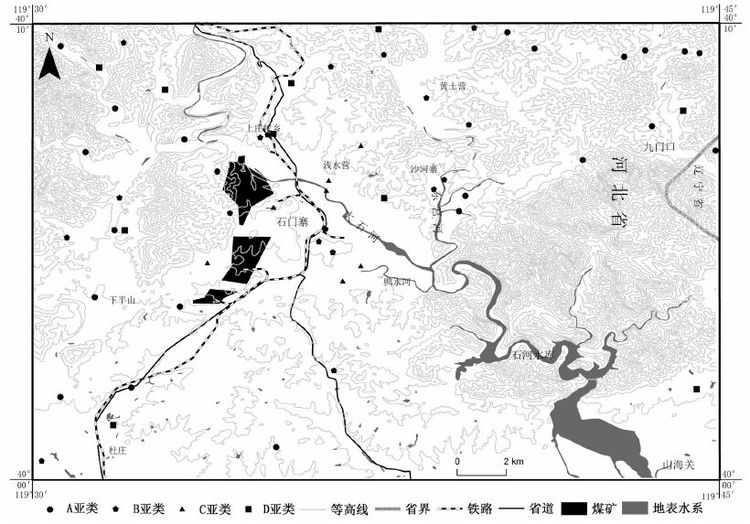
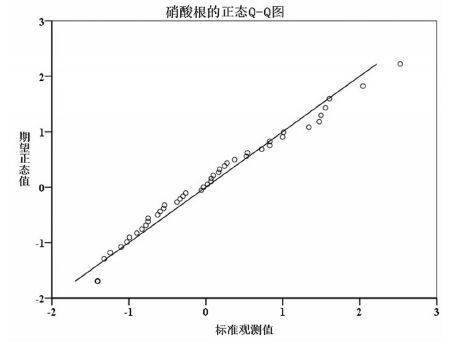
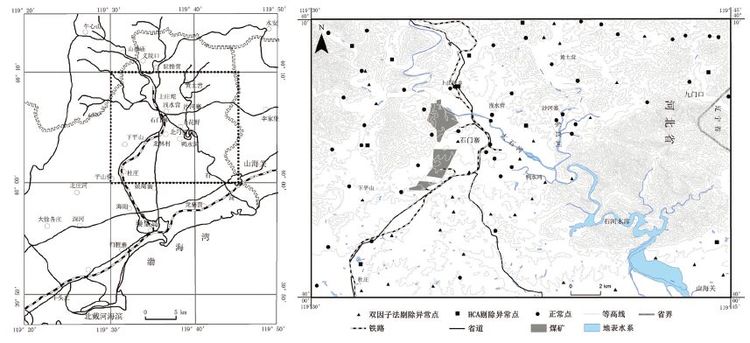
摘要: 为探索地下水硝酸盐背景值获取方法,文章以柳江盆地为研究对象,在对比分析国内外研究方法的基础上,首先采用绝对含量和毫克当量百分位数双因子法从宏观上剔除硝酸盐异常数据,然后再利用层次聚类分析结合主成分分析法,分析地下水水化学特征及识别异常分类,进一步剔除异常数据。最后剩余数据进行分布类型检验,采用浓度累计频率法确定地下水硝酸盐背景值范围。研究结果表明,绝对含量和毫克当量百分位数双因子法虽然不能完全剔除异常值,但可为后续层次聚类分析异常识别减少异常信息和子集;层次聚类分析法注重对各亚类的水化学特征分析来识别分析异常数据,具有识别人为异常和天然异常的优势。对比分析常用的数理学方法计算表明,2种方法结合,更能有效识别异常,计算出的地下水硝酸盐背景值更合理。异常数据剔除分析表明,柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸盐异常与农业化肥的超量施用和居民生活污水与垃圾粪便的下渗污染具有密切的关系。Abstract: The method of calculating groundwater nitrate background level was explored in Liujiang Basin as a research object. Based on a comparison and analysis of methods adopted both in China and abroad, the authors firstly used an absolute concentration and milliequivalent percentile double factors method to eliminate outliers macroscopically, and then employed hierarchy clustering analysis combined with principal component analysis to investigate hydrochemical characteristics and identify anomaly category for further candidate selection. The last remaining data were examined for distribution type with the range of groundwater nitrate background level being determined by the cumulative frequency method. The results show that, although the absolute concentration and milliequivalent percentile double factors method cannot completely eliminate outliers, it helps to reduce abnormal information and subset for subsequent hierarchical clustering analysis identifying outliers. Hierarchical clustering analysis method takes advantage of identification of artificial and natural anomaly in that it emphasizes groundwater hydrochemical characteristics analysis. Compared with the mathematical methods, it is more efficient to identify outliers and more reasonable to calculate groundwater nitrate background level by using the two methods in combination. The outliers analysis shows that the high nitrate content in shallow groundwater is closely related to overuse of agricultural fertilizer and living sewage and faeces infiltration in Liujiang basin.
-
Keywords:
- nitrate /
- background level /
- groundwater /
- hierarchy clustering analysis /
- Liujiang basin
-
-
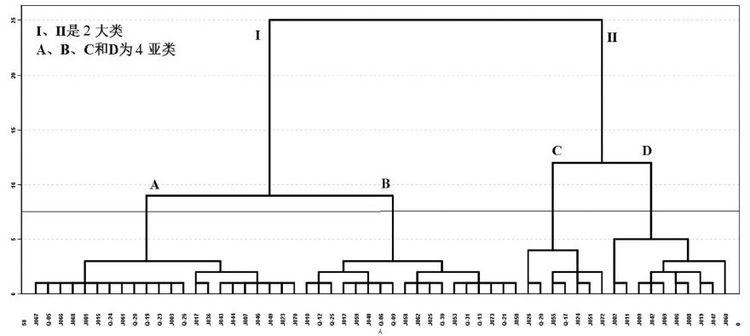
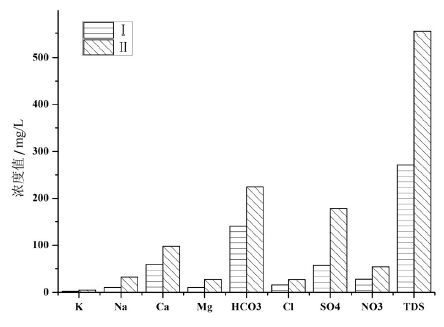
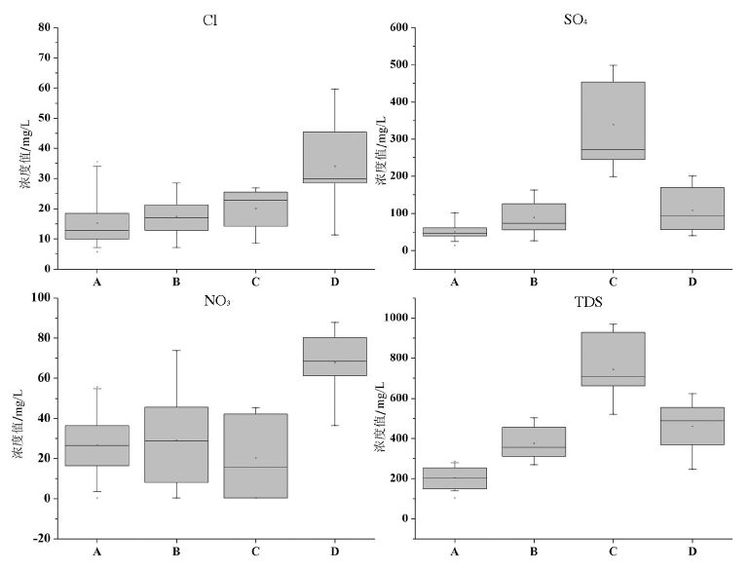
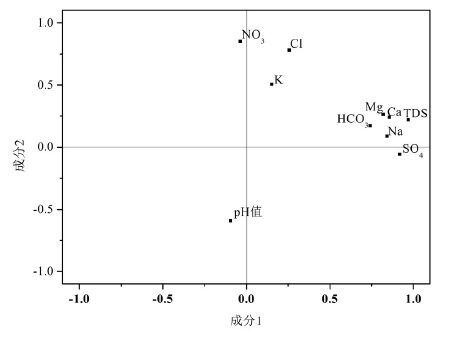
HCA各类中位数特征值
The categories of median concentrations in hierarchical clustering analysis
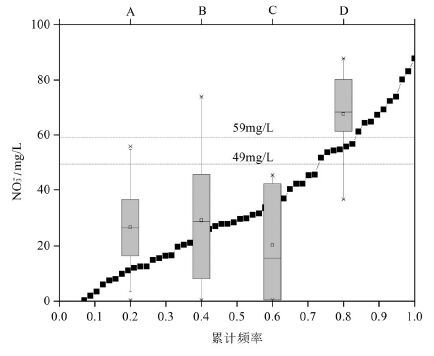
各背景值计算方法的对比
Comparison of various methods for calculating background level
-
[1] Böhlke J K. Erratum: Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2002, 10(3): 438-439.
[2] Vitousek P M, Aber J D, Howarth R W, et al. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycles: Sources and consequences[J]. Ecological Applications, 1997, 7(3): 737-750.
[3] Schlesinger W H. On the fate of anthropogenic nitrogen[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(1): 203-208.
[4] 于文礼. 吉林省地下水环境背景值特征及其变异规律[J]. 吉林地质, 1991, 10(1): 38-43. Yu Wenli. The characteristics of background values of environmental groundwater and their variation regularities in Jilin 表2 各背景值计算方法的对比 Table 2 Comparison of various methods for calculating background level 注:平均值±2σ为平均值加减2 倍标准差法;中位数± 2MAD为中位数加减2 倍绝对中位差法;I2σ为迭代平均值加减2 倍标准差法;GICPD为累计频率曲线图解法;双因子法+ HCA为双因子法和HCA结合剔除异常后计算的背景值;单位mg/L. 680 中国地质2016年 Province[J]. Jilin Geology, 1991, 10(1): 38-43 (in Chinese with English abstract). [5] 齐万秋,周金龙. 石河子市地下水环境背景值[J]. 干旱环境监测, 1994, 8(1): 14-16. Qi Wanqiu, Zhou Jinlong. Environment background values of the groundwater of Shihezi City[J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 1994, 8(1): 14-16(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] 王小玲,刘予. 北京市永定河冲洪积扇地下水环境背景值的调查研究[J]. 城市地质, 1994(2): 20-28. Wang Xiaoling, Liu Yu. The investigation of the groundwater environment background value in Beijing Yongding River Alluvial fans[J]. City Geology, 1994(2): 20-28(in Chinese). [7] 夏晨, 李金柱, 何中发. 上海市浅层地下水环境地球化学背景值研究[J]. 上海地质, 2006, (1): 24-28. Xia Chen, Li Jinzhu, He Zhongfa. Research on geochemisty background value for subsurface water in Shanghai[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2006, (1): 24-28(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 郭晓静, 周金龙, 王毅萍, 等. 塔里木盆地地下水环境背景值[J]. 人民黄河, 2011, 33(1): 61-63. Guo Xiaojin, Zhou Xiaolong, Wang Yiping, et al. Tarim basin groundwater environment background value[J]. Yellow River, 2011, 33(1): 61-63 (in Chinese). [9] 张英, 孙继朝, 黄冠星, 等. 珠江三角洲地区地下水环境背景值初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(1): 190-196. Zhang Ying, Sun Jichao, Huang Guanxing, et al. A preliminary study of natural background levels of groundwater in the Zhujiang River Delta[J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(1): 190-196. (in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 刘文波, 冯翠娥, 高存荣. 河套平原地下水环境背景值[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, (4): 147-157. Liu Wenbo, Feng Cui'e, Gao Cunrong. Background value of groundwater environment in Hetao Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, (4): 147-157 (in Chinese with English abstract). [11] Natural Environment Research Council. Natural Baseline Quality in European Aquifers, a Basis for Aquifer Management (BASELINE) [R]. BaSeLiNe, 2003.
[12] Nieto P, Custodio E, Manzano M. Baseline groundwater quality: An European approach[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2005, 8(4): 399-409.
[13] 邱汉学,黄巧珍. 地下水环境背景值及其确定方法[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 1994, (Z3): 16-20. Qiu Hanxue, Huang Qiaozhen. The concept of groundwater environment background and its determination[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China (Social Sciences), 1994, (Z3):16-20 (in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 樊丽芳, 陈植华. 地下水环境背景值的确定[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2004, 16(7): 90-92. Fan Lifang, Chen Zhihua. Determination of environment background value of groundwater[J]. West China Exploration Engineering, 2004, 16(7): 90-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 韩双宝, 张福存, 张徽, 等. 中国北方高砷地下水分布特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 747-753. Han Shuangbao, Zhang Fucun, Zhang Hui, et al. An analysis of the distribution and formation of high arsenic groundwater in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 747-753(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 鲁孟胜, 韩宝平, 武凡, 等. 鲁西南地区高氟地下水特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 294-302. Lu Mengsheng, Han Baoping, Wu Fan, et al. Characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine groundwater in southwestern Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1): 294-302(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 徐清, 刘晓端, 汤奇峰, 等. 山西晋中地区地下水高碘的地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 809-815. Xu Qing, Liu Xiaoduan, Tang Qifeng, et al. High iodic geochemical characteristics of the groundwater in central Shanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 809-815(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 王凌, 张国印, 孙世友, 等. 河北省环渤海地区地下水硝态氮含量现状及其成因分析[J]. 河北农业科学, 2009, 13(10): 89-92. Wang Ling, Zhang Guoyin, Sun Shiyou, et al. Analysis on the current situation of nitrate-n concentration in groundwater and its causes in Bohai Rim of Hebei Province[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 13(10): 89-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 茹淑华, 张国印, 孙世友, 等. 河北省地下水硝酸盐污染总体状况及时空变异规律[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, (5): 48-52. Ru Shuhua, Zhang Guoyin, Sun Shiyou, et al. Status of the contamination and spatial-temporal variations of nitrate in groundwater of Hebei Province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, (5): 48-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 徐春霞, 刘树庆, 安虹宇, 等. 秦皇岛市地下水环境质量评价与分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2007, 14(2): 330-332. Xu Chunxia, Liu Shuqing, An Hongyu, et al. The analysis and assessment of groundwater quality of Qinhuangdao[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2007, 14(2): 330-332 (in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 代伟. 秦皇岛市农业面源污染特征分析[J]. 中国环境管理干部学院学报, 2013, (5): 43-45, 62. Dai Wei. Characteristic analysis on agricultural non-point source pollution emission in Qinhuangdao City[J]. Journal of Environmental Management College of China, 2013, (5): 43-45, 62 (in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 郭高轩, 辛宝东, 刘文臣, 等. 我国地下水环境背景值研究综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(2): 95-98. Guo Gaoxuan, Xin Baodong, Liu Wenchen, et al. Review on the 第43卷第2 期廖磊等:柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸盐背景值研究681 study of the environment background values of groundwater in China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(2): 95-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). [23] 寇文杰, 谢振华, 赵立新, 等. 探讨地下水背景值确定方法及其容易忽视的几个问题[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(8): 3603-3605. KouWenjie, Xie Zhenghua, Zhao Lixin, et al. On several methods for determining the groundwater background value and some easily neglected problems[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(8): 3603-3605 (in Chinese with English abstract). [24] Edmunds W M, Shand P. Natural Groundwater Quality[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2008: 15-31..
[25] Huang Tianming, Pang Zhonghe, Yuan Lijuan. Nitrate in groundwater and the unsaturated zone in (semi) arid northern China: baseline and factors controlling its transport and fate[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(1): 145-156.
[26] Fuentes I, Casanova M, Seguel O, et al. Morphophysical pedotransfer functions for groundwater pollution by nitrate leaching in Central Chile[J]. Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 2014, 74(3): 340-348.
[27] Wang L, Stuart M E, Bloomfield J P, et al. Prediction of the arrival of peak nitrate concentrations at the water table at the regional scale in Great Britain[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2012, 26(2): 226-239.
[28] Morgenstern U, Daughney C J. Groundwater age for identification of baseline groundwater quality and impacts of land-use intensification-The National Groundwater Monitoring Programme of New Zealand[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 456-457: 79-93.
[29] J DaugRhney C, R Reeves R. Definition of hydrochemical facies in the New Zealand National Groundwater Monitoring Programme[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 44(2): 105-130.
[30] Guggenmos M R, Daughney C J, Jackson B M, et al. Regionalscale identification of groundwater-surface water interaction using hydrochemistry and multivariate statistical methods, Wairarapa Valley, New Zealand[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011, 15(11): 3383-3398.
[31] Daughney CJ, Raiber M, Moreau-Fournier M, et al. Use of hierarchical cluster analysis to assess the representativeness of a baseline groundwater quality monitoring network: comparison of New Zealand's national and regional groundwater monitoring programs[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2012, 20 (1): 185-200.
[32] 贺秀全. 地下水环境背景值研究中存在的几个问题[J]. 地下水, 1994, 16(2): 68-69. He Xiuquan. The existing problems in the study of groundwater environment background value[J]. Groundwater, 1994, 16(2): 68-69 (in Chinese). [33] Güler C, Thyne G, McCray J, et al. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2002, 10(4): 455-474.
[34] Koh D C, Chae G T, Yoon Y Y, et al. Baseline geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the mountainous area of Jeju Island, South Korea: Implications for degree of mineralization and nitrate contamination[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 376(1-2): 81-93.
[35] 杨志恒. 基于Ward 法的区域空间聚类分析[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2010, (S1): 382-386. Yang Zhiheng. Region spatial cluster algorithm based on ward method[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2010, (S1): 382-386 (in Chinese with English abstract). [36] Matschullat J, Ottenstein R, Reimann C. Geochemical background-Can we calculate it?[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(9): 173-188.
[37] Helena B, Pardo R, Vega M, et al. Temporal evolution of ground water composition in an alluvial aquifer(Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis[J]. Water Res., 2000, 34(3): 807-816.
[38] 李广贺, 张旭, 徐慧纬. 煤矿区富含硫酸盐地下水特征与治理技术[C]// 第六届世界华人地质科学研讨会和中国地质学会二零零五年学术年会论文摘要集. 2005: 124-129. li Guanghe, zhang xu, Xu Huiwei. The high sulfate groundwater characteristics and management technology in coal mining area[C]// The sixth world Chinese geological science symposium and the academic conference of geological society of China in 2005 paper and abstract set. 2005: 124-129 (in Chinese). [39] Lee L, Helsel D. Baseline models of trace elements in major aquifers of the United States[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20 (8): 1560-1570.
-
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 褚宴佳 ,何宝南 ,陈珍 ,何江涛 . 基于随机森林模型识别浅层地下水TDS异常的方法研究. 地学前缘. 2025(02): 456-468 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 涂春霖,陈庆松,尹林虎,李强,和成忠,刘振南. 我国地下水硝酸盐污染及源解析研究进展. 环境科学. 2024(06): 3129-3141 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张小文,袁伟,胡亚召. 地下水劣质劣变评价体系研究. 城市地质. 2023(03): 24-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 任坤,潘晓东,彭聪,梁嘉鹏,曾洁,甘明伟,张华,魏良帅. 氮氧同位素和水化学解析昭通盆地地下水硝酸盐来源及对环境的影响. 中国地质. 2022(02): 409-419 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王海军. 柳江盆地岩浆活动对主力煤田水文地质特征的影响. 煤炭学报. 2021(05): 1670-1684 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 何建国,王莉,章梅,王彦君,刘莉. 徐州沛县地下水应急水源地溶解性总固体(TDS)本底值调查研究. 地下水. 2021(03): 27-29+65 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 徐银凤,孔舒,梁斐斐,胡星,李晓霜. 济宁市地下水水质评价及水化学类型分布. 治淮. 2020(05): 25-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 朱亮,刘景涛,杨明楠,吕晓立,解飞,魏玉涛. 1998年以来兰州市地下水环境变化及驱动因素. 中国地质. 2020(06): 1677-1687 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 姚曦煜,梁欢,陈凯,候华毅,陈相柏. 拉曼光谱结合化学计量学在不同品位磷矿快速分类中的应用. 应用化工. 2019(04): 975-979 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 宋小庆,彭钦,王伟,屈秋楠. 贵州岩溶区浅层地下水氯化物及硫酸盐环境背景值. 地球科学. 2019(11): 3926-3938 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 边智聪,崔月菊,李静,杜建国. 柳江盆地地表水水文地球化学特征与水质评价. 矿物岩石地球化学通报. 2019(05): 953-960 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 耿婷婷,李颖智,张涛,张智印. 地下水环境背景值研究进展的分析与建议. 环境科学与管理. 2018(05): 33-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 廖磊,何江涛,彭聪,张振国,王磊. 地下水次要组分视背景值研究:以柳江盆地为例. 地学前缘. 2018(01): 267-275 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 刘思圆,马雷,刘建奎,杨章贤,龚荧. 阜阳颍东浅层地下水化学特征与空间分布规律研究. 地下水. 2018(03): 1-3+27 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 薛松,张梦竹,李琳,刘俊新. 甲烷厌氧氧化协同硝酸盐还原菌群驯化及其群落特征. 环境科学. 2018(03): 1357-1364 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 秦文婧,宋献方,谷洪彪. 基于层次聚类法的柳江煤矿对地下水水质影响分析. 水文地质工程地质. 2018(03): 30-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张小文,何江涛,彭聪,张昌延,倪泽华. 地下水主要组分水化学异常识别方法对比:以柳江盆地为例. 环境科学. 2017(08): 3225-3234 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: