The geological event and the assemblage of source-reservoir-seal rock during the Sinian-Ordovician period in Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
塔里木盆地库鲁克塔格地区是重要的油气资源战略接替区域之一,其特殊的构造背景成为研究盆山耦合及区域构造演化的有效切入点。冰川、火山、风暴、浊流等事件沉积的产物,广泛发育于塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶系的地层中。这些地质事件的发生时期与库鲁克塔格地区的构造演化具有明显的耦合关系。Rodinia超大陆的裂解是全球新元古代冰川沉积的诱发因素,也使库鲁克塔格地区在震旦纪发育冰川相的沉积。发生于早寒武世的火山事件也是Rodinia超大陆同期裂解的表现。在塔东北地区,裂解导致的持续拉张作用一直延续到早奥陶世末期,但在晚寒武世曾发生过一次持续时间较短的构造反转,区域构造应力场由拉张转为挤压,导致南、北沉积相区水体变浅,受到风暴作用影响。在挤压的区域构造背景下,中—晚奥陶世库鲁克塔格急剧隆升,物源供给的加大,为浊流事件的沉积提供了有利条件。另外,区域的构造背景变化也对于该地区的源岩和储层的产生起了决定性的因素。在震旦—早奥陶世晚期拉张的大地构造背景下,早—中寒武世及早奥陶世成为烃源岩的主要形成时期。优质储层主要为碳酸盐岩及碎屑岩,发育于晚震旦世、晚寒武世、中—晚奥陶世。孔隙类型主要为晶间孔、溶孔、裂缝等。这些源岩和储层与地层中的泥岩在垂向上组成多套生储盖组合。
Abstract:Kuruktag region of Tarim Basin is one of the most important strategic replacement areas of oil and gas resources, and is an effective entry point based on special structural setting for studying basin-mountain coupling and evolution of regional structures. Events deposited products from glacial event, volcanic event, storm event and turbidity event are developed widely in the Sinian-Ordovician sedimentary strata of Kuruktag region on the northeastern margin of Tarim Basin. The formation time of these events has obvious coupling relationship with tectonic evolution of Kuruktag region. The breakup of Rodinia supercontinent was a inducing factors for global glacial deposition of Neoproterozoic, which caused the formation of glacialfacies in the Kuruktag region. In addition, volcanic event in Early Cambrian was also a reflection of the breakup of Rodinia. Continuous tension caused by cracking continued until the end of Early Ordovician. However, shorter-period reversed structures occurred during the late Cambrian, which led to the shallowing of south and north facies and caused the formation of tempestuous deposits. The rapid uplift of Kuruktag Mountain under the pressing structural surroundings during the Middle-Late Ordovician caused the increase of material source, which offered advantage conditions for turbidity event. In addition, changing of regional tectonics was a decisive factor for the development of source rocks and reservoirs. Early and Middle Cambrian as well as Early Ordovician constitute a main stage for the development of source rocks under the extension condition. High-quality reservoirar of pore type comprised bonatite and clastic rocks, and the pores were intracrystalline pores, dissolved pores and cracks mainly distributed in Late Sinian, Late Cambrian and Middle-Late Ordovician strata. These source rocks and reservoirs with mudstone formed multiple source-reservoircaprock association in the vertical direction.
-
Keywords:
- geological events /
- favorable source-reservoir-seal rock /
- Sinian /
- Cambrian /
- Ordovician /
- Kuruktag region /
- Tarim Basin
-
1. 引言
塔里木盆地位于新疆维吾尔自治区南部,是中国最大的内陆盆地,油气资源丰富。塔里木板块是一个由南天山断裂带、康西瓦断裂带以及阿尔金断裂带所分割的于元古宙超大陆裂解出来的独立板块(贾承造等,1997)。它与其北部的哈萨克斯坦板块、西伯利亚板块及南部的羌塘—中昆仑板块及印度—欧亚大陆的碰撞造就了库鲁克塔格地区复杂的构造特征。库鲁克塔地区位于塔里木盆地的东北缘(巴音郭楞州的罗布泊北部)的隆起区,是连接天山构造带与塔里木盆地的盆山转换地带(任站利等,2009)。同时,这一区域构成一个由“源”到“汇”的油气生成系统,是塔里木盆地重要的油气资源战略接替区域之一(王成林, 等2011)。因此,该地区成为研究盆山耦合及区域构造格局的有效切入点,受到众多学者的广泛关注。长期以来,前人在层序地层学(刘忠宝等,2003;郑秀娟,2005;程日辉等,2006)、沉积环境(段吉业,2005;张艳等,2006;张月巧等,2007)、地球化学(李秋根等,2004;杨瑞东等,2006;高林志等,2013)、岩相古地理(纪友亮等,2005;赵宗举等,2009;余宽宏等,2010)等多个方面进行了深入的研究,积累了丰富的资料。另外,对于库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪的地质事件也多有报道。如刘忠宝等(2003)对塔东地区的中—上奥陶统海底扇相浊积岩进行了初步的层序分析,并识别出6个三级层序。孔庆莹等(2006)报道了库鲁克塔格地区寒武系莫合尔山组的风暴沉积,并识别出3个不同级别的周期。周肖贝等(2012)针对构造-沉积事件探讨了南华纪—寒武纪成盆演化过程。但是,对于这些地质事件的报道多集中于某一地质事件,且与构造背景的结合相对薄弱。本文通过广泛发育于塔东库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪地层中的冰川、火山、风暴、浊流等沉积产物,发现事件沉积与库鲁克塔格裂陷槽的发展具有明显的耦合关系,且控制着该地区的生储盖组合。
2. 地质概况
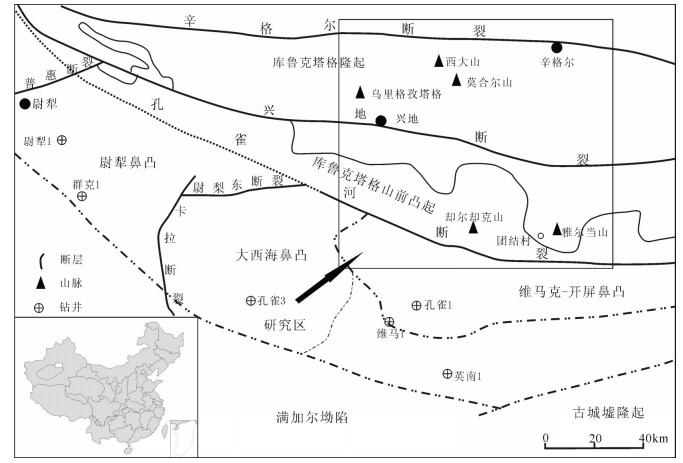
库鲁克塔格地区位于新疆塔里木盆地的东北缘,属塔里木地层分区的库鲁克塔格小区(图 1)。在大地构造上位于塔里木板块北缘和中亚造山带南缘天山造山系的结合部位(蔡志慧等,2011)。库鲁克塔格山北南两侧分别为焉耆盆地和孔雀河斜坡。焉耆盆地为碰撞造山期后地壳冷却及应力松弛导致的热塌陷沉降和伸展沉降作用下的断陷盆地,是叠加在天山造山带南缘和塔里木板块东北缘造山带中的、经历复杂构造变动和后期改造的中、新生代叠合盆地(杨斌谊,2004;胡斌等,2006),盆地的展布受中天山南缘断裂带(板块结合带)和南天山南缘断裂的控制。孔雀河斜坡为南天山前缘与满加尔凹陷北侧的斜坡地带(任战利等,2009),具有南北分带,东西分段的特征(赵永强等,2013)。区内发育多条大型断裂,且大多与盆地的边界平行(图 1)。辛格尔断裂带是塔里木地台东北缘与南天山造山带的分界线。具有区域性深大断裂特征的兴地断裂和孔雀河断裂在震旦—奥陶纪强烈活动(郭召杰和张志诚,1995),控制了南、北两个相区的岩性与岩相的组合和分布。辛格尔北相区位于兴地断裂和辛格尔断裂之间,包括乌里格孜塔格、西大山、莫合尔山等地区(图 1);孔雀河南相区位于兴地断裂以南,包括却尔却克山、元宝山、雅尔当山等地区(图 1)。
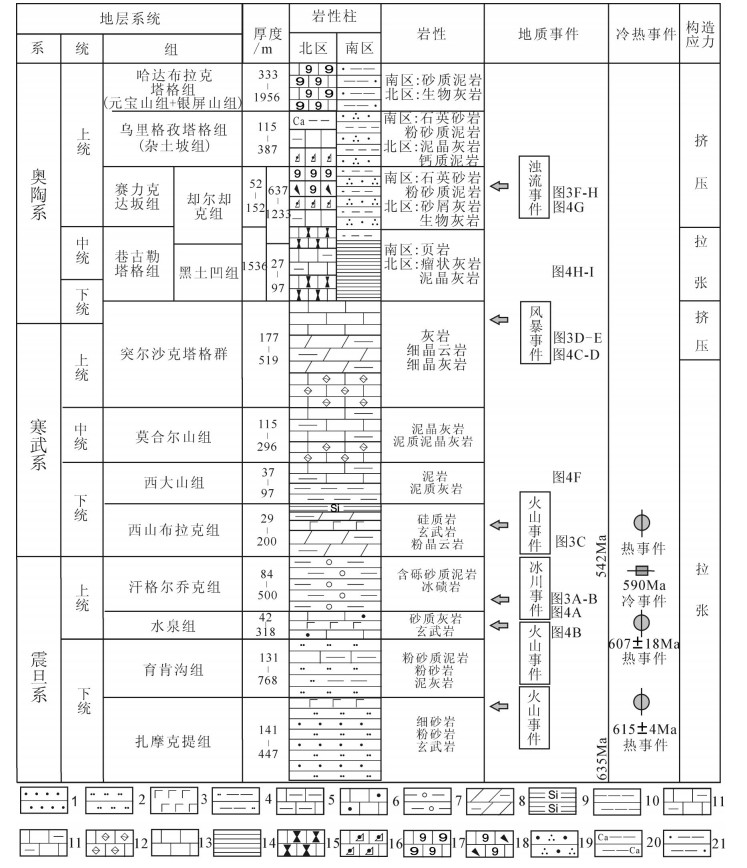
南、北相区在震旦系和寒武系具有相似的岩性和岩相,以及相同的岩石地层单元。震旦系发育碎屑岩为主的半深海-浅海沉积,由下至上依次为扎摩克提组、育肯沟组、水泉组、汉格尔乔克组(图 2);寒武系发育碳酸盐为主的台地边缘-陆棚相沉积,由下至上依次为西山布拉克组、西大山组、莫合尔山组、突尔沙克塔格群1-2段(图 2)。南、北相区在奥陶系则具有不同的岩性、岩相,岩石地层单元,孔雀河南区发育以碎屑岩为主的深水沉积,由下至上依次发育突尔沙克塔格群3段、黑凹组、却尔却克组、杂土坡组、元宝山组、银屏山组(图 2),而辛格尔北区主要发育碳酸盐为主的台地相沉积,由下至上依次为突尔沙克塔格群3段、巷古勒塔格组、赛力克达坂组、乌里格孜塔格组、哈布拉克塔格组(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪构造-事件沉积综合柱状图1—细砂岩;2—粉砂岩;3—玄武岩;4—粉砂质泥岩;5—泥灰岩;6—砂质灰岩;7—含砾泥岩;8—泥质白云岩;9—硅质岩;10—泥岩;11—泥质灰岩;12—泥晶灰岩;13—灰岩;14—页岩;15—瘤状灰岩;16—砂屑灰岩;17—生物灰岩;18—生物碎屑灰岩;19—石英砂岩;20—钙质泥岩;21—砂质泥岩Figure 2. The sedimentary composite histogram of tectonics-events deposition during the Sinian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim Basin1-Fine sandstone; 2-Siltstone; 3-Basalt; 4-Silty mudstone; 5-Marl; 6-Sandy limestone; 7-Pebbly mudstone; 8-Argillaceous dolomite; 9-Siliceous rocks; 10-Mudstone; 11-Argillaceous limestone; 12-Micrite; 13-Limestone; 14-Shale; 15-Tumor limestone; 16-Arenite limestone; 18-Bioclastic limestone; 19-Quartz sandstone; 20-Calcareous mudstone; 21-Sandy mudstone
图 2 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪构造-事件沉积综合柱状图1—细砂岩;2—粉砂岩;3—玄武岩;4—粉砂质泥岩;5—泥灰岩;6—砂质灰岩;7—含砾泥岩;8—泥质白云岩;9—硅质岩;10—泥岩;11—泥质灰岩;12—泥晶灰岩;13—灰岩;14—页岩;15—瘤状灰岩;16—砂屑灰岩;17—生物灰岩;18—生物碎屑灰岩;19—石英砂岩;20—钙质泥岩;21—砂质泥岩Figure 2. The sedimentary composite histogram of tectonics-events deposition during the Sinian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim Basin1-Fine sandstone; 2-Siltstone; 3-Basalt; 4-Silty mudstone; 5-Marl; 6-Sandy limestone; 7-Pebbly mudstone; 8-Argillaceous dolomite; 9-Siliceous rocks; 10-Mudstone; 11-Argillaceous limestone; 12-Micrite; 13-Limestone; 14-Shale; 15-Tumor limestone; 16-Arenite limestone; 18-Bioclastic limestone; 19-Quartz sandstone; 20-Calcareous mudstone; 21-Sandy mudstone3. 地质事件特征
事件沉积是地质历史过程中具有突发性、瞬时性、灾变性发生的地质过程,是沉积物再活化、再沉积的产物(田景春等,2014),对于油气生储盖的形成具有重要的约束作用。
3.1 冰川事件
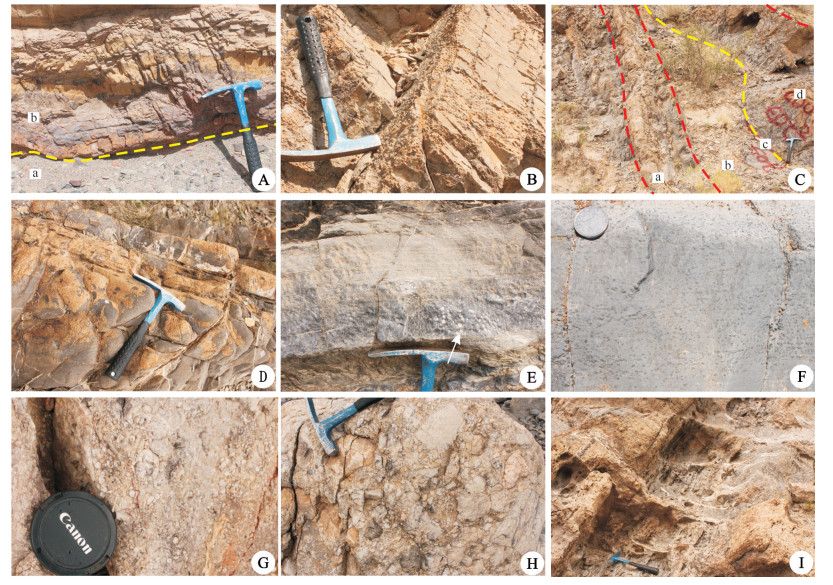
在整个地质历史时期曾经历了5次大冰期,持续时间占据了地球历史的十分之一。其中,新元古代晚期曾发生过全球性的冰川作用,甚至赤道附近也曾被冰雪覆盖,从而导致地球成为一个“雪球”(Kirschvink,1992;Hoffman,1998)。在亚洲、欧洲、非洲、北美和澳大利亚的大部分地区以及中国华北、华南、塔里木板块等广大地区均发育有震旦纪冰川沉积存在的证据。新元古代冰期进一步由老到新划分为Kaigas冰期、Sturtian冰期、Marinoan冰期以及Gaskiers冰期(田景春等,2014)。Marinoan冰期与中国前寒武纪晚期(即震旦纪大冰期)相对应。此次冰期分布广泛,可进一步把该冰期划分为3个亚冰期(高振家等,1984;Gao,1985;Evans,2000;张艳等,2006),分别对应于中国西北地区的贝义西、特瑞爱肯、汉格尔乔克沉积期(张艳等,2006)。同时也存在着一些不同的划分方案。如周肖贝(2012)则认为汉格尔乔克组的冰川相沉积对应于全球Gaskiers冰期事件。研究区震旦系上统的汉格尔乔克组由砾石粗碎屑、粉砂和泥质基质组成。同时也见有一些特殊的构造,如冰川漂砾、坠石等(图 3A,B)。漂砾是指在冰川成岩内所含与一般砾石大小相差比较悬殊的砾石或岩块,是冰川作用的主要证据之一(赵祥生等,1984)。兴地剖面可见有冰川漂砾,直径达1.5 m左右(图 3B)。在雅尔当山剖面,下部为灰黄色块状冰碛含砾岩屑砂岩,砾石成分复杂,有安山斑岩、英安斑岩、花岗岩、辉绿岩、灰岩、硅质岩等。恰克马克铁什剖面下部为灰色块状冰碛含泥岩屑砂岩,上部为灰色泥质含砾、含中粗砂粉砂岩。在向阳村剖面震旦系汗格尔乔克组冰碛岩为含砾砂质泥岩、不等粒岩屑砂岩,上部为泥晶云岩(盖帽白云岩)。砾石呈棱角-次棱角状,砾石下部泥质薄纹层绕着砾石成层分布,上覆层理也呈现出弯曲至水平的渐变。王鹏程和王约(2015)在研究豫西汝州罗圈组杂砾岩时也发现有类似的现象,并认为其成因是砾屑团块沉降至水下,在重力作用下压弯下伏塑性沉积的冰碛泥纹层所至。Reading et al(1986)将冰川沉积环境划分为冰下、冰上、冰缘的冰前沉积,其中冰下沉积包括冰海及冰湖沉积。向阳村剖面的这种沉积特征具有明显的冰下沉积特点。
![]() 图 3 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪事件沉积地质特征A—箭头所示为泥质纹层绕砾分布的冰碛岩,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;B—箭头所示为冰川漂砾,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;C—玄武岩,西山布拉克组,却尔却克山剖面;D—砾屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—箭头所示为呈倒小字型的砾屑灰岩, 突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—浊积岩中扇辫状水道沉积,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;G—箭头所示为深水异地沉积,搬运的球为灰质成分,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;H—鲍马序列A-E段,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面Figure 3. Geological characteristics of event deposition during the Simian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim BasinA-Arrows showing the tillite with muddy laminar around gravel, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; B-Arrows showing glacial boulder, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; C-Basalt, Xishanbulake Formation, Queerqueke section; D-Calcirudyte, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; E-Arrows showing the calcirudyte with the"reversed xiao"shape, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; F-Braided channel deposits in turbidite, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; G-Arrows showing the deep water allogene deposits, globoid composed by gray matter, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; H-A-E of bouma sequence, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section
图 3 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪事件沉积地质特征A—箭头所示为泥质纹层绕砾分布的冰碛岩,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;B—箭头所示为冰川漂砾,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;C—玄武岩,西山布拉克组,却尔却克山剖面;D—砾屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—箭头所示为呈倒小字型的砾屑灰岩, 突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—浊积岩中扇辫状水道沉积,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;G—箭头所示为深水异地沉积,搬运的球为灰质成分,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;H—鲍马序列A-E段,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面Figure 3. Geological characteristics of event deposition during the Simian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim BasinA-Arrows showing the tillite with muddy laminar around gravel, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; B-Arrows showing glacial boulder, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; C-Basalt, Xishanbulake Formation, Queerqueke section; D-Calcirudyte, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; E-Arrows showing the calcirudyte with the"reversed xiao"shape, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; F-Braided channel deposits in turbidite, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; G-Arrows showing the deep water allogene deposits, globoid composed by gray matter, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; H-A-E of bouma sequence, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section3.2 火山事件
火山事件主要发生于早寒武世早期西山布拉克组沉积期,西山布拉克组底部发育有火山成因的玄武岩(15~45 m),以及部分安山岩、安山角砾岩(0.6~1.83 m),并在乌里格孜塔格、却尔却克山、兴地地区的野外露头广泛出露。玄武岩颜色鲜艳,多呈灰绿色(图 3C),具有斑状结构,基质具间隐构造,主要矿物成分由斜长石、蚀变绿泥石及少量磁铁矿组成。
3.3 风暴沉积
风暴是一种重要的地质营力,也是一种周期性的灾变事件,可由海洋飓风、中纬度冬季风暴和津浪引起。其开始、发展到结束都受到独特的水动力学影响,主要发生在浅海陆棚区,且对原地和异地沉积物进行冲刷、削切、侵蚀、充填,并形成独特的沉积构造和沉积序列(刘宝珺等,1987;梁桂香等,1994;施祺和余克服,2007)。Krcisa和Bambach(1982)按照风暴的发育过程将其划分为风暴高峰期、风暴晚期和风暴后期3个阶段,经历了能量从强至弱的演化过程,形成代表风暴沉积的各种标志(李文厚等,1991)。在乌里格孜塔格地区晚寒武世突尔沙克塔格组一段顶部和二段发育有灰色砂砾屑、砾屑灰岩组成,砾屑含量为50%~60%,呈“竹叶状”,砾屑长8~15 cm,厚为0.5~1.5 cm(图 3D,E)。砾屑为颗粒支撑,填隙物的成分和颜色与砾屑相一致。见有底冲刷构造、具有放射状组构(菊花、倒小字构造)、递变层理等(图 3E,图 4C)。底冲刷构造是风暴流对海底沉积物进行冲刷而留下的各种侵蚀冲刷构造,是鉴定风暴岩的重要标志(Aigner,1982)。放射状组构是风暴流搅动、破坏海底半固结沉积物,风暴停息后破碎的碳酸盐沉积物呈菊花、倒小字型排列(图 3E)。这些特征表明晚寒武世突尔沙克塔格沉积期曾发生过风暴沉积。
3.4 浊流事件
浊流又称重力流,是地形起伏悬殊、由重力起主导作用的高密度海底流(朱起煌,1990)。浊积相最早由Mutti and Ricci Lucchi(1972)引入,并提出A、B、C、D、E、F、G七个基本相,特征性的浊积相组合可以用来鉴别海底扇(Moiola and Zhu, 1989)。塔东地区重力流沉积为典型的海底扇沉积序列,主要发育于却尔却克山、雅尔当山、元宝山等中—上奥陶统地层中,其沉积环境经历了深海平原-海底扇(斜坡)-陆棚的转变,总体上表现为一水深变浅的进积序列。刘忠宝等(2003)曾对该地区海底扇的沉积特征进行了介绍。作者一行在元宝山上奥陶统却尔却克组的考察中,也见到了主要由块状砂、砾岩,粉砂岩组成的海底扇沉积,并见到完整的鲍马序列(ABCDE段)及异地搬运沉积(图 3F,G,H)。却尔却克组的鲍马序列A段由向上变细的正粒序砂砾岩组成,与下伏泥岩具有明显的冲刷面,B段发育由细砂岩组成的平行层理,C段以粉砂岩为主,D段以泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩为主,E段为泥岩段(图 3H)。海底扇以发育相对稳定的中扇水道沉积组合为特征(图 3F),中扇辫状水道亚相主要为块状砾岩-含砾粗砂岩,具正粒序,见斜层理、平行层理、冲刷面等强水动力所具有的沉积构造。中扇近源浊积岩亚相由多个厚层状辫状水道砂体叠置组成,主要为中粒长石砂岩、岩屑长石砂岩、长石岩屑砂岩组成。
4. 讨论
4.1 沉积事件与盆地构造演化耦合关系
在塔东北地区震旦—奥陶纪沉积演化过程中,发育的冰川事件、火山事件、风暴沉积、浊流沉积与盆地的构造演化之间具有明显的耦合关系。震旦—奥陶纪塔北与南天山地区经历了一个伸展、裂陷和挤压、聚合的完整旋回(汪新文和陈发景,1997)。塔里木板块曾经是Rodinia超大陆的一部分(Li and Powell, 1996;Li et al., 2003;陆松年等,2004;Zhan et al., 2007;王飞等,2010)。Rodinia超大陆是通过格林威尔造山运动(中元古代末期—新元古代早期)将塔里木、华南和澳大利亚板块的碰撞拼合形成的,并于新元古代晚期发生裂解(陆松年,2001;陆松年等,2004;王飞等,2010;王洪浩等,2015)。地球历史中的冰期与超大陆的汇聚和解体具有一定的关系(Eyles,2008)。Hoffman(1998)认为Rodinia超大陆的裂解导致大陆边缘的面积增加并促进了有机碳的埋藏,导致空气中CO2浓度降低,引发全球的“雪球事件”。因此,Rodinia超大陆的裂解是全球新元古代冰川沉积的诱发因素。震旦纪位于赤道附近的塔里木周缘(塔西南,库鲁克塔格地区)均见有冰川沉积(图 3A,B)。在库鲁克塔格地区,上震旦统汉格尔乔克组砾石下部的泥质薄纹层绕着砾石成层分布,上覆层理也呈现出弯曲至水平的渐变,具有典型的冰下沉积的特征(图 3A)。汉格尔乔克组顶部的盖帽白云岩与下寒武统西山布拉克组硅质岩呈角度不整合接触,且在硅质岩层之上发育有火山事件成因的玄武岩、安山岩等(图 3C)。杨瑞财等(1999)认为该不整合界面是加里东运动第一幕的体现。
由于岩石圈的伸展作用(图 2),导致塔里木克拉通周缘发育有裂谷(王洪浩等,2015),并促进塔里木盆地的东北缘库鲁克塔格—满加尔拗拉槽开始形成。通过阿克苏地区拉斑玄武岩的地球化学数据及锆石U-Pb年代学表明,裂谷形成时代晚于755 Ma,与新元古代Rodinia超大陆之下的地幔柱活动有关,是Rodinia超大陆裂解的直接表现(杨树峰等,1998;李向民等,2006)。火山活动通常发生在引张应力构造背景下(冯玉辉等,2015),早寒武世库鲁克塔格火山事件形成于扎摩克提组沉积期((615±4)Ma)和水泉组沉积期((607±18)Ma)火山事件之后(Xu et al., 2005, 2009)(图 2),且处于大陆裂谷发展的构造拉张应力场下,并为深水盆地烃源岩创造了条件。杨瑞东等(2006)通过新疆库鲁克塔格地区兴地大坂穷木库杜克剖面早寒武世硅质岩地球化学特征的研究,认为硅质岩系早寒武世早期库鲁克塔格地区强烈的拉张作用引起的热水沉积所致,是Rodinia大陆在早寒武世裂解的岩石记录。因而推测早寒武世的火山事件系Rodinia大陆裂解的产物。
风暴沉积是突发性事件沉积,对于古大陆边缘的构造性质及盆地构造背景有重要意义(张斌等,2009)。中寒武世基本上继承了早期的古地理格局,反映了该时期构造活动区域稳定。至晚寒武世,北相区由开阔陆棚相变为台地边缘斜坡相,南相区由次深海盆地相过渡为广海陆棚相,整体表现为一套向上变浅的沉积序列。因而推测裂解导致的持续拉张作用一直延续到早奥陶世末期,但在晚寒武世曾发生过一次持续时间较短构造反转。在挤压的构造背景下(图 2),新疆库鲁克塔格地区整体抬升,导致晚寒武世突尔沙克塔格组发育有风暴作用而沉积的砾屑灰岩(见生物碎屑),厚40~150 cm。另外,Bose et al.(1988)认为古生代风暴浪基面水深为40 m,表明晚寒武世库鲁克塔格地区处于一个相对较浅的沉积环境。目前,多数学者认为Rodinia超大陆裂解引起的拉张构造环境第一次发生构造反转是在早奥陶纪末期或中奥陶世。如程日辉等(2006)通过层序地层学并结合地质事件沉积认为,盆地性质在中奥陶世初(却一段)由拉张盆地转变为挤压盆地。
中—晚奥陶世却尔却克组主要为浊积岩沉积,稳定期夹灰岩沉积,向上为盆地相的砂页岩沉积。伴随着挤压作用的不断进行(图 2),至中奥陶世库鲁克塔格地区已经由裂谷盆地转变为前陆盆地。晚奥陶世,随着库鲁克塔格急剧隆升,其沉积环境经历了深海平原—海底扇(斜坡)—陆棚的转变,总体上表现为一水深变浅的进积序列。物源供给的加大,为浊流事件的沉积提供了有利条件。刘宝忠等(2003)通过岩性以及重矿物(ZTR指数)在区域上的分布,认为浊流成因的海底扇物源来自库鲁克塔格地区。
4.2 区域构造演化对烃源岩及储盖层的控制作用
塔里木盆地东北缘的库鲁克塔格地区经历了长期的构造演化,构造控制下的沉积演化对烃源岩及储盖层的形成及分布具有重要的控制作用。
4.2.1 烃源岩的形成
烃源岩的发育通常受到海平面变化的制约。在海平面上升的背景下,水体较深的区域往往会有烃源岩的存在,如深海盆地、深水陆棚、台内凹陷等地区(张水昌等,2012),而海平面的波动往往与区域构造和盆地的演化具有一定的耦合性(康志宏,1996)。寒武纪—早奥陶世塔东北地区处于古塔里木板块边缘,发育大陆边缘裂谷盆地。在拉张的构造应力场作用下,发育了辛格尔、兴地、孔雀河等一些正断层,断裂主要以北西西-近东西向和北西-南北向为主。兴地断裂在加里东早期控制了断裂两侧寒武—奥陶纪岩相、岩石组合,断裂南北差异明显(贾承造等,1997;纪友亮等,2002;孙晓猛等,2006)。断裂南盘在早寒武世主要发育次深海盆的深水沉积,沉积物主要为深灰、灰黑色的泥岩、泥灰岩等。这些特征表明兴地断裂以南发生大规模沉降。冯乔(1997)通过对与孔雀河斜坡相邻的满加尔凹陷埋藏史的分析,认为满加尔凹陷在寒武纪快速沉降,且为沉积和沉降的中心(张守安和罗传容,2005)。大规模沉降,形成欠补偿的沉积盆地,发育黑色泥岩、黑色泥质灰岩、页岩等岩石类型。晚寒武世发生抬升,处于台地边缘斜坡的环境,发育泥晶灰岩、粉晶灰岩。至早奥陶世,盆地继续下降,发育黑色笔石页岩、放射虫硅质岩以及硅质泥岩等具有明显深水盆地相的沉积。康志宏(1996)认为早奥陶纪库鲁克塔格地区在拉张背景下处于被动大陆边缘的演化阶段,为裂谷的中心。欠补偿盆地形成的暗色泥岩、碳酸盐岩在塔东北地区分布稳定,是重要的烃源岩。元宝山—南雅尔当山—却尔却克山地区出露的暗色泥岩及碳酸盐岩的残余有机碳含量换算成原始TOC平均含量分别为2.24%和0.94%~1.19%❶。对于碳酸盐烃源岩的评价标准,不同学者具有不同的标准(Tissot,1978;赵靖舟,2001),有人提出有机碳含量在0.3%以及0.1%为碳酸盐岩烃源岩有机质丰度的下限值。与较低的0.1%相较,远超其值。中奥陶统却尔却克组发育有陆源碎屑浊流沉积,王成林等(2011)在却尔却克组的泥岩中发现了有效烃源岩达200 m,有机质含量达8.59%。
4.2.2 储盖层的形成
震旦系—奥陶系储层发育层系多,储层类型多样(吴兴宁等,2012),孔隙类型主要为晶间孔、溶孔和裂缝(图 4)。震旦系是塔里木盆地基底之上的第一套沉积盖层,南北相区具有相似性,整体以潮坪相及冰川沉积为主,发育有泥晶白云岩以及汉格尔乔克组顶部的盖帽白云岩,细小的溶孔和溶缝被硅质和沥青充填,构成了震旦系的主要储层(图 4A,B)。上震旦统顶部的盖帽白云岩与下寒武统呈不整合接触,在长期的风化及强烈的大气淡水作用下形成孔、洞、缝,为油气聚集提供了良好的储集空间。上寒武统发育陆棚-盆地边缘的储集层岩石类型包括碳酸盐岩及碎屑岩储层,其中晶粒白云岩、砾屑灰岩的平均孔隙率和渗透率分别为1.62%和0.57×10-3μm2,面孔率0.1%~5%,属于Ⅱ类储层❶。在南雅尔当山地区,中寒武统云质灰岩、白云岩、灰岩孔隙度平均1.47%,渗透率0.015×10-3μm2❶。晚寒武世发育的风暴沉积一般仅持续几天,风暴天气与晴好天气沉积在垂向上组成良好的生储盖组合关系(图 4C)。下奥陶统南相区为泥质泥晶灰岩及白云岩化泥晶灰岩与黑色泥岩互层,储层较差。中上奥陶统发育浊流事件,储层物性有所改善。浊流沉积由中粒长石砂岩、岩屑长石砂岩、长石岩屑砂岩组成多个厚层状辫状水道砂体。主要发育粒内溶孔及粒间溶孔与斜坡相黑色泥页岩构成良好的生储关系。而处于兴地断裂以北的北相区,奥陶系为一个向上变浅的碳酸盐岩沉积相序列(广海陆棚一台地边缘—开阔海台地—半局限海台地相),主要发育亮晶生屑灰、亮晶中砂屑灰岩、亮晶棘屑灰岩,储集物性相对较好。
![]() 图 4 库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶系储层发育特征A—盖帽白云岩,由泥晶白云岩组成,细小的溶孔及溶缝被硅质及沥青充填, 上震旦统汉格尔乔克组,向阳村地区, a—冰碛岩,b—盖帽白云岩;B—白云岩中发育溶蚀孔洞,上震旦统水泉组,兴地地区;C—风暴成因的储盖组合,上奥陶统突尔沙克塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面, a—灰色中层状亮晶含砾砂屑灰岩,b—深灰、灰黑色中层状钙质泥岩,c—风暴事件作用面,d—灰色块状砾屑灰岩;D—砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—亮晶砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—鲕粒灰岩,寒武系西大山组,却尔却克山地区;G—生物灰岩,三叶虫、海百合和腹足印模等生物丰富,上奥陶统赛力克达坂组,乌里格孜塔格地区;H—岩溶角砾,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面;I—溶蚀孔洞,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面Figure 4. The characteristics of reservoir development during Sinian-Cambrian A-Cap domolite, composed of dolomicrite, and the small dissolved pores and cracks filled with silica and asphalt, Hangeerqiaoke Formation of Upper Sinian, Xiangyangchun region.a-Tillite, b-Cap dolomite; B-Dissolved pores and caves developed in domolite, Shuiquan Formation, Xingdi region; C-Reservoir cap association caused by storm, Tuershaketage Formation of Upper Sinian, Wuligezitage section; a-Gray, middle-level thickness sparry gravell-bearing limestone, b-Dark-black gray, middle-level thickness carbonaceous mudstone, c-Acting surface of storm event, d-Gray, blocky calcirudite; D-Limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; E-Sparry limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; F-Oolitic limestone, Xidashan Formation of Cambrian, Queerquekeshan region; G-Biolithite limestone, containing abundant Trilobitas, Metacrinus, and pleopods moulage, Sailikedaban Formation of the Upper Ordovician, Wuligezitage region; H-Karse rubble, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section; dissolved pores and caves, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section
图 4 库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶系储层发育特征A—盖帽白云岩,由泥晶白云岩组成,细小的溶孔及溶缝被硅质及沥青充填, 上震旦统汉格尔乔克组,向阳村地区, a—冰碛岩,b—盖帽白云岩;B—白云岩中发育溶蚀孔洞,上震旦统水泉组,兴地地区;C—风暴成因的储盖组合,上奥陶统突尔沙克塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面, a—灰色中层状亮晶含砾砂屑灰岩,b—深灰、灰黑色中层状钙质泥岩,c—风暴事件作用面,d—灰色块状砾屑灰岩;D—砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—亮晶砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—鲕粒灰岩,寒武系西大山组,却尔却克山地区;G—生物灰岩,三叶虫、海百合和腹足印模等生物丰富,上奥陶统赛力克达坂组,乌里格孜塔格地区;H—岩溶角砾,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面;I—溶蚀孔洞,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面Figure 4. The characteristics of reservoir development during Sinian-Cambrian A-Cap domolite, composed of dolomicrite, and the small dissolved pores and cracks filled with silica and asphalt, Hangeerqiaoke Formation of Upper Sinian, Xiangyangchun region.a-Tillite, b-Cap dolomite; B-Dissolved pores and caves developed in domolite, Shuiquan Formation, Xingdi region; C-Reservoir cap association caused by storm, Tuershaketage Formation of Upper Sinian, Wuligezitage section; a-Gray, middle-level thickness sparry gravell-bearing limestone, b-Dark-black gray, middle-level thickness carbonaceous mudstone, c-Acting surface of storm event, d-Gray, blocky calcirudite; D-Limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; E-Sparry limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; F-Oolitic limestone, Xidashan Formation of Cambrian, Queerquekeshan region; G-Biolithite limestone, containing abundant Trilobitas, Metacrinus, and pleopods moulage, Sailikedaban Formation of the Upper Ordovician, Wuligezitage region; H-Karse rubble, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section; dissolved pores and caves, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section5. 结论
通过对塔里木盆地东北缘库鲁克塔格地区震旦纪—奥陶纪地层的研究,初步得出以下结论:
(1)库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪地层中广泛发育有冰川事件、火山事件、风暴事件、浊流等事件沉积。冰川沉积主要发育于晚震旦世汉格尔乔克沉积期,具有冰川漂砾、坠石等典型的冰川特征。火山事件主要发育于早寒武世的西山布拉克组沉积期,发育有玄武岩、安山岩及安山角砾岩等。风暴事件沉积发育于晚寒武世的突尔沙克塔格组沉积期,主要为“竹叶状”灰岩,具有倒小字、云朵状等构造。浊流事件沉积发育于晚奥陶世却尔却克组沉积期,见有完整的鲍马序列(ABCDE段)及异地搬运沉积。
(2)沉积事件与库鲁克塔格的构造演化具有明显的耦合关系,Rodinia超大陆的拼合和裂解是新元古代最为重要的超大陆事件。Rodinia超大陆的裂解是全球新元古代冰川沉积的诱发因素,并导致库鲁克塔格地区发育冰下沉积。同时,拉张构造背景下的早寒武世火山事件是Rodinia超大陆在早寒武世裂解的岩石记录。至晚寒武世发生了持续时间较短的构造反转,导致南、北相区变浅,沉积了风暴成因的砾屑灰岩。早奥陶世又转变为拉张的区域构造背景直至中—晚奥陶世,伴随着挤压作用的不断进行,随着库鲁克塔格急剧隆升,物源供给的加大,为浊流事件的沉积提供了有利条件。
(3)库鲁克塔格地区的区域构造演化控制了该地区的沉积演化,同时,沉积演化决定了源岩和储层的形成和发育,为油气形成创造了条件。在震旦纪—早奥陶世晚期拉张的大地构造背景下,早—中寒武世、早奥陶世成为烃源岩的主要时期。而优质储层为碳酸盐岩及碎屑岩,主要发育于晚震旦世、晚寒武世、中—晚奥陶世。孔隙类型主要为晶间孔、溶孔、裂缝等。这些源岩和储层与地层中的泥岩在垂向上组成多套生储盖组合。
注释
❶中国石化勘探西北分公司. 2008.塔里木盆地东北缘山前带构造演化及其与孔雀河地区油气的关系(内部报告).
致谢: 参加野外工作的还有成都理工大学的林小兵老师和杨辰雨同学以及成都地质矿产研究所的康建威研究员,在此表示衷心的感谢! -
图 2 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪构造-事件沉积综合柱状图
1—细砂岩;2—粉砂岩;3—玄武岩;4—粉砂质泥岩;5—泥灰岩;6—砂质灰岩;7—含砾泥岩;8—泥质白云岩;9—硅质岩;10—泥岩;11—泥质灰岩;12—泥晶灰岩;13—灰岩;14—页岩;15—瘤状灰岩;16—砂屑灰岩;17—生物灰岩;18—生物碎屑灰岩;19—石英砂岩;20—钙质泥岩;21—砂质泥岩
Figure 2. The sedimentary composite histogram of tectonics-events deposition during the Sinian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim Basin
1-Fine sandstone; 2-Siltstone; 3-Basalt; 4-Silty mudstone; 5-Marl; 6-Sandy limestone; 7-Pebbly mudstone; 8-Argillaceous dolomite; 9-Siliceous rocks; 10-Mudstone; 11-Argillaceous limestone; 12-Micrite; 13-Limestone; 14-Shale; 15-Tumor limestone; 16-Arenite limestone; 18-Bioclastic limestone; 19-Quartz sandstone; 20-Calcareous mudstone; 21-Sandy mudstone
图 3 塔东北库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶纪事件沉积地质特征
A—箭头所示为泥质纹层绕砾分布的冰碛岩,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;B—箭头所示为冰川漂砾,汉格尔乔克组,兴地剖面;C—玄武岩,西山布拉克组,却尔却克山剖面;D—砾屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—箭头所示为呈倒小字型的砾屑灰岩, 突尔沙克塔格组2段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—浊积岩中扇辫状水道沉积,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;G—箭头所示为深水异地沉积,搬运的球为灰质成分,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面;H—鲍马序列A-E段,却尔却克组,元宝山剖面
Figure 3. Geological characteristics of event deposition during the Simian-Ordovician in the Kuruktag region of northeastern Tarim Basin
A-Arrows showing the tillite with muddy laminar around gravel, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; B-Arrows showing glacial boulder, Hangeerqiaoke Formation, Xingdi section; C-Basalt, Xishanbulake Formation, Queerqueke section; D-Calcirudyte, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; E-Arrows showing the calcirudyte with the"reversed xiao"shape, Member 2 of Tuershaketage Formation, Wuligezitage section; F-Braided channel deposits in turbidite, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; G-Arrows showing the deep water allogene deposits, globoid composed by gray matter, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section; H-A-E of bouma sequence, Queerqueke Formation, Yuanbaoshan section
图 4 库鲁克塔格地区震旦—奥陶系储层发育特征
A—盖帽白云岩,由泥晶白云岩组成,细小的溶孔及溶缝被硅质及沥青充填, 上震旦统汉格尔乔克组,向阳村地区, a—冰碛岩,b—盖帽白云岩;B—白云岩中发育溶蚀孔洞,上震旦统水泉组,兴地地区;C—风暴成因的储盖组合,上奥陶统突尔沙克塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面, a—灰色中层状亮晶含砾砂屑灰岩,b—深灰、灰黑色中层状钙质泥岩,c—风暴事件作用面,d—灰色块状砾屑灰岩;D—砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克塔格组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;E—亮晶砂屑灰岩,突尔沙克组一段,乌里格孜塔格剖面;F—鲕粒灰岩,寒武系西大山组,却尔却克山地区;G—生物灰岩,三叶虫、海百合和腹足印模等生物丰富,上奥陶统赛力克达坂组,乌里格孜塔格地区;H—岩溶角砾,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面;I—溶蚀孔洞,下奥陶统巷古勒塔格组,乌里格孜塔格剖面
Figure 4. The characteristics of reservoir development during Sinian-Cambrian A-Cap domolite, composed of dolomicrite, and the small dissolved pores and cracks filled with silica and asphalt, Hangeerqiaoke Formation of Upper Sinian, Xiangyangchun region.
a-Tillite, b-Cap dolomite; B-Dissolved pores and caves developed in domolite, Shuiquan Formation, Xingdi region; C-Reservoir cap association caused by storm, Tuershaketage Formation of Upper Sinian, Wuligezitage section; a-Gray, middle-level thickness sparry gravell-bearing limestone, b-Dark-black gray, middle-level thickness carbonaceous mudstone, c-Acting surface of storm event, d-Gray, blocky calcirudite; D-Limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; E-Sparry limearenite, Member 1 of Tuershaketage Formation Wuligezitage section; F-Oolitic limestone, Xidashan Formation of Cambrian, Queerquekeshan region; G-Biolithite limestone, containing abundant Trilobitas, Metacrinus, and pleopods moulage, Sailikedaban Formation of the Upper Ordovician, Wuligezitage region; H-Karse rubble, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section; dissolved pores and caves, Xiangguletage Formation of Lower Ordovician, Wuligezitage section
-
Aigner T. 1982. Calcareous tempestites: Storm-dominated stratification in upper Muschelkalk limestones[C]//Einsele G, Seilacher A(eds. ). Cyclic and Event Stratification. BerlinHeidelberg, New York: Springer, 180-198.
Bose PradipK, Chaudhuri AmitK, Seth Ashoke. 1988. Facies flow and bedform patterns across a strom dominated inner shelfs continental:Proterozoic kaimur Formation, Rajasthan, India[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 59, 275-293. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(88)90081-4
Cai Zhihui, Xu Zhiqin, Tang Zhemin, He Bizhu, Chen Fangyuan. 2011. The crustal deformation during the Early Paleozoic period and the timing of orogeny in Kuruktag area on the northeast margin of Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4):855-867(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286739189_The_crustal_deformation_during_the_Early_Paleozoic_period_and_the_timing_of_orogeny_in_Kuruktag_area_on_the_northeast_margin_of_Tarim_Basin
Cheng Rihui, Wang Pujun, Sun Xiaomeng, Bai Yufeng. 2006.Sequence stratigraphy and sea level changes of Ordovician in Kuruktag, Xinjiang[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 30(3):283-293 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-dgyk200603002.htm
Duan Jiye, Xia Dexin, An Sulan. 2005. Deep-water Sedimentation and sedimento-tectonopaleogeography of the Neoproterozoic-Early Palaeozoic Aulacogen in Kuruktag, Xingjiang, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(1):7-16. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2005.79.issue-1
Evans David A D.2000. Stratigraphic, geochronological, and paleom agnetic constraints upon the Neoproterozoic climatic paradox[J]. American Journal of Science, 300:347. doi: 10.2475/ajs.300.5.347
Eyles Nick. 2008. Glacio-epochs and the supercontinent cycle after~3.0 Ga:Tectonic boundary conditions for glaciation[J]. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol, 258:89-129. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.09.021
Feng Qiao. 1997. Burial history of stratigraphy and maturity evolution of organic matter in Manjiaer Depression Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, (1):173-177 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.030.htm
Feng Yuhui, Yu Xiaojian, Huang Yulong, Liu Baohong, Gu Guozhong, Li Hanyue, Wang Pujun. 2015. Eruption cycles and stages of Cenozoic volcanic rocks and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulations in Liaohe Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 39(5):50-57(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201505007.htm
Gao Linzhi, Guo Xianpu, Ding Xiaozhong, Zong Wenming, Gao Zhenjia, Zhang Chuanheng, Wang Ziqing. 2013. Nanhuan glaciation event and its stratigraphic correlation in Tarim plate, China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(1):39-57 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201301008.htm
Gao Zhenjia, Zhu Chengshun, Peng Changwen. 1984. Precambian Geology of Xinjiang[M]. Urunqi:Xinjiang People's Publishing House, 1-151 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao Zhenjia. 1985. Sinian glacial deposit in Xinjiang, Northwest China[J]. Precambrian Research, 29(1/3):143-149. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0301926885900658
Guo Zhaojie, Zhang Zhicheng. 1995. The geological interpretation of the forming and evolution of lopnur, China[J]. Geological Journal of Universities, 1(2):82-84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hoffman Paulf. 1998. The break-up of Rodinia, birth of Gondwana, true polar wander and the Snowball Earth[J]. Journal of African Earth Science, 28:17-33. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899536299000184
Hu Bin, Qi Lijun, Zhang Hui, Feng Quandong, Fang Jiangxue. 2006.Studying structural evolution of the Yanqi Basin with balancesection technique[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 28(4):17-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1002070506600058
Ji Youliang, Peng Chuansheng, Zhang Liqiang. 2002. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Ordovician in Kuruketage region of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 4(1):43-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11707-007-0033-2
Jia Chengzao, Wei Qiguo, Wang Liangjie. 1997. Tentonic Characteristics and Oil Gas in Tarim Basin of China[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press, 1-438(in Chinese).
Kang Hongzhi. 1996. Prototype basin analysis of Tarim[C]//Collected Works of Petroleum Geology in Tarim of China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 7: 136-145 (in Chinese).
Kirschvink Josephl. 1992. Late Proterozoic low-latitude global glaciation: The snowball Earth[C]//Schopf J W, Klein C(eds. ). The Proterozoic Biosphere. London: Cambridge University Press, 51-52.
Kong Qingying, Cheng Rihui, Wang Pujun, Liu Wanzhu. 2006.Characteristics of tempestite in the Moheershan formtion and sealevel changes in Kuruktag[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 24(4):377-380(in Chinese with English abstract). http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_xjdz200604009
Li Qiugen, Liu Shuwen, Han Baofu, Zhang Zhicheng, Zheng Haifei, Yang Bin. 2004. Geochemical characteristics of tillite and its indicade for source region in Sinian, Kuruktag region of Xinjiang[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 14(9):999-1005 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenhou, Liang Jinze, Shao Lei, Lin Jinyan. 1991. Stom and submarine fans deposits of the Liulin Group in Shanyang region, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Northwest University, (1):95-99(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Xiangmin, Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi, Ma Zhongping, Wang Lishe. 2006. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of Neoproterozoic-Early Cambrian volcanic rocks in Tianshan area[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 25(5):412-422 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200605006.htm
Li Z X, Li X H, Kinny P D, Wang J, Zhang S, Zhou H. 2003.Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents:Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 122(1/4):85-109. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926802002085
Li Z X, Zhang L, Powell C M. 1996. Positions of East Asian cratons in the Neoproterozoic supercontinent Rodinia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 43(6):593-604. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728281
Liang Guixiang. 1994. Storm deposit and its structural setting[J]. Global Geology, 13(3):131-135 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007%2Fs00126-016-0660-1
Liu Baojun, Xu Xiaosong, Luo Anping, Kang Chenglin. 1987. Storm events and phosphate deposition in Cambrian on the western margin of the Yangtze platform, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 5(3):28-39 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Zhongbao, Yu Bingsong, Chen Xiaolin, Gao zhiqian, Cao Qinggu, Li Tingyan. 2003. Sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary characters of submarine fan of Middle-Upper Ordovician in Tadong area, the Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 17(4):408-414(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200901025.htm
Lu Songnian, Li Huaikun, Chen Z, Yu Haifeng, Jin Wei, Guo Kunyi. 2004. Relationship between Neoproterozoic cratons of China and the Rodinia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(2):515-523 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285862139_Relationship_between_Neoproterozoic_cratons_of_China_and_the_Rodinia
Lu Songnian. 2001. From Rodinia to Gondwanland supercontinentsthinking about problems of researching Neoproterozoic supercontinents[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 8(4):441-448 (in Chinese).
Moiola R J, Zhu Qihuang. 1989. Sedimentary characteristics, sedimentary model, classify and submarine fan[J]. Collection of Translations of Marine Geology, (02):34-47 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.scientific.net/AMR.1073-1076.2058
Mutti E, Ricci Lucchi F. 1972. Le torbiditi dell 'Appennino settentrionale:introduzione all' analisi di facies[J]. Memorie Della Societa Geologia Italiana, 11:161-199. http://www.worldcat.org/title/torbiditi-dellappennino-settentrionale-introduzione-allanalisi-di-facies/oclc/804186562
Reading H C, compiled, Zhou M J, et al, Translated. 1986. Sedimentary environment and Facie[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 528-552 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren Zhanli, Xiao Hui, Han Wei, Liang Yu, Qing Ying, Teng Zhihong, Shi zheng. 2009. Research on basin mountain tectonic thermal history of Kongquehe Slope and Kuruketag Uplift[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39(3):510-516 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Shi Qi, Yu Kefu. 2007. Storm event records from the Lagoon sediment on Yongshu reef of the Nansha islands since Late Holocene[J]. Tropical Geography, 27(1):1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-RDDD200701000.htm
Sun Xiaomeng, Wang Pujun, Liu Pengju, Hao Fujiang. 2006.Structural features and tectonic evolutionnary history of Xingdi fault[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 24(4):348-344 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tian Jingchun, Zhang Xiang, Lin Xiaobing, Meng Wanbin, Wang Feng. 2014. Event Sedimentology[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-247 (in Chinese).
Tissot B, Welte D H. 1978. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence, 2nd Ed[M]. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 1-699.
Wang Chenglin, Lu Yuhong, Wu Guanghui, Zhang Liping, Sang Hong, Cao Yinghui. 2011. The discovery and its significance of the Queerueke Formation source rocks in the eastern Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 31(5):45-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cngascn.com:81/ngi_wk/EN/abstract/abstract11987.shtml
Wang Fei, Wang Bo, Shu Liangshu. 2010. Continental tholeiitic basalt of the Akesu area and its implication for the Neoproterozoic rifting in the northern Tarim[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2):547-558(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1473021
Wang Honghao, Li Jianghai, Zhou Xiaobei, Li Weibo, Wang Jieqiong. 2015. New opinion on the position of the Tarim block in the Rodinia supercontient:Constraints from stratigraphic correlation and paleomagnetism[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(2):589-600(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWX201502021.htm
Wang Pengcheng, Wang Yue. 2015. The geological cause of the Luoquan Formation in Ruzhou, wester Henan[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 32(6):49-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289038523_Negative_anomaly_of_carbon_isotope_from_carbonates_of_Sinian_Dongpo_Formation_in_Ruzhou_and_Lushan_Henan_province_and_its_geological_significance
Wang Xinwen, Chen Fajing. 1997. Sinian-Ordovician tectonic evolution of North Tarim and South Tianshan region and its relation to oil and gas[J]. Geoscience, 11(3):313-321 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-6010-z
Wu Xingning, Shou Jianfeng, Zhang Huiliang, Pan Wenqing. 2012.Characteristics of the petroleum system in Cambrian and Ordovician sequence frameworks of the Tarim Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(2):225-231(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYXB201202007.htm
Xu Bei, Jian Ping, Zheng Haifeng, Zhou Haibo, Zhang Lifei, Liu Dunyi. 2005. U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Neoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the Tarim Block of northwest China:Implications for the breakup of Rodinia supercontinent and Neoproterozoic glaciations[J]. Precambrian Research, 136:107-123. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.09.007
Xu Bei, Xiao Shuhai, Zou Haibo, Chen Yan, Li Zhengxiang, Song Biao, Liu Dunyi, Zhou Chuanming, Yuan Xunlai. 2009. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age constraints on Neoproterozoic Quruqtagh diamictites in NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 168:247-258. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.10.008
Yang Binyi. 2004. Tectonic Evolution and Petroleum Accumulation in Mesozoic and Cenozoic Yanqi Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Ruicai, Du Lan, Ou Yanghua, Su Wu, Gao Weizhong. 1999.Sedimentary evolution of upper Sinian-Paleozoic in northeastern Tarim basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 20(3):239-243 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Ruidong, Zhang Chuanlin, Luo Xinrong, Tian Jingquan, Bao Yafan, Song Guoqi. 2006. Geochemical characteristics of Early Cambrian cherts in Quruqtagh, Xinjiang, West China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(4):598-605(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290099282_Geochemical_characteristics_of_Early_Cambrian_cherts_in_Quruqtagh_Xinjiang_west_China
Yang Shufeng, Chen Hanlin, Dong Chuanwan, Zhao Dongdong, Jia Chengzao, Wei Qiguo. 1998. Geochemical properties of Late Sinian basalt in the northwestern boundary of Tarim Basin and its tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Zhenjiang University, 32(6):753-740(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Kuanhong, Jin Zhenkui, Li Peng, Zhang Hongfeng. 2010.Lithofacies paieogeography of Cambrian-Ordovician, eastern Tarim Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 43(4):113-118(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhan Sheng, Chen Yan, Xu Bei, Faure Michel. 2007. Late Neoproterozoic paleomagnetic results from the Sugetbrak Formation of the Aksu area, Tarim basin(NW China) and their implications to paleogeographic reconstructions and the snowball earth hypothesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 154(3/4):143-158. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260953541_Late_Neoproterozoic_paleomagnetic_results_from_the_Sugetbrak_Formation_of_the_Aksu_area_Tarim_basin_NW_China_and_their_implications_on_the_paleogeographic_reconstruction_and_snowball_Earth_hypothesis
Zhang Bing, Deng Maolin, Shui Wei, Zhou Wei, Wang Xinggui. 2009.A review of the study of tempetite of special reference to significance of tempetite of Xingwen County[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 29:35-38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Shouan, Luo Chuanrong. 2005. Sedimentary development and petroliferous prospects in northeast region, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 14(4):307-313(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XJSD199304002.htm
Zhang Shuichang, Gao Zhiyong, Li Jianjun, Zhang Baomin, Gu Qiaoyuan, Lu Hongyu. 2012. Identification and distribution of marine hydrocarbon source rocks in the Ordovician and Cambrian of the Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(3):285-294 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60044-5
Zhang Yan, Wang Pujun, Liu Wanzhu, Li Jinlong. 2006. Sedimentary environment of the Neoproterozoic in Quruqtagh region[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 24(4):365-368(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2096249517301060
Zhang Yueqiao, Jia Jindou, Jin Jiuqiang, Liu Quanyou. 2007.Characteristics of Cambrian-Ordovician sedimentary facies in Tadong region and its sedimentary model[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 18(2):229-234(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1418220
Zhao Jingzhou. 2001. Evoluation on the Cambrian-Ordovician marine source rocks from the North Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 19(1):117-124(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Xiangsheng, Zou Xianghua, Niu Daoyun, Zhang Ruilin, Zhang Luyi, Wang Shuxi. 1984. The sinian system and its glacial deposits in beishan distrct[J]. Bulletion of Xi'an Institute of Geology and Mineral Resource, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, (7):29-37(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yongqing, Zhang Genfa, Wang Bin, Luo Yun, Zhou Yushuang, Lin Xueqing, Chen Xuyun. 2013. Main controlling factors for petroleum accumulation in Kongquehe slope, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 35(5):487-494(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Zongju, Wu Xingning, Pan Wenqing, Zhang xingyang, Zhang Lijuan, Ma Peiling, Wang Zhenyu. 2009. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography of Ordovician in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta sedimentologica Sinica, 27(5):939-955(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cjxb.ac.cn/EN/abstract/abstract702.shtml
Zheng Xiujuan. 2005. The Sequence Stratigraphic Frame Works and Depositional Facies of the Lower Paleozoic in the Northeast of Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Xiaobei, Li Jianghai, Fu Chenjian, Li Wenshan, Wang Honghao. 2012. A discussions on the Cryogenian-Cambrian tectonicsedimentary event and tectonic setting of northern Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 39(4):900-911(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201204006.htm
Zhu Qihuang. 1990. Genetic characterization of submarinefans and their poientialities for oil-gas storage[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 11(1):79-83 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/export!exportTopEndNoteXML.action?agrovocString=Phoenix&onlyFullText=false
Moiola R J, 朱起煌. 1989.海底扇的沉积特征、沉积模式、分类及储层潜力[J].海洋地质译丛, 02:34-47. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95970X/198902/55027.html Reading H C, 著, 周明鉴, 等译. 1986. 沉积环境和相[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 528-552. 蔡志慧, 许志琴, 唐哲民, 何碧竹, 陈方远. 2011.塔里木盆地东北缘库鲁克塔格地区的早古生代地壳变形以及造山时限[J].中国地质, 38(4):855-867. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110405&flag=1 程日辉, 王璞珺, 孙晓猛, 白云风. 2006.库鲁克塔格地区奥陶系层序地层与海平面变化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 30(3):283-293. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DGYK200603002.htm 段吉业, 夏德馨, 安素兰. 2005.新疆库鲁克塔格新元古代-早古生代裂陷槽深水沉积与沉积-构造古地理[J].地质学报, 79(1):7-16. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1012460901.htm 冯乔. 1997.塔里木盆地满加尔凹陷地层埋藏史与有机质成熟演化[J].沉积学报, (1):173-177. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4157879 冯玉辉, 于小健, 黄玉龙, 刘宝鸿, 顾国忠, 李涵月, 王璞珺. 2015.辽河盆地新生界火山喷发旋回和期次及其油气地质意义[J].中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 39(5):50-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYDX201505007.htm 高林志, 郭宪璞, 丁孝忠, 宗文明, 高振家, 张传恒, 王自强. 2013.中国塔里木板块南华纪成冰事件及其地层对比[J].地球学报, 34(1):39-57. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.01.05 高振家, 朱诚顺, 彭昌文. 1984.新疆前寒武纪地质[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆人民出版社, 1-151. 郭召杰, 张志诚. 1995.罗布泊形成及演化的地质新说[J].高校地质学报, 1(2):82-84. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90539X/199502/1661426.html 胡斌, 齐丽军, 张辉, 冯全东, 方江雪. 2006.平衡剖面在焉耆盆地构造演化分析中的应用[J].西南石油学院学报, 28(4):17-21. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93402X/200604/22665125.html 纪友亮, 彭传圣, 张立强. 2002.新疆库鲁克塔格地区奥陶纪岩相古地理[J].古地理学报, 4(1):43-51. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2002.01.005 贾承造, 魏国齐, 王良杰. 1997.中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1-438. 康志宏. 1996. 塔里木原型盆地分析[C]//中国塔里木盆地石油地质文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 7: 136-145. 孔庆莹, 程日辉, 王璞珺, 刘万洙. 2006.新疆库鲁克塔格地区寒武系莫合尔山组风暴岩特征及其对海平面变化的响应[J].新疆地质, 24(4):377-380. https://www.doc88.com/p-4794412021231.html 李秋根, 刘树文, 韩宝福, 郭召杰, 张志诚, 郑海飞, 杨斌. 2004.新疆库鲁克塔格震旦系冰碛岩的地球化学特征及其对物源区的指示[J].自然科学进展, 14(9):999-1005. http://www.oalib.com/paper/1697198 李文厚, 梁金哲, 邵磊, 林晋炎. 1991.陕西山阳地区刘岭群的风暴沉积和海底扇沉积[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), (1):95-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ199101023.htm 李向民, 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 马中平, 王立社. 2006.天山地区新元古代-早寒武世火山岩地球化学和岩石成因[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 25(5):412-422. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200605005 梁桂香. 1994.风暴沉积及其构造背景[J].世界地质, 13(3):131-135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD199904003.htm 刘宝珺, 许效松, 罗安屏, 康承林. 1987.中国扬子地台西缘寒武纪风暴事件与磷矿沉积[J].沉积学报, 5(3):28-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198703005.htm 刘忠宝, 于炳松, 陈晓林, 高志前, 曹清古, 李廷艳. 2003.塔里木盆地塔东地区中-上奥陶统海底扇浊积岩层序地层格架及沉积特征[J].现代地质, 17(4):408-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200304008.htm 陆松年, 李怀坤, 陈志宏, 于海峰, 金巍, 郭坤一. 2004.新元古时期中国古大陆与罗迪尼亚超大陆的关系[J].地学前缘, 11(2):515-523. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/200402/9517565.html 陆松年. 2001.从罗迪尼亚到冈瓦纳超大陆——对新元古代超大陆研究几个问题的思考[J].地学前缘, 8(4):441-448. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DXQY200104039.htm 任战利, 肖晖, 韩伟, 梁宇, 卿颖, 腾志宏, 史政. 2009.孔雀河斜坡与库鲁克隆起构造-热演化史研究[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 39(3):510-516. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdxxb200903022 施祺, 余克服. 2007.南沙群岛永暑礁潟湖沉积的晚全新世风暴事件记录[J].热带地理, 27(1):1-5. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95558X/200701/23679887.html 孙晓猛, 王璞珺, 刘鹏举, 郝福江. 2006.兴地断裂构造特征及其演化历史[J].新疆地质, 24(4):348-344. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XJDI200604002.htm 田景春, 张翔, 林小兵, 孟万斌, 王峰. 2014.事件沉积学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-247. 汪新文, 陈发景. 1997.塔北-南天山地区震旦-奥陶纪盆-山构造演化及其油气关系[J].现代地质, 1997, 11(3):313-321. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/a80829e705087632311212ed.html 王成林, 卢玉红, 邬光辉, 张立平, 桑洪, 曹颖辉. 2011.塔里木盆地塔东地区却尔却克组烃源岩的发现及其意义[J].天然气工业, 31(5):45-48. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4981017 王飞, 王博, 舒良树. 2010.塔里木西北缘阿克苏地区大陆拉斑玄武岩对新元古代裂解事件的制约[J].岩石学报, 26(2):547-558. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100216 王洪浩, 李江海, 周肖贝, 李维波, 王杰琼. 2015.塔里木陆块在Rodinia超大陆中位置的新认识——来自地层对比和古地磁的制约[J].地球物理学报, 58(2):589-600. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150221 王鹏程, 王约. 2015.豫西汝州罗圈组杂砾岩的成因浅析[J].贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 32(6):49-52. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10657-1015910585.htm 吴兴宁, 寿建峰, 张惠良, 潘文庆. 2012.塔里木盆地寒武系-奥陶系层序格架中生储盖组合特征与勘探意义[J].石油学报, 33(2):225-231. doi: 10.7623/syxb201202006 杨斌谊. 2004. 焉耆盆地中新生代构造演化与油气聚集[D]. 西安: 西北大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2004104011.htm 杨瑞财, 杜岚, 欧阳华, 苏武, 高伟中. 1999.塔东北地区上震旦统-下古生界沉积演化[J].新疆石油地质, 20(3):65-69. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-2006139681.htm 杨瑞东, 张传林, 罗新荣, 田敬全, 包亚范, 宋果奇. 2006.新疆库鲁克塔格地区早寒武世硅质岩地球化学特征及其意义[J].地质学报, 80(4):598-605. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4874186 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 董传万, 赵冬冬, 贾承造, 魏国齐. 1998.塔里木盆地西北缘晚震旦世玄武岩地球化学特征及大地构造背景[J].浙江大学学报, 32(6):753-740. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC806.016.htm 余宽宏, 金振奎, 李鹏, 张宏峰. 2010.塔东地区寒武-奥陶纪岩相古地理分析[J].西北地质, 43(4):113-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201004013 张斌, 邓茂林, 税伟, 周维, 王兴贵. 2009.风暴岩研究述评兼论兴文风暴岩研究的意义[J].四川地质学报, (29):35-38. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/83117X/2009S1/1003863716.html 张守安, 罗传容. 2005.塔里木盆地东北地区沉积发育特征与含油气性[J].新疆石油地质, 14(4):307-313. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XJSD199304017.htm 张水昌, 高志勇, 李建军, 张宝民, 顾乔元, 卢玉红. 2012.塔里木盆地寒武系-奥陶系海相烃源岩识别与分布预测[J].石油勘探与开发, 39(3):285-294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201203004 张艳, 王璞珺, 刘万洙, 李金龙. 2006.库鲁克塔格地区震旦系冰碛岩沉积环境及意义[J].新疆地质, 24(4):365-368. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjdz200604006 张月巧, 贾进斗, 靳久强, 刘全有. 2007.塔东地区寒武-奥陶系沉积相与沉积演化模式[J].天然气地球科学, 18(2):229-234. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/97226X/200702/24128120.html 赵靖舟. 2001.塔里木盆地北部寒武-奥陶系海相烃源岩重新认识[J].沉积学报, 19(1):117-124. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_cjxb200101020 赵祥生, 邹湘华, 牛道韫, 张瑞林, 张录易, 王树洗. 1984.北山地区震旦系及冰川沉积[J].中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所所刊, (7):29-37. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198406001004.htm 赵永强, 张根发, 王斌, 罗宇, 周雨双, 林学庆, 陈绪云. 2013.塔里木盆地孔雀河斜坡成藏主控因素探讨[J].石油实验地质, 35(5):487-494. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201305487 赵宗举, 吴兴宁, 潘文庆, 张兴阳, 张丽娟, 马培领, 王振宇. 2009.塔里木盆地奥陶纪层序岩相古地理[J].沉积学报, 27(5):939-955. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/CJXB200905019.htm 郑秀娟. 2005. 塔里木盆地东北地区下古生界层序格架与沉积相研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1784704 周肖贝, 李江海, 傅臣建, 李文山, 王洪浩. 2012.塔里木盆地北缘南华纪-寒武纪构造背景及构造-沉积事件探讨[J].中国地质, 39(4):900-911. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120405&flag=1 朱起煌. 1990.海底扇的成因特征与储集油气潜力[J].新疆石油地质, 11(1):79-83. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93464X/199001/439812.html -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张立涛,余君鹏,余吉远,陈杰,赵吉昌,樊新祥. 中祁连西段德勒诺尔一带南华系的重新厘定及其与Rodinia超大陆裂解的关系. 地质通报. 2021(04): 491-498 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 易士威,李明鹏,郭绪杰,范土芝,杨帆,方辉,缪卫东,林世国,高阳,李德江. 塔里木盆地南华纪古裂谷对寒武系沉积的控制及勘探意义. 石油学报. 2020(11): 1293-1308 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: