Geochronology, geochemistry and genesis of Na-rich volcanic rocks of the Zhaibeishan copper deposit in Eastern Tianshan Mountains
-
摘要:
寨北山矿区海相火山岩为一套富钠的玄武安山玢岩、安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩组合,属于钙碱性系列岩石,具有低MgO(0.51%~5.93%,平均2.54%)、FeO(0.54%~6.39%,平均2.84%)和钛(TiO2=0.09%~1.10%,平均0.58%),富铝(Al2O3=12.23%~17.75%,平均15.20%,A/CNK=0.79~1.42,平均1.11)以及富钠(Na2O/K2O平均为7.30)、富水的特征。火山岩中斜长石主要为钠长石,少量更长石。轻、重稀土分馏较明显((LREE/HREE)N=3.68~9.00),微量元素显示大离子亲石元素(如Th、U、Rb)、轻稀土的富集和高场强元素(如Nb、Ta、Ti、P)相对亏损的特征。获得矿区雅满苏组钠质玄武安山玢岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb谐和年龄为(337.6±3.3)Ma,为早石炭世火山活动的产物。火山岩岩石学及地球化学特征表明研究区钠质火山岩可能形成于俯冲带近大陆方向的岛弧构造环境,是早石炭世洋壳俯冲熔融产生的岩浆在海底喷发过程中与海水相互反应后,经低变质相作用产生的。成矿元素在钠长石化过程中可能被淋滤出来进入含矿热液,后期在适当的温压等条件下沉淀形成本区的矿床。
-
关键词:
- 东天山 /
- 寨北山铜矿 /
- 雅满苏组 /
- 钠质火山岩 /
- SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄
Abstract:Marine Na-rich volcanic rocks of Yamansu Formation belong to calc-alkaline series and are dominated by basaltic andesitic porphyrite, andesite, dacite and rhyolite. These volcanic rocks are characterized by low MgO (0.51%-5.93%, averaging 2.54%), FeO (0.54%-6.39%, averaging 2.84%) and TiO2 (0.09%-1.10%, averaging 0.58%) values, high Al2O3 (12.23%-17.75%, averaging 15.2%; A/CNK=0.79-1.42, averaging 1.11), and Na2O (Na2O/K2O 7.30 on average). A majority of plagioclases in the Narich volcanic rocks consist of albite with less oligoclase. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns show the fractionation between LREE and HREE ((LREE/HREE)N=3.68-9.00). The volcanic rocks are also rich in LILE (Th, U, Rb) and depleted in Nb, Ta, Sr, Ti, P. The SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating yielded (337.6±3.3) Ma. Based on a comparative study of geochemical characteristics and inherited zircon age, the authors hold that Yamansu Na-rich volcanic rocks were formed in an island arc setting with continental basement and were the products of reaction between erupted magma and convective seawater during the subduction of oceanic plate in Early Carboniferous.
-
1. 引言
在海底喷发的安山岩-流纹岩由于经历海水热蚀变和变质作用,使得岩石成分上具有Na2O含量高的特点(一般Na2O/K2O > 1),这种岩石被称为石英角斑岩系(Vallance et al., 1974;Mengel et al., 1987;姜福芝和王玉往,2005),且产于活动大陆边缘的海相火山环境中的铁、铜等多金属矿床的成矿作用多与该类岩石有密切联系(Galley et al., 1993;周济元等,1996;Lentz et al., 1998;Doyle et al., 2003;Oliver et al., 2004;姜福芝,2001;张招崇等,2016)。位于东天山南部的阿奇山—雅满苏成矿带发育许多与石炭纪海相火山岩有关的铁矿床,如雅满苏铁矿、红云滩铁矿、百灵山铁矿、赤龙峰铁矿等,这些铁矿体大都呈层状、似层状,与石炭纪火山岩地层呈整合接触关系,与火山活动有密切关系(姜福芝等,2002;董连慧等,2011;徐仕琪等,2011;李厚民等,2014)。近年来,带内与火山-次火山有关的铜矿床(点)(如铜鱼梁铜矿、寨北山铜矿、沙泉子北铜矿、雅西371-西北坡金铜矿)的研究(高珍权,2002;肖昱,2003;方维萱等, 2006a, 2006b;张达玉,2012;孙志远等,2016),显示成矿带具一定的铜多金属找矿潜力。本文拟对与铜矿关系密切的钠质火山岩年代学、矿物学和地球化学进行研究,探讨成岩成矿时代、富钠火山岩浆的成因、产出的构造背景及其与铜矿的关系。
2. 区域及矿床地质
2.1 区域地质概况
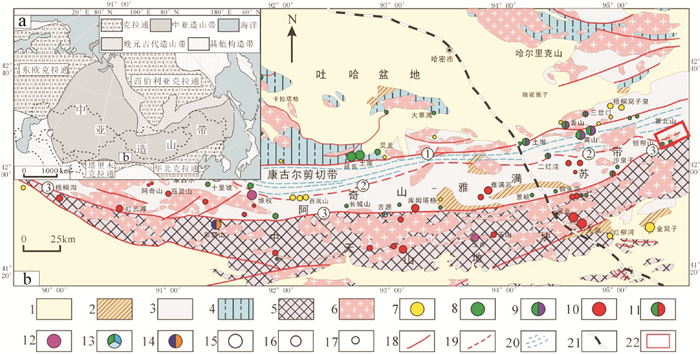
中亚造山带在大地构造位置上处于西伯利亚、准噶尔—哈萨克斯坦和塔里木三大板块的交汇处(Windley et al., 2007;何国琦等,1994;肖序常等,1992;秦克章等,2002)(图 1a)。东天山作为中亚造山带的一部分,其在晚古生代经历了复杂的构造-岩浆演化事件,形成中国重要的Au、Cu(Ni)、Fe等矿产富集区之一(Han et al., 2006)。从北向南依次为博格达—哈尔里克构造带、吐哈盆地、觉罗塔格构造带、中天山地块。觉罗塔格构造带位于东天山的南部,是吐哈盆地和中天山地块的中间部分(图 1),根据断裂构造及矿床类型展布关系,进一步可以把觉罗塔格构造带划分为吐哈盆地南缘铜矿带(北带)、康古尔金矿带(中带)和阿奇山—雅满苏铁(铜)-银多金属矿带(南带)3个不同的单元(王京彬等,2006)。
![]() 1—新生代沉积盖层;2—二叠纪陆相火山-沉积岩系;3—石炭纪火山沉积岩系;4—奥陶—泥盆纪火山沉积岩系;5—前寒武纪变质岩;6—花岗岩类;7—金矿床;8—铜矿床;9—铜镍矿床;10—铁矿床;11—铜铁矿床;12—银多金属矿床;13—铜多金属矿床;14—铅锌矿床;15—大型矿床;16—中型矿床;17—小型矿床;18—断裂;19—推测断裂;20—剪切带;21—铁路;22—研究区. ①—康古尔断裂;②—雅满苏—苦水断裂;③—阿奇克库都克—沙泉子断裂Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of the Central Asia Orogenic Belt (a, after Jahn et al., 2000) and geological map and deposits distribution in Eastern Tianshan Mountains (b, modified from Wang et al., 2006)1-Meso-Cenozoic sedimentary cover; 2-Permian continental volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 3-Carboniferous volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 4-Ordovician-Devonian volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 5-Precambrian metamorphic rocks; 6-Granitoids; 7-Au deposits; 8-Cu deposits; 9-Cu-Ni sulfide deposits; 10-Fe deposits; 11-Fe-Cu deposits; 12-Ag-polymetallic deposits; 13-Cu-polymetallic deposits; 14-Pb-Zn deposits; 15-Large mineral deposits; 16-Middle mineral deposits; 17-Small mineral deposits; ; 18-Faults; 19-Inferred faults; 20-Shear zone; 21-Railway; 22-Study area ①-Kangguer Fault; ②-Yamansu Fault; ③-Aqikekuduke-Shaquanzi Fault
1—新生代沉积盖层;2—二叠纪陆相火山-沉积岩系;3—石炭纪火山沉积岩系;4—奥陶—泥盆纪火山沉积岩系;5—前寒武纪变质岩;6—花岗岩类;7—金矿床;8—铜矿床;9—铜镍矿床;10—铁矿床;11—铜铁矿床;12—银多金属矿床;13—铜多金属矿床;14—铅锌矿床;15—大型矿床;16—中型矿床;17—小型矿床;18—断裂;19—推测断裂;20—剪切带;21—铁路;22—研究区. ①—康古尔断裂;②—雅满苏—苦水断裂;③—阿奇克库都克—沙泉子断裂Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of the Central Asia Orogenic Belt (a, after Jahn et al., 2000) and geological map and deposits distribution in Eastern Tianshan Mountains (b, modified from Wang et al., 2006)1-Meso-Cenozoic sedimentary cover; 2-Permian continental volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 3-Carboniferous volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 4-Ordovician-Devonian volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 5-Precambrian metamorphic rocks; 6-Granitoids; 7-Au deposits; 8-Cu deposits; 9-Cu-Ni sulfide deposits; 10-Fe deposits; 11-Fe-Cu deposits; 12-Ag-polymetallic deposits; 13-Cu-polymetallic deposits; 14-Pb-Zn deposits; 15-Large mineral deposits; 16-Middle mineral deposits; 17-Small mineral deposits; ; 18-Faults; 19-Inferred faults; 20-Shear zone; 21-Railway; 22-Study area ①-Kangguer Fault; ②-Yamansu Fault; ③-Aqikekuduke-Shaquanzi Fault阿奇山—雅满苏成矿带位于东天山南缘,向南以阿奇克库都克—沙泉子断裂为界和中天山地块相邻,向北以雅满苏—苦水断裂为界与康古尔剪切带相邻。带内石炭纪地层包括下石炭统阿奇山组(C1a)、雅满苏组(C1y)和上石炭统底坎儿组(C2d)、土古土布拉克组(C2tg)。阿奇山组(C1a)主要由灰绿色玄武岩、灰褐色蚀变英安岩、熔结角砾岩、熔结凝灰岩组成,夹透镜状砂岩和灰岩,该组中流纹英安岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(341.7±2.7)Ma(苏春乾等,2009)。雅满苏组(C1y)为一套浅海相火山岩-碳酸盐建造,含棱菊石化石(杨兴科等,1998),火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄在334.0~348.0 Ma(罗婷等,2012)。底坎儿组(C2d)出露于带内南部,主要为中基-酸性火山岩熔岩和火山碎屑岩,包括玄武安山岩、安山岩、流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩等,夹碳酸盐岩(含珊瑚化石),属钙碱性系列,该组流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(321.7±1.7) Ma(徐璐璐等,2014)。土古土布拉克组(C2tg)主要分布在阿其克库都克断裂带两侧,为一套火山碎屑岩夹正常沉积岩,含有海百合茎和腕足化石,以火山熔岩为主,其中含砾砂岩中花岗闪长斑岩砾石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为(314±4.2) Ma(宋安江等,2006)。二叠系阿奇克布拉克组(P1a)主要分布在库姆塔格东部和雅满苏东部景峡—木头井子地区,主要岩石组合为砾岩、砂砾岩。带内侵入岩体有闪长质岩体和花岗质岩体,包括花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩、钾长花岗岩岩体等,主要为晚古生代岩体(吴昌志等,2006;唐俊华等,2008;周涛发等,2010),部分早中生代岩体(雷如雄等,2013)。
成矿带内主要发育海相火山岩型铁(铜)矿、矽卡岩型矿床、火山热液型铜矿以及产于玄武岩中的自然铜矿等(王京彬等,2006)。与海相火山岩有关的“雅满苏式”铁矿,包括雅满苏铁矿、红云滩铁矿、赤龙峰铁矿、百灵山铁矿等,主要产于上石炭统雅满苏组火山岩地层中,少数产于下石炭统,矿体大都呈层状、似层状产出,成矿时代为石炭纪(王龙生等,2005a;黄小文等,2014;Hou et al., 2014)。与火山热液活动有关的铜矿主要有寨北山铜矿、铜鱼梁铜矿、景峡铜矿和沙泉子北铜矿等,方维萱等(2006a)认为该类型铜矿是与大陆边缘钙碱性火山岩和斑岩有密切关系的斑岩-浅成低温热液型铜多金属矿床。与花岗岩侵入体有关的维权矽卡岩型银多金属矿床其成矿年龄为(297±3) Ma(王龙生等,2005b)。此外,该带内产出许多玄武岩有关的自然铜矿(化),如十里坡、长城山形成于晚石炭世到早二叠世的后碰撞伸展期,是由熔融的原生岩浆分异演化形成的玄武质岩浆上升喷发形成的(袁峰等,2010)。
2.2 寨北山矿区地质特征
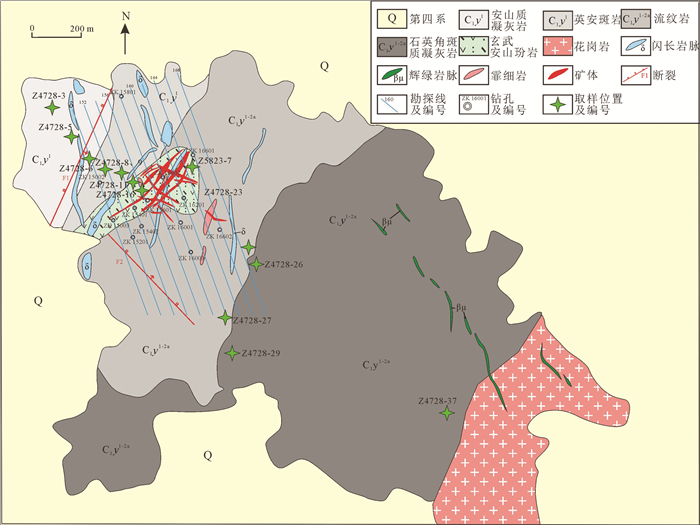
寨北山铜矿区位于新疆哈密市东南部,直线距离约150 km。矿区出露地层主要为下石炭统雅满苏组火山岩和第四系沉积物(图 2)。雅满苏组可分为两个岩性段:第一岩性段下部砂岩、凝灰质砂岩,中部为角砾凝灰岩、钠质玄武安山玢岩,夹少量霏细斑岩,其中钠质玄武安山玢岩为主要含矿层位,位于该区域的中部,是该区铜矿的含矿岩体,走向北东35°~50°,倾向南倾。上部为钠质英安岩、霏细斑岩;第二岩性段下部为钠质流纹岩、硅质岩夹生物碎屑灰岩,上部主要为灰白色石英角斑质凝灰岩。矿区属银帮山—野马山复背斜北翼的一部分,且断裂构造发育,构造线方向为北东向和南东向。矿区内侵入岩主要以岩体、岩脉状产出。岩体主要为花岗岩体,其出露面积较大,分布于矿区的东南侧。岩脉以闪长岩脉和辉绿岩脉为主。闪长岩脉宽2 ~15 m不等,长50 ~350 m不等,产状近直立,走向北东、北西、南北均有,岩脉穿插于地层之中,应为后期侵入生成。辉绿岩脉近北西向,呈雁列线状零散展布。
铜矿主要赋存于钠质玄武安山玢岩中。目前共圈定了20条矿(化)体,其中北东向5号矿体为主矿体。5号矿体长度约200 m,平均水平厚度4.84 m,深部最厚达11 m,平均品位0.49%,最高品位5.43%,其中矿体向深部有后期热液叠加富集现象。
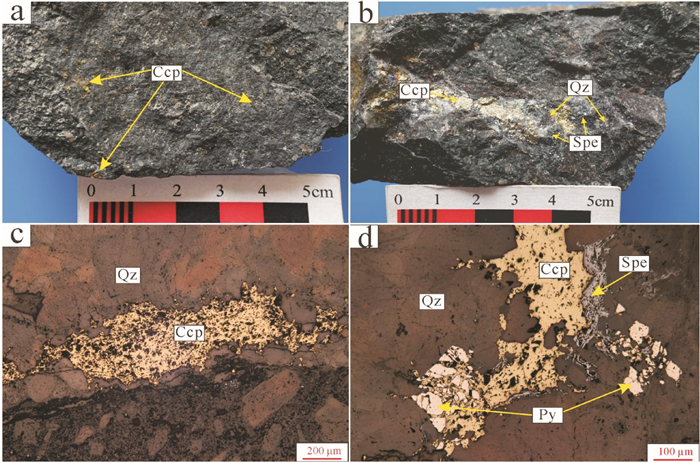
寨北山铜矿矿石类型可分为浸染状矿石和脉状矿石,矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿,少量斑铜矿。浸染状矿石(图 3a)黄铜矿颗粒呈星点状、斑杂状分布在玄武质安山玢岩中,黄铜矿颗粒较小,呈半自形-他形粒状结构,粒径2 ~5 mm。脉状矿石为矿区的主要矿石类型(图 3b),偶见网脉状矿石。脉状矿石主要有石英-黄铜矿脉和石英-黄铜矿-黄铁矿脉。石英-黄铜矿脉中黄铜矿呈碎布状,他形结构(图 3c);石英-黄铜矿-黄铁矿脉中黄铁矿呈自形结构,黄铜矿半自形-他形结构,可见黄铜矿溶蚀交代早期黄铁矿(图 3d),后期被束状镜铁矿沿边部交代。
![]() 图 3 寨北山铜矿岩石标本和矿物镜下特征a—侵染状矿石;b—脉状矿石;c—石英+黄铜矿脉, 黄铜矿交代黄铁矿呈交代残余结构;Ccp—黄铜矿;Qz—石英;Py—黄铁矿;Spe—镜铁矿Figure 3. Characteristics of the rocks and microscope photographs of the Zhaibeishan copper deposita-disseminated ore; b-vein ore; c-quartz+chalcopyrite vein; d-quartz+chalcopyrite+pyrite vein. Pyrite replaced by chalcopyrite as metasomatic relict structure. Abbreviation:Ccp-chalcopyrite; Qz-quartz; Py-pyrite; Spe-specularite
图 3 寨北山铜矿岩石标本和矿物镜下特征a—侵染状矿石;b—脉状矿石;c—石英+黄铜矿脉, 黄铜矿交代黄铁矿呈交代残余结构;Ccp—黄铜矿;Qz—石英;Py—黄铁矿;Spe—镜铁矿Figure 3. Characteristics of the rocks and microscope photographs of the Zhaibeishan copper deposita-disseminated ore; b-vein ore; c-quartz+chalcopyrite vein; d-quartz+chalcopyrite+pyrite vein. Pyrite replaced by chalcopyrite as metasomatic relict structure. Abbreviation:Ccp-chalcopyrite; Qz-quartz; Py-pyrite; Spe-specularite3. 火山岩岩相学及矿物学特征
寨北山矿区主要岩石类型有钠质玄武安山玢岩、钠质安山岩、钠质安山岩、钠质英安岩和钠质流纹岩。
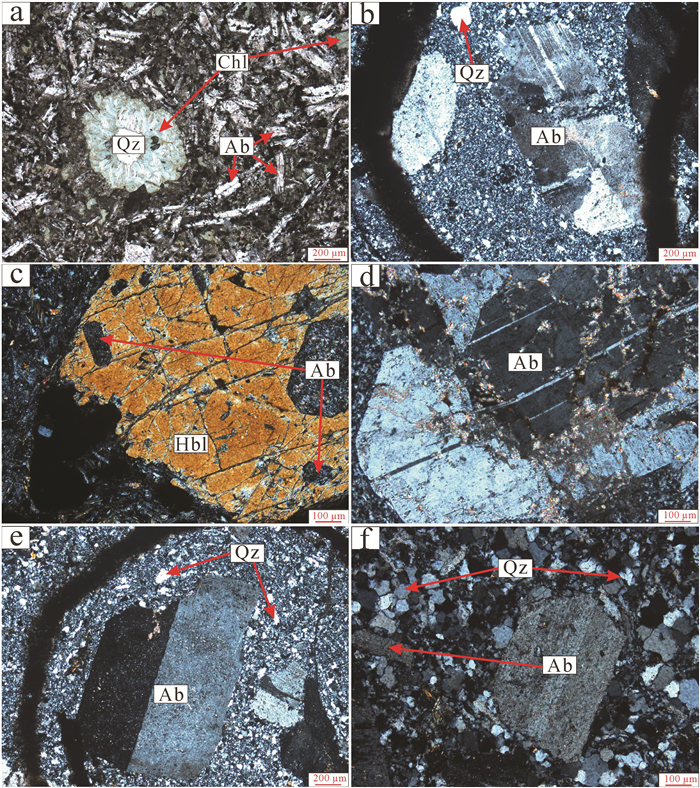
钠质玄武安山玢岩:手标本呈灰绿色,杏仁构造,杏仁中心由石英充填,周围被绿泥石交代呈“绿泥石反应边”(图 4a)。斑状或少斑结构,斑晶主要为角闪石,少量斜长石。角闪石斑晶黄褐色-褐色,自形-半自形,粒状、椭圆六边形状,粒径300~500 μm,单偏光下有弱的多色性,大部分角闪石边部都具有钠长石蚀变反应边,中心被自形晶的钠长石交代溶蚀呈包含结构,交代角闪石的长石牌号An0.82(图 4b)。基质主要有杂乱微晶钠长石组成,构成玻晶交织结构。微晶斜长石粒径100~200 μm,晶体顶端呈燕尾分叉状,具中空骸晶结构,为淬火条件下的产物。电子探针测得斜长石牌号除三个为更长石外(平均An14.20),其余均为钠长石(平均An3.20)。
![]() 图 4 雅满苏组钠质火山岩显微照片a—单偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),杏仁构造,钠质斜长石中空骸晶结构;b—正交偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),角闪石边部具有钠长石蚀变反应边,中心被钠长石交代溶蚀呈包含结构;c—正交偏光,钠质安山岩(Z4728-3),钠长石交代早期斜长石,基质碳酸盐化;d—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石聚片双晶,石英蚀变呈浑圆状;e—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石具简单双晶结构,斑晶边部被熔蚀;f—正交偏光,钠质流纹岩(Z4728-16),钠长石斑晶被溶蚀成浑圆状。照片中缩写符号:Ab—钠长石;Qz—石英;Hbl—角闪石;Chl—绿泥石Figure 4. Microphotographs for textures of the Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formationa-Plainlight, Na-Richbasaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), almond texture, central absent skeleton crystal texture in plagioclase; b-crossedpolarized light, Na-rich basaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), The rim of the hornblende was albite alteration and the center was dissolved into poikilitic texture; c-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich andesite(Z4728-3), albite altered the early stage plagioclase, groundmass were carbonated; d-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), polysynthetic twin, quartzs were resorbed into round shapes; e-Crossed nicols, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), albite twins, the rim of the phenocrysts experienced corrosion; f-Crossed nicols, Na-rich rhyolite (Z4728-16), albite phenocrysts altered into round shapes. Abbreviation: Ab-Albite; Qz-Quartz; Hbl-Hornblende; Chl-Chlorite
图 4 雅满苏组钠质火山岩显微照片a—单偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),杏仁构造,钠质斜长石中空骸晶结构;b—正交偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),角闪石边部具有钠长石蚀变反应边,中心被钠长石交代溶蚀呈包含结构;c—正交偏光,钠质安山岩(Z4728-3),钠长石交代早期斜长石,基质碳酸盐化;d—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石聚片双晶,石英蚀变呈浑圆状;e—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石具简单双晶结构,斑晶边部被熔蚀;f—正交偏光,钠质流纹岩(Z4728-16),钠长石斑晶被溶蚀成浑圆状。照片中缩写符号:Ab—钠长石;Qz—石英;Hbl—角闪石;Chl—绿泥石Figure 4. Microphotographs for textures of the Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formationa-Plainlight, Na-Richbasaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), almond texture, central absent skeleton crystal texture in plagioclase; b-crossedpolarized light, Na-rich basaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), The rim of the hornblende was albite alteration and the center was dissolved into poikilitic texture; c-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich andesite(Z4728-3), albite altered the early stage plagioclase, groundmass were carbonated; d-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), polysynthetic twin, quartzs were resorbed into round shapes; e-Crossed nicols, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), albite twins, the rim of the phenocrysts experienced corrosion; f-Crossed nicols, Na-rich rhyolite (Z4728-16), albite phenocrysts altered into round shapes. Abbreviation: Ab-Albite; Qz-Quartz; Hbl-Hornblende; Chl-Chlorite钠质安山岩:灰色、灰黑色,块状构造,少斑结构,斑晶主要为长石,含量10%~15%。斜长石斑晶自形-半自形,长条状、短柱状,也被钠长石交代(图 4c),测得交代斜长石的长石牌号An0.86。基质为隐晶质结构,受到后期绢云母化和碳酸盐化蚀变。
钠质英安岩:手标本灰色,致密块状,少斑结构,斑晶以钠长石为主,少量他形晶石英,斑晶含量15%~20%。钠长石斑晶半自形-他形柱状,粒径300~500 μm,发育聚片双晶和钠长石双晶(图 4d、4e),牌号An1.22~2.38;石英斑晶较钠长石斑晶粒度小,表面干净,多被溶蚀成浑圆状或港湾状。基质以长英质矿物为主,呈霏细结构。
钠质流纹岩:暗灰白色,块状构造,少斑结构,斑晶含量约5%,为钠长石斑晶和少量石英斑晶。钠长石斑晶多为自形-半自形短柱状,粒径100~ 400 μm,具简单双晶,周围被溶蚀成浑圆状(图 4f),测得牌号An0.14~1.55。基质微晶隐晶质,由长英质组成霏细结构和显微微晶结构。
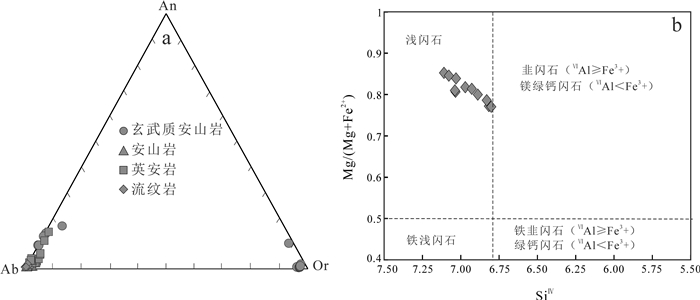
对雅满苏组钠质火山岩长石类矿物进行电子探针分析,结果列于表 1和图 5,从分析结果看,除Z4728-38和Z4728-23样品中斜长石为少量更长石外,其余为钠长石(图 5a)。
表 1 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩斜长石电子探针分析结果(%)Table 1. Electron microprobe analyses of plagioclase from the Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
![]() Figure 5. Classification of the feldspar (a, after Smith, 1974) and hornblende (b, after Leake et al., 1997) in the Zhaibeishan Na-rich volcanic rocks
Figure 5. Classification of the feldspar (a, after Smith, 1974) and hornblende (b, after Leake et al., 1997) in the Zhaibeishan Na-rich volcanic rocks角闪石电子探针结果见表 2,总体上角闪石显示出富铁(FeO=12.37% ~13.82%)、镁(MgO=13.94% ~ 15.62%)和钙(CaO=10.44%~10.99%),贫钠(Na2O= 1.06%~1.46%)和钾(K2O=0.24%~0.4%)的特征。单矿物计算结果可知,阳离子CaB=1.62~1.73,(Ca+Na)B= 1.62~1.75,(Na+K)A=0.37~0.47,根据国际矿物学会命名原则,角闪石应为钙质角闪石(CaB≥1.34,NaB < 0.67,(Ca+Na)B≥1.34),且在SiⅣ-Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)图解上,都落入到浅闪石区域(图 5b),该闪石亦为钠质火山岩系的主要产出类型。
表 2 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩角闪石电子探针分析结果(%)Table 2. Electron microprobe analyses of hornblende from the Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
4. 锆石U-Pb年代学
4.1 样品及分析方法
样品野外采自矿区地表采坑处,样重约20 kg,粉碎至80目后,采用重力和磁选方法分选出锆石,然后在显微镜下挑出实验所用锆石,锆石纯度大于99%。锆石单矿物分选工作由河北廊坊地质服务公司实验室完成。将分选出的锆石和标样一起黏在玻璃板上,用环氧树脂浇铸,待环氧树脂固化后将样品制成样品靶。制靶和阴极发光扫描电镜照相由中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所完成。SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年实验在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心完成,测试原理、流程和方法等参考Williams(1998)和Compston(1992)。在实验时尽量选择环带结构清晰以及锆石核部与边部之间的过度位置为测试点。
4.2 分析结果
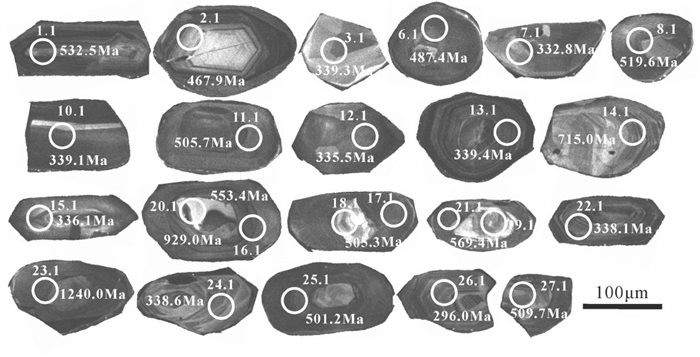
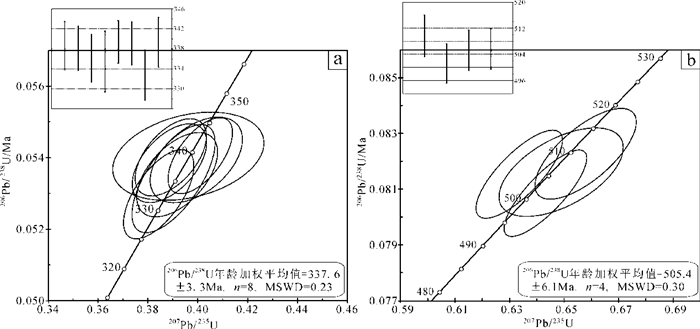
挑选出的100多颗锆石在阴极发光图像中形态均为无色透明-半透明的自形粒状、棱柱状、短柱状,粒径多在100~200 μm,大都显示出清晰的震荡韵律环带(图 6),应属岩浆锆石。对较为新鲜的钠质玄武安山玢岩样品Z5823-7的21颗锆石点进行离子探针分析,样品锆石离子探针U-Pb同位素分析数据结果见表 3。从表中可以看出,所测样品锆石U平均含量为411.49 × 10-6,Th/U比值平均为0.51。其中数据处理采用ISOPLOT3.0程序(Ludwig,2003),普通Pb采用204Pb校正。结果显示,钠质玄武安山玢岩中样品数据都在谐和线上或其附近,年龄主要集中在330 Ma和500 Ma(图 7)。其中有8个点获得206Pb/238U年龄分布在332.8~ 339.4 Ma,加权平均年龄为(337.6 ± 3.3) Ma(n=8,MSWD=0.23)(图 7a),在误差范围内一致,代表该火山岩的结晶年龄;另有4个点获得206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为(505.4 ± 6.1)Ma(n=4,MSWD=0.3)(图 7b),可能继承了中天山前寒武纪古老结晶基底的锆石。此外,在14.1、18.1、19.1、20.1、23.1测试点中分别获得零散的较老的元古宙谐和年龄,可能代表了来自元古宙的继承性锆石。
表 3 寨北山矿区钠质玄武安山玢岩锆石SHRIMPU-Pb同位素分析结果Table 3. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb isotopic data of basaltic andesitic porphyrite from the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
5. 岩石地球化学
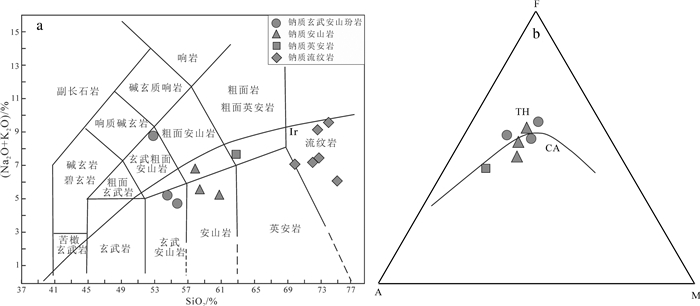
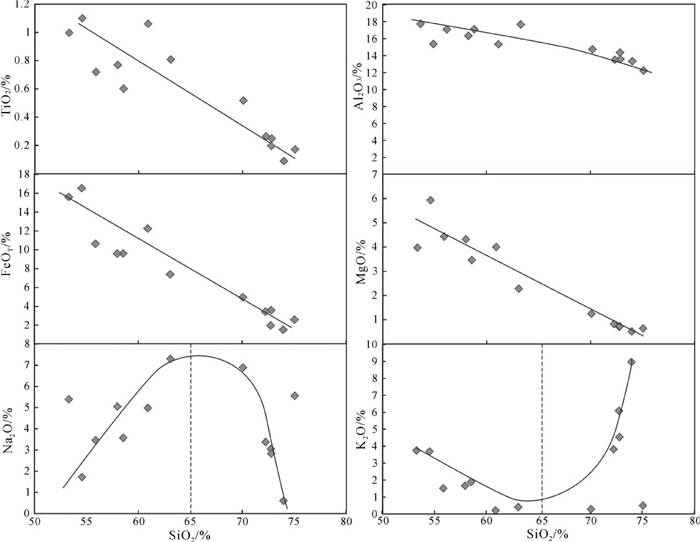
雅满苏组钠质火山岩各项主量元素氧化物含量及数值参数见表 4,可知所有样品SiO2含量在53.32%~75.06%,主体为安山岩-英安岩-流纹岩岩石组合特征,属中性-酸性岩石。样品MgO(0.51% ~5.93%,平均2.54%)、FeO(0.54% ~6.39%,平均2.84%)、MnO(0.01%~0.24%,平均0.08%)含量较低,具高铝(Al2O3=12.23%~17.75%,平均15.20%,A/ CNK=0.79~1.42,平均1.11)、低钛(TiO2=0.09% ~ 1.10%,平均0.58%)的典型俯冲消减带火山岩地球化学特征(Gill et al., 1981;Wilson et al., 1989)。岩石烧失量较高(平均为2.01%),全碱含量(Na2O+K2O)为4.97%~9.56%,其中Na2O/K2O除一个样品外,为0.47~23.68,平均7.30,具有富Na2O、贫TiO2、CaO、K2O的特征,属典型角斑岩-石英角斑岩系。在TAS图解(图 8a)中,火山岩样品大都落在亚碱性区域,在AFM图解中进一步分类,岩石属无富铁趋势的钙碱性岩石系列(图 8b)。从SiO2与部分氧化物含量Harker图解中,TiO2、Al2O3、FeOT、MgO与SiO2呈负相关关系,而Na2O、K2O与SiO2呈抛物线关系(图 9),且Na2O的最高含量接近中性岩与酸性岩的分界点(SiO2=65.00%),为钠质火山岩系的主要特征之一(宋子季等,1988)。
表 4 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩主量(%)、微量元素(10-6)地球化学数据Table 4. Major element (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
![]() Figure 8. Total alkali silica diagram (a, after Le Bas et al., 1986) and AFM diagram (b, after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) of Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
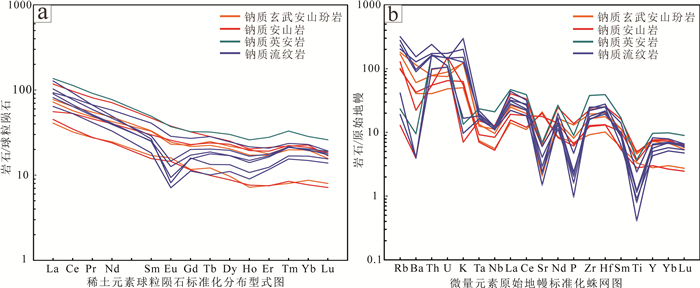
Figure 8. Total alkali silica diagram (a, after Le Bas et al., 1986) and AFM diagram (b, after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) of Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit样品稀土元素元素总量(∑REE)为55.91×10-6~ 184.11×10-6,平均为111.55×10-6;(LREE/HREE)N= 3.68~9.00,轻重稀土分馏较明显;δCe=0.94~1.05,δEu=0.38~1.11,且酸性火山岩较中性火山岩铕负异常明显(图 10a),表明斜长石在岩浆演化后期分离结晶作用明显,与微量元素Sr的亏损相吻合。在球粒陨石标准化分布图中显示轻稀土富集的右倾且重稀土略平缓的样式。在多元素原始地幔标准化图解中,雅满苏组火山岩显示大离子亲石元素(如Th、U、Rb)、LREE及Zr、Hf的富集和高场强元素(如Nb、Ta、Ti、P)相对亏损的特征(图 10b),特别是Nb、Ta和Ti的亏损,指示物源区有难熔矿物(钛铁矿、金红石或韭闪石),这些矿物通常存在于俯冲消减带中流体交代的亏损地幔中(Hawkins, 2003)。
![]() 图 10 雅满苏组钠质火山岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)与原始地幔标准化微量元素配分图(b)(球粒陨石与原始地幔数据Sun and McDonough, 1989)Figure 10. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram (b) (chondrite and primitive mantle data from Sun and McDonough, 1989) for Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation
图 10 雅满苏组钠质火山岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)与原始地幔标准化微量元素配分图(b)(球粒陨石与原始地幔数据Sun and McDonough, 1989)Figure 10. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram (b) (chondrite and primitive mantle data from Sun and McDonough, 1989) for Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation6. 讨论
6.1 成岩成矿时代
由于雅满苏组其上下亚组存在差异,前人将其解体为下部的阿奇山组和上部的雅满苏组(姬金生等,1994;罗桂昌等,1999)。罗婷等(2012)测得雅满苏成矿带东段、中段和西段的雅满苏组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄分别为(348.0±1.7) Ma、(335.9±2.4) Ma和(334.0±2.5) Ma;郑仁乔(2015)测得红云滩矿区雅满苏组石英角斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(324.1±3.1) Ma;李厚民等(2014)测定雅满苏矿区侵入到雅满苏火山岩地层中的辉绿岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄为(335± 4) Ma,同时将矿化和火山岩时代限定于335 Ma之前。本文测得雅满苏组下部玄武安山玢岩锆石UPb年龄为(337.6±3.3) Ma,与前人对该组火山岩定年结果一致,代表该区在早石炭世的火山活动。同时,笔者测得侵入到该区雅满苏组火山岩地层中的花岗岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为(334.5±2.6) Ma(未发表数据),进一步限定该火山岩的年龄。
根据矿体有选择性地呈浸染状和脉状产在玄武安山玢岩中,可以推测该铜矿床与火山岩有密切的成因关系,因此,成矿时代应不早于337 Ma。与前人研究区域上阿奇山—雅满苏成矿带和火山岩有关的铁-铜矿床的成矿时代结果一致(刘德权等,1996;郑仁乔,2015;Hou et al., 2014)。
6.2 火山岩构造背景
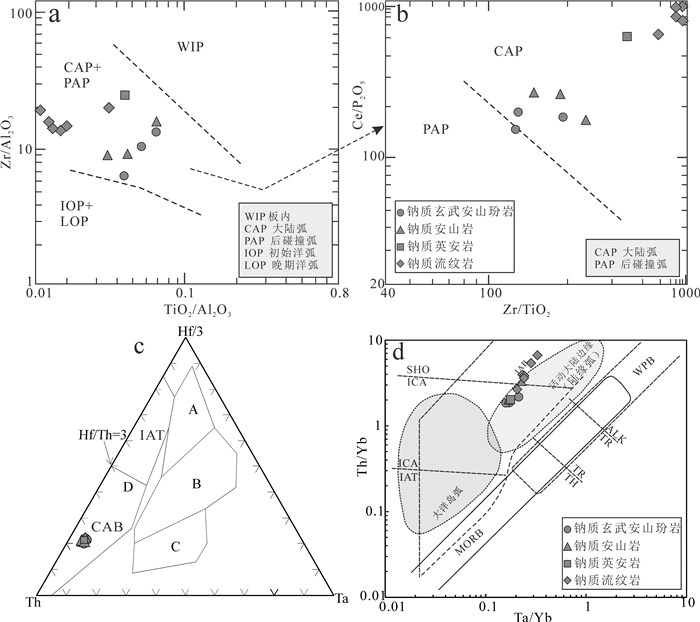
研究表明,钠质火山岩系多产于具有古老结晶基底的构造区域,且时期多处在火山岩浆活动的早—中阶段(裂谷-岛弧阶段)(姜福芝和王玉往,2005)。寨北山地区雅满苏组钠质火山岩为一套中性-酸性火山岩组合,岩石地球化学表明,该组火山岩具富钠(Na2O/K2O平均为7.30)、富铝(A/CNK=0.79~1.42,平均1.11)、贫钙、钾特征,且La/Nb=1.92~3.49(原始地幔La/Nb为0.98~1.00,岛弧岩浆La/Nb > 1,Condie, 1982),与流体参与的岛弧岩浆岩特征相似。富集轻稀土、相对亏损重稀土的稀土配分曲线、富集Th、U、Rb、LREE等大离子亲石元素和出现Ta、Nb、Ti等高场强元素的亏损(TNT异常)特征,指示与火山岛弧环境有关(赵振华,2007)。对于富钾或富钠火山岩,Muller等指出应采用其特殊判别图解(Muller et al., 1922;Muller and Groves, 1977),在Zr/Al2O3-TiO2/ Al2O3图解中(图 11a),样品都落入到大陆弧和后碰撞弧区域,进一步判别,在Ce/P2O5-Zr/TiO2图解中(图 11b),样品落入大陆弧构造区域,与微量元素Hf/3- Th-Ta和Ta/Yb-Th/Yb构造判别图一致(图 11c、11d),此外,在该组火山岩中获得一些元古代古老继承性锆石,可能为岛弧岩浆捕获的中天山古老基底锆石。综合以上表明本区钠质火山岩可能为俯冲带近大陆一侧的岛弧构造环境。
6.3 火山岩成因及与成矿关系
关于钠质火山岩系(也称为细碧角斑岩系)的成因一直存有争议,目前主要有两种主流观点:一是岩浆结晶学说(Amstutz, 1974;邓尔新,1986;夏林圻和夏祖春,1989;Smith et al., 2009),指出钠质火山岩是由一种富钠质岩浆熔融体直接结晶而成的。二是变质蚀变成因说(Smith, 1968;Cann, 1969;Coombs et al., 1970;Carmichael et al., 1974;Vallance, 1974;Seyfried and Bischoff, 1979;Hajash and Archer, 1980;Mengel et al., 1987;Engvik et al., 2008;Sheibi, 2014),指出富钠质火山岩是由普通岩浆在海底喷发后与海水相互反应,吸附钠质后经过变质或自变质作用产生。研究区雅满苏组钠质火山岩具杏仁构造、斜长石的中空骸晶及燕尾状淬火结构、角闪石和斜长石后期都受到钠长石化蚀变作用而呈包含结构或反应边结构等特点并不支持原生岩浆结晶观点,岩石中角闪石主要为浅闪石表明岩石曾经经历了一定程度的蚀变或变质作用。在矿物组合上,岩石由钠长石(包括更长石)、绿泥石、黝帘石等低变质绿片岩相矿物组成,也与含钠质岩浆直接分离结晶形成相矛盾。据地球中钠元素的分配统计研究可知,钠主要集中于海洋(约2.00%)和地壳(约2.30%)中,而地幔中钠的含量极微(< 0.90%),因此,钠质火山岩系的钠来源于海水目前已得到普遍认可。实验岩石学研究亦表明,不可能有单独的钠质玄武岩岩浆(细碧质岩浆)的存在(Yorder and Tilley, 1962),而在低温蚀变和低变质作用下,矿物重结晶作用或产生新次生矿物是存在的,代表着变质物理条件下矿物间新的平衡关系(Smith, 1968;Coombs et al., 1970),且迄今为止还未曾发现未变质的钠质火山岩系(宋志高和贾群子,1987)。本区岩石遭受了钠质交代作用和低温动力变质作用,具低温变质矿物组合(钠长石、绿泥石、绿帘石等),表明雅满苏组钠质火山岩是由岩浆变质作用产生的。
前已叙及,本区钠质火山岩可能与洋壳俯冲的靠近大陆侧形成的岩浆有成因联系,在早石炭世,古康古尔洋向南部中天山地块俯冲,安山质-流纹质火山岩可能在是俯冲带初始岛弧向成熟岛弧转化过程中的产物(郭原生等, 2000, 王焰等,2000),岩浆在海底喷出过程中,海水沿火山喷发裂隙下渗到海底岩浆喷发区域,岩浆将海水加热,并产生热对流,在此过程中岩浆与富钠的海水发生交换反应得到Na、H2O等,产生钠长石化、绿泥石化等低变质作用,形成本区的富钠质火山岩,同时海水从岩浆中活化淋滤出Cu、Fe等形成含矿物质,当温度降低等环境下在火山岩中形成浸染状矿石。随着火山岩浆的演化和喷发,提供了更多的动力和热源,促进火山岩和海水进一步反应,更多的含矿物质被淋滤出来并在火山喷发的间歇期大量逸出形成含矿热液,含矿热液沿通道上升到浅部时,由于温度下降和氧逸度的升高在适宜的位置沉淀形成本区形成脉状矿石。
7. 结论
(1)寨北山矿区发育一套从中性到酸性的钠质火山岩组合,具低MgO(0.51% ~5.93%,平均2.54%)、FeO(0.54% ~6.39%,平均2.84%)和TiO2(TiO2=0.09%~1.10%,平均0.58%),高Al2O3(Al2O3= 12.23%~17.75%,平均15.20%,A/CNK=0.79~1.42,平均1.11)以及富Na2O(Na2O/K2O平均为7.30)的特征;岩石轻、重稀土分馏较明显,总体上显示出富集大离子亲石元素而亏损高场强元素。
(2)获得钠质玄武安山玢岩中锆石U-Pb加权平均年龄为(337.6±3.3) Ma(n=8,MSWD=0.23),代表雅满苏组火山岩的年龄,同时限定成矿时代应不早于337 Ma。
(3)研究区雅满苏组钠质火山岩具杏仁构造,斜长石具中空骸晶及燕尾状淬火结构,角闪石和斜长石斑晶后期都受到钠长石交代而呈包含结构或熔蚀骸晶结构,具低变质绿片岩相矿物组成等特点,表明雅满苏组钠质火山岩可能是由岩浆与富钠的海水发生反应形成的,同时海水从火山岩浆中淋滤出含矿物质,并在适宜的位置沉淀形成本区矿床。
致谢: 野外工作中得到鑫汇公司宁福泉工程师的大力帮助;实验过程中得到张迪和毛骞老师的指导和帮助;成稿完善过程中承蒙审稿人对本文的仔细审阅和提出的宝贵修改意见,笔者在此表示诚挚的感谢。 -
图 1 中亚造山带构造简图(a,据Jahn et al., 2000)和东天山地区地质矿产简图(b,据王京彬等,2006改编)
1—新生代沉积盖层;2—二叠纪陆相火山-沉积岩系;3—石炭纪火山沉积岩系;4—奥陶—泥盆纪火山沉积岩系;5—前寒武纪变质岩;6—花岗岩类;7—金矿床;8—铜矿床;9—铜镍矿床;10—铁矿床;11—铜铁矿床;12—银多金属矿床;13—铜多金属矿床;14—铅锌矿床;15—大型矿床;16—中型矿床;17—小型矿床;18—断裂;19—推测断裂;20—剪切带;21—铁路;22—研究区. ①—康古尔断裂;②—雅满苏—苦水断裂;③—阿奇克库都克—沙泉子断裂
Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of the Central Asia Orogenic Belt (a, after Jahn et al., 2000) and geological map and deposits distribution in Eastern Tianshan Mountains (b, modified from Wang et al., 2006)
1-Meso-Cenozoic sedimentary cover; 2-Permian continental volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 3-Carboniferous volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 4-Ordovician-Devonian volcanic-sedimentary rocks; 5-Precambrian metamorphic rocks; 6-Granitoids; 7-Au deposits; 8-Cu deposits; 9-Cu-Ni sulfide deposits; 10-Fe deposits; 11-Fe-Cu deposits; 12-Ag-polymetallic deposits; 13-Cu-polymetallic deposits; 14-Pb-Zn deposits; 15-Large mineral deposits; 16-Middle mineral deposits; 17-Small mineral deposits; ; 18-Faults; 19-Inferred faults; 20-Shear zone; 21-Railway; 22-Study area ①-Kangguer Fault; ②-Yamansu Fault; ③-Aqikekuduke-Shaquanzi Fault
图 3 寨北山铜矿岩石标本和矿物镜下特征
a—侵染状矿石;b—脉状矿石;c—石英+黄铜矿脉, 黄铜矿交代黄铁矿呈交代残余结构;Ccp—黄铜矿;Qz—石英;Py—黄铁矿;Spe—镜铁矿
Figure 3. Characteristics of the rocks and microscope photographs of the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
a-disseminated ore; b-vein ore; c-quartz+chalcopyrite vein; d-quartz+chalcopyrite+pyrite vein. Pyrite replaced by chalcopyrite as metasomatic relict structure. Abbreviation:Ccp-chalcopyrite; Qz-quartz; Py-pyrite; Spe-specularite
图 4 雅满苏组钠质火山岩显微照片
a—单偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),杏仁构造,钠质斜长石中空骸晶结构;b—正交偏光,钠质玄武安山玢岩(Z4728-23),角闪石边部具有钠长石蚀变反应边,中心被钠长石交代溶蚀呈包含结构;c—正交偏光,钠质安山岩(Z4728-3),钠长石交代早期斜长石,基质碳酸盐化;d—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石聚片双晶,石英蚀变呈浑圆状;e—正交偏光,钠质英安岩(Z4728-39),钠长石具简单双晶结构,斑晶边部被熔蚀;f—正交偏光,钠质流纹岩(Z4728-16),钠长石斑晶被溶蚀成浑圆状。照片中缩写符号:Ab—钠长石;Qz—石英;Hbl—角闪石;Chl—绿泥石
Figure 4. Microphotographs for textures of the Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation
a-Plainlight, Na-Richbasaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), almond texture, central absent skeleton crystal texture in plagioclase; b-crossedpolarized light, Na-rich basaltic andesitic porphyrite (Z4728-23), The rim of the hornblende was albite alteration and the center was dissolved into poikilitic texture; c-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich andesite(Z4728-3), albite altered the early stage plagioclase, groundmass were carbonated; d-crossed-polarized light, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), polysynthetic twin, quartzs were resorbed into round shapes; e-Crossed nicols, Na-rich dacite (Z4728-39), albite twins, the rim of the phenocrysts experienced corrosion; f-Crossed nicols, Na-rich rhyolite (Z4728-16), albite phenocrysts altered into round shapes. Abbreviation: Ab-Albite; Qz-Quartz; Hbl-Hornblende; Chl-Chlorite
图 5 寨北山钠质火山岩长石(a,底图据Smith, 1974)和角闪石(b,底图据Leake et al., 1997)分类图解
Figure 5. Classification of the feldspar (a, after Smith, 1974) and hornblende (b, after Leake et al., 1997) in the Zhaibeishan Na-rich volcanic rocks
图 8 寨北山铜矿区火山岩TAS图(a,底图据Le Bas et al., 1986)与FAM图(b,底图据Irvine and Baragar, 1971)
Figure 8. Total alkali silica diagram (a, after Le Bas et al., 1986) and AFM diagram (b, after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) of Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit
图 10 雅满苏组钠质火山岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)与原始地幔标准化微量元素配分图(b)(球粒陨石与原始地幔数据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 10. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram (b) (chondrite and primitive mantle data from Sun and McDonough, 1989) for Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation
图 11 雅满苏组钠质火山岩构造环境判别图
(a、b底图据Muller et al., 1922, Muller and Groves, 1977;c底图据Wood, 1980;d底图据Pearce, 1982)
Figure 11. Discrimination diagrams for tectonic setting of Na-rich volcanic rocks from Yamansu Formation
(a, b after Muller et al., 1922, Muller and Groves, 1977; c after Wood, 1980; d after Pearce, 1982)
表 1 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩斜长石电子探针分析结果(%)
Table 1 Electron microprobe analyses of plagioclase from the Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit

表 2 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩角闪石电子探针分析结果(%)
Table 2 Electron microprobe analyses of hornblende from the Na-rich volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit

表 3 寨北山矿区钠质玄武安山玢岩锆石SHRIMPU-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 3 SHRIMP zircon U-Pb isotopic data of basaltic andesitic porphyrite from the Zhaibeishan copper deposit

表 4 寨北山矿区钠质火山岩主量(%)、微量元素(10-6)地球化学数据
Table 4 Major element (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the volcanic rocks in the Zhaibeishan copper deposit

-
Amstutz B A. 1974.Spilite and spilitic rocks[M]. Berlin, Hieceberg. New York.
Carmichael I S E, Turner F J, Verhoogen J. 1974. Igneous Petrology[M]. McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Cann J R. 1969. Spilites from the Carlsberg Gidge, Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Petrology, 10:1-19. doi: 10.1093/petrology/10.1.1
Compston W, Williams I S, Krischvink J L, Zhang Z, Guogan M A. 1992.Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 149(2):171-184. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171
Condie K C. 1982. Plate tectonics and crustal evolution(Second Edition)[M]. Pergamon Press.
Coombs D S, Horodysky R J, Naylor R S. 1970. Occurrence of prehnite-pumpellyite facies metamorphism in north marine[J]. American Journal of Science, 268:141-156. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1970AmJS..268..142C
Deng Erxin. 1986. The petrological and petrochemical characteristics of spilitic rocks and their origin in Zhonggao, Zhejiang Province[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 11(5):507-515(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198605008.htm
Dong Lianhui, Feng Jing, Zhuang Daoze, Li Fengming, Qu Xun, Liu Dequan. 2011. Discussion of metallogenic models, mineralization characteristic and main type of rich iron ore of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 29(4):416-422 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Doyle M G, Allen R L. 2003. Subsea-floor replacement in volcanichosted massive sulfide deposits[J]. Ore Geology Review, 23(3/4):183-222. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136803000350
Engvik A K, Putnis A, Gerald J D F, Austrheim H. 2008. Albitization of granitic rocks:the mechanism of replacement of oligoclase by albite[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 46(6), 1401-1415. doi: 10.3749/canmin.46.6.1401
Fang Weixuan, Gao Zhenquan, Jia Runxing, Liu Zhengtao, Li Fengshou, Xu Guoduan. 2006a. Geological exploration potentials and geochemical study on rocks and ores in Shaquanzi copper and copper-iron deposits, east Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5):1413-1424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fang Weixuan, Gao Zhenquan, Jia Runxing, Huang Zhuanying, Liu Zhengtao, Li Fengshou, Xu Guoduan. 2006b. Metallogenic background and geochemical characteristics of Lower Carboniferous volcanic rocks in No. 371-Xibeipo copper-gold mineralization belt in the Yaxi area, eastern Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(1):215-224.
Galley A G, 1993. Semi Conformable alteration zones in volcanogenic massive sulphide districts[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 48:175-200. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(93)90004-6
Gao Zhenquan. 2002. copper-gold Polymetal Metallogeny and Prospecting Systematic Engineering of East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China[D]. Central South University for Degree of Doctor, 1-189(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gill J B. 1981. Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonics[M]. SpringerVerlag, New York, 1-390.
Guo Yuansheng, Wang Jinrong, Xie Xianli, Meng Guisheng, Yang Yongjun, Tian Yuxuan. 2000. Geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of the early and middle Cambrian volcanic rocks in Baiyin mining field[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(3):337-344(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200003003.htm
Hajash A, Archer P. 1980. Experimental seawater/basalt interaction:effect of cooling[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy & Petrology, 75:1-13. doi: 10.1007/BF00371884
Han Chunming, Xiao Wenjiao, Zhao Guochun, Mao Jingwen, Li Sanzhong, Yan Zhen, Mao Qigui. 2005. Major types, characteristics and geodynamic mechanism of Upper Paleozoic copper deposits in northern Xinjiang, northwestern China[J]. Ore Geology Reciews, 28(3):308-328. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200702001044.htm
Hawkins J W. 2003. Geology of supra-subduction zones-implications for the origin of ophiolites[C]//Dilek Y and Newcomb S (eds.). Ophiolite Concept and the Evolution of Geological Thought. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 373: 227-268.
He Guoqi, Li Maosong, Liu Dequan, Tang Yanling, Zhou Ruhong. 1994. Paleozoic Crustal Evolution and Mineralization in Xinjiang of China[M]. Urumqi:Xinjiang People's Publication House, 1-437(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Tong, Zhang Zhaochong, Santosh M, John Encarnacion, Zhu Jiang, Luo Wenjuan. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of submarine volcanic rocks in the Yamansu iron deposit, Eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China:Constraints on the metallogenesis[J]. Ore Geology Review, 56:487-502. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.03.008
Huang Xiaowen, Qi Liang, Wang Yichang, Liu Yingying. 2014. ReOs dating of magnetite from the Shaquanzi Fe-Cu deposit, eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 44(4):605-616 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4660-z
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8:523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
Jahn B M, Wu Fuyuan, Chen Bin. 2000. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic belt and continental growth in the phanerozoic. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh:Earth Sciences, 91:181-193. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007367
Jiang Fuzhi. 2001. Bimodal Volcanic Association and Massive Sulfide Deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 20(4):331-338 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200104006
Jiang Fuzhi, Qin Kezhang, Fang Tonghui, Wang Shulai. 2002. Types, geological characteristics, metallogenic, regularity and exploration target of irondeposits in Eastern Tianshan Mountains[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4):379-383 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Fuzhi, WangYuwang. 2005. Marine Volcanic Rocks and Related Metallic Ore Deposits[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 1-248 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ji Jinsheng, Tao Hongxiang, Zeng Zhangren, Yang Xingke. 1994. Geology and Mineralization of the Kangguertage Gold Metallogenic Belt inEastern Tianshan[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
Leake B E, Woolley A R, Arps C E S, Birch W D, Gilbert M C, Grice J D, Hawthorne E, Kato A, Kisch H J, Krivovichev V G, Linthout K, Laird J, Mandarino J, Nickel E H, Rock N M S, Schumacher J C, Smith D C, Stephenson N C N, Ungaretti L, Whittaker E J W, Youzhi G. 1997. Nomenclature of amphiboles Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names[J]. European Journal Mineralogy, 9(3):623-651. doi: 10.1127/ejm/9/3/0623
Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A, Zanettin P. 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkalisillica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27:745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
Lei Ruxiong, Wu Changzhi, Zhang Zunzhong, Gu Lianxing, Tang Junhua, Li Guangrong. 2013. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significances ofthe Yamansubei pluton in eastern Tianshan, Northwest China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(8):2653-2664 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201308003.htm
Lentz DR. 1998. Petrogenetic evolution of felsic volcanic sequences associated with Phanerozoic volcanic-hosted massive sulphide systems:The role of extensional geodynamics[J]. Ore Geology Review, 12(5):289-327. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(98)00005-5
Li Houmin, Ding Jianhua, Li Lingli, Yao Tong. 2014. The genesis of the skarn and the genetic type of the Yamansu iron deposit, Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12):2477-2489(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95783X/2015S1/75878866504849538349555151.html
Liu Dequan, Tang Yanling, Zhou Ruhong. 1996. Metallogenic series types of ore deposits in Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 15(3):207-215(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ603.001.htm
Ludwig K R. 2003. Using ISOPLOT/Ex:A Geochronological toolkit forMicrosoft excelversion 3.0[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 1-40.
Luo Guichang, Yang Xingke, Cheng Hongbin. 1999. Establish of lower Carboniferous Aqishan Formation in Jueluoyage zone of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Xi'an engineering University, 21:39-44(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XAGX1999S1010.htm
Luo Ting, Liao Qunan, Chen Jiping, Zhang Xionghua, Guo Dongbao, Hu Zaochu. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Volcanic Rocks from Yamansu Formation in the Eastern Tianshan, and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geoscience, 37(6):1338-1352 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201206024
Mengel K, Borsuk A M, Gurbanov A G, Wedepohl K H, Baumann A, Hoefs J. 1987. Origin of spilitic rocks from the southern slope of the Greater Caucasus[J]. Lithos, 20(2):115-133. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(87)90002-8
Muller D, Rock N M S, Groves D I. 1922. Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks from different tectonic setting:a plot study[J]. Mine. Petrology, 46:259-289. doi: 10.1007/BF01173568
Muller D, Groves D I. 1997. Pottassic Igneous Rocks and Associated Gold-copper Mineralization[M]. Berlin: Springer, 11-40.
Oliver N H S, Cleverley J S, Mark G, Pollard P J, Fu B, Marshall L J, Bastrakov E N, Williams P, Nemchin A A, Baker T. 2004. Modeling the role of sodic alteration in the genesis of iron oxidecopper-gold deposits, eastern mount Isa block, Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 99(99), 1145-1176. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=econgeo&resid=99/6/1145
Pearce J A. 1982. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorpe R S, Andesits. Chichester: Wiley, 525-548.
Qin Kezhang, Fang Tonghui, Wang Shulai, Zhu Baoqing, Feng Yimin, Yu Haifeng, Xiu Qunye. 2002. Plate tectonics division, evolution and metallogenic settings in eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4):302-308 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Seyfried W E, Bischoff J E. 1979. Low temperature basalt alteration by seawater, an experimental study at 70℃ and 150℃[J]. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta, 43:1937-1947. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90006-1
Sheibi M. 2014. Chemistry of minerals and mass changes of elements during sodic-calcicalteration of the Panj-Kuh intrusive body(Damghan, Iran)[J]. Jour. Geope., 4(1):87-102.
Smith D J, Petterson M G, Saunders A D, Millar I L, Jenkin G R T, Toba T, Naden J, Cook J M. 2009. The petrogenesis of sodic island arc magmas at savo volcano, solomon islands[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 158(6), 785-801. doi: 10.1007/s00410-009-0410-9
Smith JV. 1974.Feldspar mineral 2: Chemical and Textural Properties[M]. Berlin, Springer, 1-690.
Smith R E. 1968. Zone of progressive regional burial metamorphism in part of Tasman geosyncline, eastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 10:143-163. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/31178460_Zones_of_Progressive_Regional_Burial_Metamorphism_in_Part_of_the_Tasman_Geosyncline_Eastern_Australia
Song Anjiang, Zhu Zhixin, Shi Ying, Li Shenghu. 2006. SHRIMP UPb dating of zircons from the Tugutu Bulak Formation in the western segment of the Aqikkuduk fault in the East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(8):953-956(in Chinese with English abstract).
Song Zhigao, Jia Qunzi. 1987. On the fabric, mineral assemblages and metamorphic origin of spilite[J]. Bulletin of Xi'an Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 19:31-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK198705001.htm
Song Ziji, Zhang Weiji, An Sanyuan. 1988. On the characteristic of volcanic rocks and its environment formed in graben zone of northern part of the north Qinling mountains in Early Cenozoic era[J]. Bulletin of Xi'an Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 24:5-63 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XBFK198824002.htm
Su Chunqian, Jiang Chaiyi, Xia Mingzhe, Wei Wei, Pan Rong. 2009. Geochemistry and zircons SHRIMP U-Pb age of volcanic rocks of Aqishan Formation in the eastern area of north Tianshan, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(4):901-915 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB200904014.htm
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematicof oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. In Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Sun Zhiyuan, Long Lingli Wang Yuwang, Wang Jingbin, Du Yangsong, Zhao Lutong, Xie Hongjing, Li Dedong, Shi Yu. 2016. Geochemical characteristics of the volcanic rocks of Zhaibeishan Copper deposit in eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang and its geological implication[J]. Mineral Exploration, 7(2):248-260(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201602003.htm
Tang Junhua, Gu Lianxing, Zhang Zunzhong, Wu Changzhi, San Jinzhu, Wang Chuansheng, Liu Sihai, Li Guangrong. 2008. Peraluminous granite in Huangshan-Jingerquan area of eastern Tianshan:Geochemistry, mineralogy and geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(5):921-946(in Chinese with English abstract).
Vallance T G. 1974. Spilitic Degradation of a Tholeiitic Basalt[J]. Journal of Petrology, 15(1):79-96. doi: 10.1093/petrology/15.1.79
Wang Jingbin, Wang Yuwang, He Zhijun. 2006. Ore deposits as a guide to the tectonic evolution in the East Tianshan Mountains, NW China[J]. Geology in China, 33(3):461-469 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200603001.htm
Wang Longsheng, Li Huaqin, Chen Yuchuan, Liu Dequan. 2005a. Geological feature and mineralization epoch of Bailingshan iron deposit, Hami, Xinjiang, China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(3):264-269 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200503004.htm
Wang Longsheng, Li Huaqin, Liu Dequan, Chen Yuchuan. 2005b. Geological characteristics and mineralization epoch of Weiquan silver (copper) deposit, Hami, Xinjiang, China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(3):280-284 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200503006.htm
Wang Yan, Qian Qing, Liu Liang, Zhang Qi. 2000. Major geochemical characteristics of bimodal volcanic rocks in different geochemical environments[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(2):169-173(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1471494
Williams I S. 1998. U-Th-Pb geochronology by ionmicroprobe[C]//McKibben M A, Shanks W C, Ridley W I (eds.). Applications of Microanalytical Techniques to Understanding Mineralizing Processes.Reviews in Economic Geology, 7: 1-35.
Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenssis[J]. London:Unwin Hyman. https://www.springer.com/la/book/9780412750809
Windley BF, Alexeiev D, Xiao WJ, Kröner A, Badarch G. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 164:31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Wood D A. 1980. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonic magmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary volcanic province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50:11-13. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
Wu Changzhi, Zhang Zunzhong, Zaw K, Della-Pasque F, Tang Junhua, Zheng Yuanchuan, Wang Chuansheng, San Jinzhu. 2006. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significances of Hongyuntan granitoids in the Qoltag area, Eastern Tianshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5):1121-1134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun. 1989. Newly evidences of magma originating of spilite-pristine Na-rich magma inclusions are found in the clinopyroxene phenocryst in pyroxene-bearing spilite porphyrite from the Low Paleozoic Erathem in northern Qilianshan[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 13:1010-1013(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao Xuchang, Tang Yaoqing, Feng Yimin, Zhu Baoqing, Li Jinyi, Zhao Min. 1992. Tectonic Evolution of the Northern Xinjiang and Its Adjacent Regions[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-167(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao Yu. 2003. The geological characteristics and prospecting orientation in Shaquanzi copper deposit of Hami, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 97(17):345-347 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Lulu, Chai Fengmei, Li Qiang, Zeng Hong, Geng Xinxia, Xia Fang, Denggang. 2014.Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of volcanic rocks from the Shaquanzi Fe-Cu deposit in East Tianshan Mountains and their geological significance[J]. Geology in China, 41(6):1771-1790 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Shiqi, Zhao Tongyang, Feng Jing, Gao Yongfeng, Tian Jiangtao, Yang Zaifeng, Liu Dequan. 2011. Study on regional metallogenic regularity of marine volcanic type iron ore in the East Tianshan of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 29(2):173-177 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Xingke, Ji Jinsheng, Zhang Lianchang, Zeng Zhangren. 1998. Basic features and gold prognosis of the regional ductile shear zone in eastern Tianshan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 22(3):209-218 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yorder H S, Tilley C E. 1962. Origin of basalt magama:Aexperimental study of natural and synthetic system[J]. J. Petrol, 3:43-530. doi: 10.1093-petrology-3.3.342/
Yuan Feng, Zhou Taofa, Zhang Dayu, Fan Yu, Liu Shuai, Peng Mingxing, Zhang Jiandian. 2010. Source, evolution and tectonic setting of the basalts from the native copper mineralization area in eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2):533-546 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-ysxb201002017.htm
Zhang Dayu. 2012. Petrogenesis, Mineralization and Geodynamic Evolution in Jueluotage Area, Eastern Tianshan, Northwest China[D]. Hefei University of Technology for Degree of Doctor, 1-217 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Zhenhua. 2007. How to use the trace element diagrams to discriminate tectonic setting[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 31(1):92-103(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200701012.htm
Zheng Renqiao. 2015. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Hongyuntan Iron Deposits in the Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences for Master Degree, 1-102(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Jiyuan, Zhang Bin, Zhang Chaowen, Wei Guanyi, Lu Yan, Xia Jun, Cui Bingfang, Wang Chongyun, Li Baohua. 1996. Geology of the Silver, Rhenium-Molybedum, Gold and Copper Deposits in the Eastern Tianshan and Its Adjacent Regions[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 62-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Taofa, Yuan Feng, Zhang Dayu, Fan Yu, Liu Shuai, Peng Mingxing, Zhang Jiandian. 2010. Geochronology, tectonic setting and mineralization of granitoids in Jueluotage area, Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2):478-502 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1471237
邓尔新. 1986.浙江省中岙细碧岩类岩石学、岩石化学特征及其成因[J].地球科学——武汉地质学院学报, 11(5):507-515. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198605008.htm 董连慧, 冯京, 庄道泽, 李凤鸣, 屈迅, 刘德权. 2011.新疆富铁矿成矿特征及主攻类型成矿模式探讨[J].新疆地质, 29(4):416-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2011.04.012 方维萱, 高珍权, 贾润幸, 刘正桃, 李丰收, 徐国端.2006a.东疆沙泉子铜和铜铁矿床岩(矿)石地球化学研究与地质找矿前景[J].岩石学报, 22(5):1413-1424. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605030 方维萱, 高珍权, 贾润幸, 黄转盈, 刘正桃, 李丰收, 徐国端. 2006b.东疆雅西371-西北坡铜金矿化带下石炭统火山岩地球化学特征与成矿背景[J].岩石学报, 22(1):215-224. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200601021 高珍权. 2002.东天山铜金多金属成矿学及找矿系统工程学[D].博士学位论文, 长沙: 中南大学, 1-189. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10533-2004116213.htm 郭原生, 王金荣, 谢宪丽, 孟桂生, 杨永军, 田玉轩. 2000.白银厂矿田早中寒武世火山岩地球化学及成因分析[J].岩石学报, 16(3):337-344. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200003004 何国琦, 李茂松, 刘德权, 唐延龄, 周汝洪. 1994.中国新疆古生代地壳演化与成矿[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆人民出版社, 1-437. 黄小文, 漆亮, 王怡昌, 刘莹莹.2014.东天山沙泉子铜铁矿床磁铁矿Re-Os定年初探[J].中国科学:地球科学, 44(4):606-616. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JDXK201404004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 姜福芝. 2001.双峰式火山岩与块状硫化物矿床[J].矿床地质, 20(4):331-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.04.006 姜福芝, 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来. 2002.东天山铁矿类型、地质特征成矿规律与找矿方向[J].新疆地质, 20(4):379-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.019 姜福芝, 王玉往. 2005.海相火山岩与金属矿床[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1-248. 姬金生, 陶洪祥, 曾章仁, 杨兴科.1994.东天山康古尔塔格金矿带地质与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社. 雷如雄, 吴昌志, 张遵忠, 顾连兴, 唐俊华, 黎广荣. 2013.东天山雅满苏北岩体的年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 29(8):2653-2664. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201308003 李厚民, 丁建华, 李立兴, 姚通. 2014.东天山雅满苏铁矿床矽卡岩成因及矿床成因类型[J].地质学报, 88(12):2477-2489. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201412024 刘德权, 唐延龄, 周汝洪. 1996.中国新疆矿床系列类型[J].矿床地质, 15(3):207-215. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/93610X/19961503/2144710.html 罗桂昌, 杨兴科, 程宏宾. 1999.新疆觉罗塔格地区下石炭统阿奇山组的确立[J].西安工程学院报, 21:39-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xagcxyxb1999Z1011 罗婷, 廖群安, 陈继平, 张雄华, 郭东宝, 胡兆初. 2012.东天山雅满苏组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].地球科学, 37(6):1338-1352. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201206024 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 朱宝清, 冯益民, 于海峰, 修群业. 2002.东天山板块构造分区、演化与成矿地质背景研究[J].新疆地质, 20(4):302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.002 宋安江, 朱志新, 石莹, 李生虎. 2006.东天山阿其克库都克断裂带西段土古土布拉克组锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年[J].地质通报, 25(8):953-956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.08.010 宋子季, 张维吉, 安三元. 1988.北秦岭北部早古生代断陷带古海相火山岩特征及其形成环境[J].西北地质科学, (4):4-63. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198800007004.htm 宋志高, 贾群子. 1987.论细碧岩的岩石组构、矿物组合和变质成因[J].中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所所刊, 19:31-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFK198705001.htm 苏春乾, 姜常义, 夏明哲, 魏巍, 潘荣. 2009.北天山东段阿奇山组火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年龄[J].岩石学报, 25(4):901-915. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200904014 孙志远, 龙灵利, 王玉往, 王京彬, 杜杨松, 赵路通, 解洪晶, 李德东, 石煜. 2016.新疆东天山寨北山铜矿区火山岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J].矿产勘查, 7(2):248-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2016.02.002 唐俊华, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 三金柱, 汪传胜, 刘四海, 黎广荣. 2008.东天山黄山-镜儿泉过铝花岗岩矿物学、地球化学及年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 24(5):921-946. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200805001 王京彬, 王玉往, 何志军. 2006.东天山大地构造演化的成矿示踪[J].中国地质, 33(3):461-469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.002 王龙生, 李华芹, 陈毓川, 刘德权. 2005a.新疆哈密百灵山铁矿地质特征及成矿时代[J].矿床地质, 24(3):264-269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200503005 王龙生, 李华芹, 刘德权, 陈毓川.2005b.新疆哈密维权银(铜)矿床地质特征和成矿时代[J].矿床地质, 24(3):280-284. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200503007 王焰, 钱青, 刘良, 张旗. 2000.不同构造环境中双峰式火山岩的主要特征[J].岩石学报, 16(2):169-173. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200002004 吴昌志, 张遵忠, Zaw K, Della-PasqueF, 唐俊华, 郑远川, 汪传胜, 三金柱. 2006.东天山觉罗塔格红云滩花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 22(5):1121-1134. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605006 夏林圻, 夏祖春. 1989.细碧岩岩浆成因的最新证据——北祁连山下古生代辉石细碧玢岩单斜辉石斑晶中发现原生富钠质岩浆包裹体[J].科学通报, 34(13):1010-1013. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB198913015.htm 肖序常, 汤耀庆, 冯益民, 朱宝清, 李锦轶, 赵民. 1992.新疆北部及邻区大地构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-167. 肖昱. 2003.新疆哈密市沙泉子铜矿地质特征及找矿方向[J].矿产与地质, 97(17):345-347. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=KCYD2003S1023&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 徐璐璐, 柴凤梅, 李强, 曾红, 耿新霞, 夏芳, 邓刚.2014.东天山沙泉子铁铜矿区火山岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].中国地质, 41(6):1771-1790. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.002 徐仕琪, 赵同阳, 冯京, 高永峰, 田江涛, 杨在峰, 刘德权. 2011.东天山海相火山岩型铁矿区域成矿规律研究[J].新疆地质, 29(2):173-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2011.02.011 杨兴科, 姬金生, 张连昌, 曾章仁. 1998.东天山大型韧性剪切带基本特征与金矿预测[J].大地构造与成矿学, 22(3):209-218. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3153888 袁峰, 周涛发, 张达玉, 范裕, 刘帅, 彭明兴, 张建滇. 2010.东天山自然铜矿化带玄武岩的起源、演化及成岩构造背景[J].岩石学报, 26(2):533-546. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201002015 张达玉. 2012.新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区成岩成矿作用及地球动力学过程[D].博士学位论文, 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 1-217. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10359-1013259645.htm 张招崇, 柴凤梅, 谢秋红. 2016.热幔-冷壳背景下的高角度俯冲:海相火山岩型铁矿的形成[J].中国地质, 43(2):367-379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.001 赵振华. 2007.关于岩石微量元素构造环境判别图解使用的有关问题[J].大地构造与成矿学, 31(1):92-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.01.011 郑仁乔. 2015.新疆东天山红云滩铁矿床地质特征与矿床成因研究[D].博士学位论文, 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-102. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391527.htm 周济元, 张斌, 张朝文, 卫管一, 陆彦, 夏军, 崔炳芳, 王崇云, 李保华.1996.东天山古大陆及其边缘银、铼钼、金和铜矿地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 62-63. 周涛发, 袁峰, 张达玉, 范裕, 刘帅, 彭明兴, 张建滇. 2010.新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区花岗岩类年代学、构造背景及其成矿作用研究[J].岩石学报, 26(2):478-502. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201002012 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. Zhiyuan Sun,Wang Jingbin,Yuwang Wang,Lingli Long,Zhaohua Luo,Xiaohua Deng,Qitao Hu,Menglong Wang. Sodium-rich volcanic rocks and their relationships with iron deposits in the Aqishan-Yamansu belt of Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Geoscience Frontiers. 2020(02): 697-713 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 张鑫,聂逢君,张树明,张成勇,杨彦波,乔海明,刘治国,伍群. 新疆十红滩铀矿床西山窑组物源分析:Pb同位素组成的制约. 矿物学报. 2019(02): 201-210 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 龙灵利,王京彬,王玉往,邓小华,毛启贵,孙燕,孙志远,张忠义. 东天山古弧盆体系成矿规律与成矿模式. 岩石学报. 2019(10): 3161-3188 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨永春,余君鹏,赵得龙,李生栋,刘家军,王学银,王小强,孔维琼,王作刚. 甘肃省滴水山金矿区火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学特征及其形成的构造背景. 中国地质. 2019(06): 1454-1480 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 龙灵利,王京彬,王玉往,孙志远,赵路通,石煜. 东天山寨北山热液脉状铜矿地质特征、成矿时代及矿床成因初探. 矿产勘查. 2018(12): 2282-2291 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: