Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and genesis of acid intrusive rocks in the Yuejinshan skarn type copper-gold deposit, Wandashan block
-
摘要:
跃进山小型矽卡岩型铜金矿床位于完达山地体西南部,矿体主要赋存于矽卡岩、花岗斑岩及其构造裂隙中,呈扁豆状或脉状。本文对矿区花岗闪长岩和花岗斑岩进行锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究,以了解矿床形成时代、成岩(矿)构造背景及矿床成因。测年结果表明,花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩成岩年龄分别为(115.8±1.0)Ma和(126.9±1.7)Ma,铜金矿化时代与花岗斑岩成岩时代基本一致,为早白垩世晚期。岩石地球化学研究表明,花岗闪长岩属过铝质钙碱性系列岩石,稀土配分模式图为轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,具较强的铕负异常,无铈异常,岩浆主要来源于壳源物质;花岗斑岩属过铝质钙碱性系列岩石,轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损,具弱铕负异常,无铈异常,相对富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、K、Sr)和不相容元素(U、Th),亏损高场强元素(Ta、Nb、P、Ti)和HREE,岩浆来源于壳幔物质混合源区,形成于碰撞后构造环境,成岩成矿作用与太平洋板块强烈俯冲作用后的伸展体制密切相关。
Abstract:Located in the southwest part of the Wandashan block, the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit is a skarn type deposit, and its orebodies are hosted in skarns, granite porphyries and the tectonic fractures. The orebodies show lenticular or veined forms. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical data are reported for granite porphyries and granodiorites in the Yuejinshan coppergold deposit in order to constrain its formation time, petrogenesis and the minerogenetic geotectonic background. The zircon LAICP-MS U-Pb age dating results show that the petrogenic ages of granite porphyries and granodiorites respectively are(115.8±1.0) Ma and(126.9 ±1.7)Ma respectively, and the copper-gold mineralization age is consistent with petrogenetic age of granite porphyry. Geochemical study indicates that the granodiorites are peraluminous calc-alkaline granite. The chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granodiorites display LREE enrichment and HREE depletion, with a distinct Eu anomaly, and their magma came from the lower crust. The granite porphyries belong to peraluminous calc-alkaline granite. The REE patterns show that granite porphyries exhibit pronounced LREE enrichment and HREE depletion, enrichment of large-ion lithosphile elements (Rb, Ba, K, Sr) and incompatible elements (U, Th), and depletion of high field-strength elements (Ta, Nb, P, Ti) and HREE. The magma of granite porphyries came from crust-mantle mixture, and the copper-gold deposit formed in the collision of post-collision extensional tectonic setting. The metallogenic materials formed intermediate-acid magma heat source, and magmatism and mineralization took place in the extensional tectonics after the Pacific plate subduction.
-
1. 引言
完达山地块位于中国东北地区东部,是完达山—锡霍特—阿林超地体在中国境内的出露部分(张国宾,2014),为中国东部唯一的中生代海相地层发育区(周建波等,2005;田东江等,2006)。中三叠世以前,完达山地块位于赤道附近,早—中侏罗世迅速向中高纬度迁移,中—晚侏罗世时位于佳木斯地块东缘,并于早白垩世早期逆冲于佳木斯地块之上(Kirillova, 2005, 2005;Wu et al., 2011),其主体为太平洋板块俯冲拼贴增生杂岩体(Kojima, 1987, 1989;Zheng et al., 1990)。在晚中生代晚期,完达山地块处于碰撞后伸展环境,地壳伸展减薄,加厚岩石圈发生拆沉,软流圈物质上涌,与地壳物质发生部分熔融形成富含Au、Cu、Fe等成矿元素的酸性岩浆,成矿岩浆在侵位或喷出地表过程中,物理化学条件改变,成矿元素大量富集形成了一系列的金、银、铜、铁等矿床(点)(张国宾,2014;王庆磊等,2015),如:跃进山铜金矿床、四平山金矿床、先锋北山金矿床、258高地金矿床、358高地金矿床、蛤蟆河金矿点、宝丰村金矿点和龙间山金矿点等(李光辉,2011;王庆双等,2015;韦延兰等,2015)。其中,跃进山铜金矿床位于完达山地块西南部,为一座小型的矽卡岩型矿床,在研究区内具有重要的研究意义。张国宾(2014)研究表明跃进山花岗闪长岩形成时代为(129.1±0.8)Ma,形成于碰撞后构造背景;韦延兰等(2015)研究表明跃进山铜金矿体赋存于矽卡岩,花岗斑岩成岩时代为(109.17±0.91)Ma,形成于岛弧构造背景;曾振等(2017)研究表明跃进山矿区内辉长岩形成时代为(287±2)Ma。总之,前人对跃进山矿床地质特征、花岗斑岩、花岗闪长岩和辉长岩成岩时代、构造背景进行初步探讨,形成了初步共识,但花岗斑岩、花岗闪长岩与成矿关系,以及矿床成矿构造背景还存在争议。基于此,笔者在详实的野外勘查基础上,对跃进山铜金矿床地质特征、酸性侵入岩岩石地球化学特征和锆石U-Pb同位素年龄进行了分析和研究,探讨矿区花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩与成矿关系、成岩(矿)时代、成岩(矿)地球动力学背景,为矿区的进一步研究奠定了基础,同时为国内外地质工作者寻找类似矿床提供借鉴。
2. 矿区地质特征
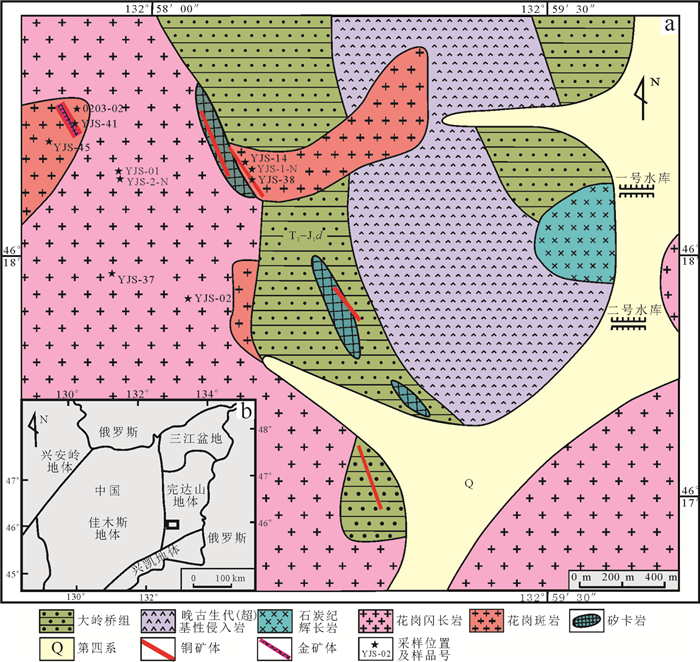
跃进山铜金矿床位于黑龙江省宝清县,地处密山—敦化断裂与大和镇断裂分割成的完达山地体西南端。区内出露地层主要为上三叠统—下侏罗统大岭桥组(T3-J1d)和第四系。大岭桥组地层呈单斜构造出露,走向北西向,倾向北东向,倾角为40°~ 55°,岩性主要为石英斜长角闪片岩和黑云石英片岩。由于后期岩浆侵入,地层被岩浆岩侵入体肢解成狭长带状或不规则状的块体,矽卡岩发育,以石榴子石矽卡岩和阳起石矽卡岩为主(图 1)。
区域断裂构造较为发育,主要以北西向和北东向断裂构造为主。北西向断裂构造为矿区的控矿构造,铜金矿化带与北西向构造平行分布,北东向构造和北西向构造交汇处,矿体具有膨大现象;北东向构造形成时间晚于北西向构造,在成矿后期将矿化带错断,但断距不大。
区内岩浆岩极为发育,主要有晚古生代透闪石化蛇纹石化橄榄岩、辉长岩、辉石岩和晚中生代花岗闪长岩、花岗斑岩和闪长玢岩等。晚古生代透闪石化蛇纹石化橄榄岩、辉长岩、辉石岩为蛇绿岩的重要组成部分;晚中生代花岗闪长岩、花岗斑岩和闪长玢岩等为成矿提供了成矿物质和成矿热液来源(张国宾,2014)。
跃进山铜金矿床为一座小型矽卡岩型矿床,铜金矿体主要赋存于矽卡岩内,其次产于花岗斑岩和构造裂隙中。区内共圈出铜(金)矿化带3条。Ⅰ号矿化带位于矿区北部,长约3000 m,宽100 m,可进一步划分为南北两个带。北带出露岩性为黑云石英片岩、石英角闪片岩和花岗斑岩,包含有4条矿体,矿体呈脉状或扁豆状,走向为北西向,倾向为50°~ 60°,倾角为45°~50°,其中Ⅰ-1、Ⅰ-2号矿体为盲矿体,除Ⅰ-4号矿体赋存于矽卡岩带中,其余3条矿体主要赋存于花岗斑岩中。南带出露岩性主要为绿泥石云母片岩及大理岩,目前已发现铜矿体2条,矿体长100~150 m,厚度平均为5.40~7.60 m。Ⅰ号矿化带的铜矿(化)体中普遍伴生有金矿化,Ⅰ号矿化带中共圈出金(化)矿体4条,Ⅰ-Au-1号金矿体赋存于花岗斑岩中,长约为100 m,斜深为20 m,平均厚度为4.38 m,金平均品为2.53×10-6;Ⅰ-Au-2号金矿化体赋存于矽卡岩中,长约为50 m,斜深为50 m,平均厚度为3.75 m,金平均品位0.86×10-6;Ⅰ-Au-3号金矿化体赋存于Ⅰ-3号铜矿体中,长约为50 m,斜深为150 m,平均厚度为4.9 m,金平均品位为0.74×10-6;Ⅰ-Au-4号金矿化体赋存于矽卡岩与花岗斑岩中,长约为50 m,斜深为20 m,平均厚度为3.00 m,金平均品位为3.83×10-6。Ⅱ号矿化带位于矿区中部,长约为2000 m,宽约为30 m,赋存于绿泥黑云母片岩、绿泥黑云石英片岩和花岗斑岩,钻孔中见铜矿化,但未发现矿体。Ⅲ号矿化带位于矿区西南部,长约为1200 m,宽约为20 m,岩性主要为石英角闪片岩、黑云石英片岩和矽卡岩。
矿石类型复杂,以原生矿石为主,局部含有氧化矿石。原生矿石包括浸染状、细(网)脉状矽卡岩型铜矿石。原生矿石中金银矿物多成半自形粒状、团斑状结构,斑杂状、细脉状和块状构造。金属矿物有斑铜矿、黄铜矿、自然铜、蓝铜矿、赤铜矿、黄铁矿、辉铜矿、辉钼矿和磁铁矿等。脉石矿物为阳起石、透闪石、辉石、石榴石、黑柱石和石英等。根据矿石矿物共生组合关系和矿石结构构造特征,可将跃进山金矿区成矿作用划分为矽卡岩化阶段、硫化物热液阶段和次生氧化阶段。矽卡岩化阶段主要形成磁铁矿,硫化物热液阶段主要形成黄铜矿、斑铜矿、蓝铜矿、辉铜矿、黄铁矿和辉钼矿等,次生氧化阶段形成褐铁矿、孔雀石、铜蓝、黄钾铁矾等。
3. 岩体地质和岩石学
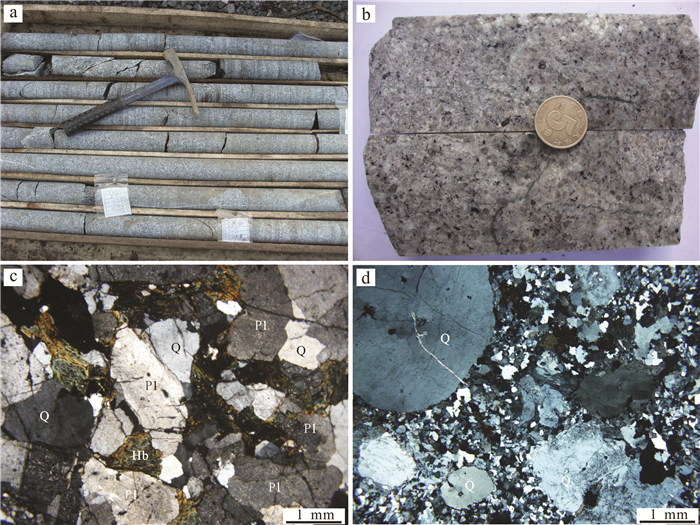
完达山地块出露酸性侵入岩体主要有哈蚂河岩体、太平村岩体、三元坝岩体、蛤蟆通岩体和尖山子岩体。其中,蛤蟆通岩体位于宝清县蛤蟆通水库附近,呈岩基状,北西向展布,出露面积约为150 km2,是完达山地块第二大的酸性侵入岩体。主要岩石类型为花岗闪长岩和二长花岗岩,其次为花岗斑岩。跃进山矿区侵入岩正是蛤蟆通岩体的一部分,出露岩性主要为花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩(图 2a、b)。
花岗斑岩新鲜面为灰白-浅肉红色,斑状结构,块状构造;斑晶主要为石英(8%)、斜长石(4%)、钾长石(3%)等,粒径在0.5~3.5 mm,斑晶交代溶蚀,具有较窄的反应边,局部可见钾长石交代石英形成显微文象结构;基质为显微细粒结构,主要由细粒石英、斜长石及钾长石组成,含量约为85%(图 2c)。花岗闪长岩为中细粒结构,块状构造,主要矿物为石英、碱性长石、斜长石、黑云母;石英为灰白色、粒状,油脂光泽,无解理,干涉色一级黄白,粒径在0.5~2.5 mm,含量约为25%;斜长石为板柱状,聚片双晶发育,粒径在0.5~3.0 mm,含量约为45%;碱性长石以正长石为主,粒径为0.3~2.0 mm,含量约为15%;黑云母为片状,红褐色-棕黄色多色性,粒径为0.5~ 1.5 mm,含量约为15%(图 2d)。
4. 样品准备及分析
锆石制靶、阴极发光(CL)图像采集、U-Pb年龄测定在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。对制成靶的锆石抛光后,进行透视光、反射光及阴极发光观察和图像采集,观测锆石内部结构,锆石样品测定中时采用30 μm的激光术斑。数据测试使用德国Lambda Physik公司生产的ComPex102型ArF准分子激光器(波长193 nm)和Shield Torch的Agilient 7500a ICP-MS仪器,用高纯的He气作为剥蚀物质的载体,用人工合成硅酸盐物质NIT610进行仪器优化,用哈佛大学国际标准锆石91500校正剥蚀、传输和离子化过程中同位素分馏和质量歧视效应。年龄计算与谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot程序完成(Yuan et al., 2004)。
全岩样品主微量元素分析测试工作在中国地质科学院应用地球化学重点开放实验室完成。主量元素使用熔片法X-射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测试,分析准确度和精度优于5%;微量元素及稀土元素采用酸溶法制备样品,在ICP-MS上获取数据,测试准确度和精度优于10%;烧失量采用重量法(GR)测试;Fe2O3、FeO采用容量法(VOL)测试;As、Sb采用氢化物-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS)测试。
5. 分析结果
5.1 锆石U-Pb同位素
选取矿区北部含矿花岗斑岩(YJS-1-N)和矿区西部大面积出露的花岗闪长岩(YJS-2-N)进行锆石U-Pb同位素测定。所测岩石样品的LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果见表 1。
表 1 跃进山铜金矿区花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS data for the granite porphyry and granodiorite in the the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit
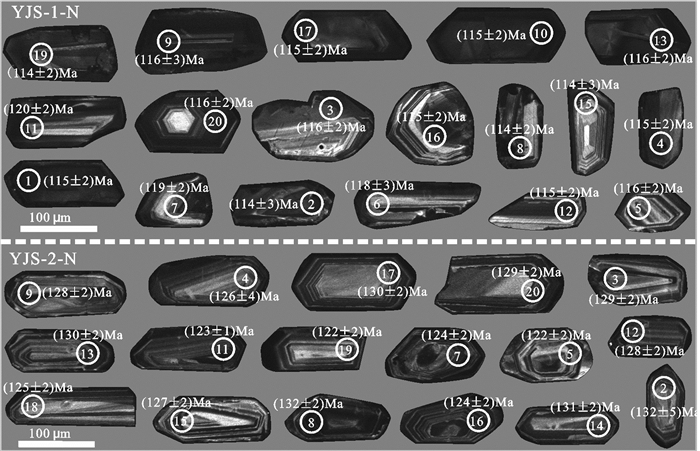
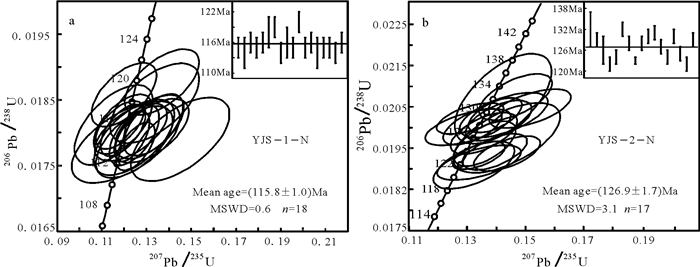
花岗斑岩样品(YJS-1-N)的锆石自形程度较好,为自形-半自形,长柱状,长短轴均在60~150 μm,震荡环带结构明显(图 3),锆石Th/U比值为0.32~0.71 (> 0.1)(表 1),具有岩浆成因锆石的特征(Hoskin et al., 2003, 2005)。18个锆石测点均位于谐和线上或其附近(图 4a),206Pb/238U年龄变化于114~120 Ma,加权平均年龄为(115.8±1.0) Ma (MSWD=7.2)。
花岗闪长岩样品(YJS-2-N)中锆石为自形,长柱状,长短轴均在60~200 μm,锆石震荡环带明显(图 3),锆石Th/U比值为0.15~0.42(> 0.1)(表 1),具有岩浆成因锆石的特征(Hoskin et al., 2003, 2005)。17个锆石测点均位于谐和线上或其附近(图 4b),206Pb/238U年龄变化于122~132 Ma,加权平均年龄为(126.9±1.7) Ma (MSWD=3.1)。
5.2 岩石地球化学特征
5.2.1 主量元素
矿区花岗斑岩样品(0230-02、YJS-14、YJS- 45)、花岗闪长岩样品(YJS-01、YJS-02、YJS-37)和磁铁矿矿石岩样品(YJS-38、YJS-41)均采自铜(金)矿体及围岩中,所测样品的主量、微量及稀土元素的分析结果见表 2。
表 2 跃进山铜金矿侵入岩岩石地球化学分析结果Table 2. Geochemical data of intrusive rocks in the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit
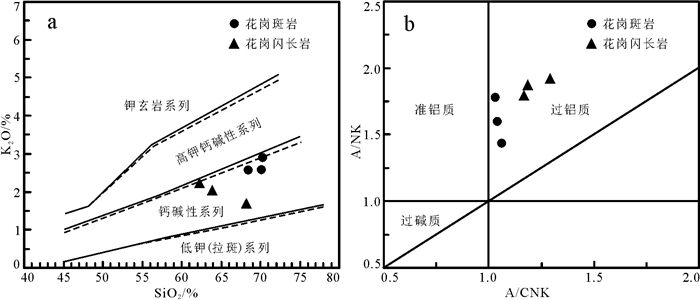
花岗斑岩样品的SiO2含量为68.50%~70.30%,Al2O3含量为14.65%~15.35%,(Na2O+K2O) =6.13%~ 7.08%,相对富钠K2O/Na2O=0.57~0.79,CaO含量为1.98%~3.44%,Fe2O3含量为2.54%~3.37%,具有较低的MgO、MnO、TiO2、P2O5含量,A/CNK=1.03~1.06,里特曼指数(σ)为1.47~1.85。岩石样品在SiO2- K2O图解中落入钙碱性岩石系列中(图 5a),在A/ CNK-A/NK图解中落入过铝质区域内(图 5b),在TAS图解(图略)中落入了亚碱性岩石系列区域内。由此可知,跃进山铜金矿区花岗斑岩属于亚碱性过铝质钙碱性系列岩石。
![]() 图 5 跃进山铜金矿床SiO2-K2O(实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976;虚线据Middlemost, 1985)(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)(b)Figure 5. K2O versus SiO2(full line after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; imaginary line after Middlemost, 1985) (a), and A/NK versus A/ CNK (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) (b) diagrams in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit
图 5 跃进山铜金矿床SiO2-K2O(实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976;虚线据Middlemost, 1985)(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)(b)Figure 5. K2O versus SiO2(full line after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; imaginary line after Middlemost, 1985) (a), and A/NK versus A/ CNK (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) (b) diagrams in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit花岗闪长岩样品具有富硅(62.10%~68.10%)、富铝(A2O3=15.15% ~19.40%)、高钾(K2O=1.67% ~ 2.29%)、高钠(Na2O=3.90% ~4.63%)、低钛(TiO2= 0.50% ~0.72%)、低钙(CaO=0.41% ~1.24%)、低磷(P2O5=0.01%~0.02%)的特征,A/CNK=1.17~1.29,里特曼指数(σ)为1.24~5.70,均值为2.89(σ < 3.3)。岩石样品在SiO2-K2O图解中落入钙碱性岩石系列中(图 5a),在A/CNK-A/NK图解中落入过铝质区域内(图 5b),在TAS图解(图略)中落入了亚碱性岩石系列区域内,花岗闪长岩属于亚碱性过铝质钙碱性系列岩石。
磁铁矿矿石样品具有低硅(SiO2=18.60% ~ 33.20%)、低铝(A2O3=0.72% ~0.54%)、低钾(K2O= 0.04% ~0.05%)、低钠(Na2O=0.12% ~0.19%)、低钛(TiO2=0.02%)和磷(P2O5=0.01%~0.02%),高铁(Fe2O3= 50.39%~74.58%)和钙(CaO=6.85%~13.95%)的特征。
5.2.2 微量元素
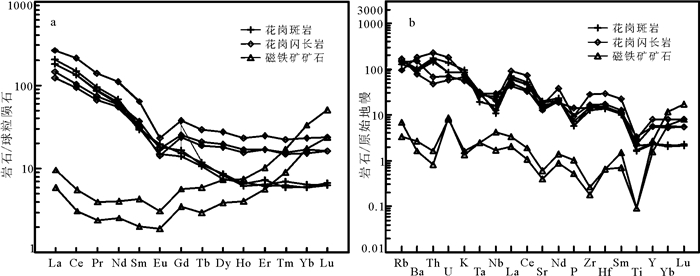
花岗斑岩的稀土元素配分模式为轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损的右倾型(图 6a)。稀土总量(∑REE)为174.67×10-6~194.86×10-6(均值为181.52×10-6),轻重稀土分馏程度较高,LREE/HREE=19.45~21.00(均值为20.37),(La/Yb)N=26.29~31.35(均值为28.60),重稀土元素相对平坦,(Gd/Yb)N=2.31~2.70,具有较弱的铕负异常(δEu=0.67~0.88),无铈异常(δCe= 0.99)。微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中(图 6b)岩石样品富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、K、Sr)和化学性质活泼的不相容元素(U、Th),相对亏损高场强元素(Ta、Nb、P、Ti)和重稀土元素。
![]() Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized trace element patterns (after Boynton, 1984) (a), and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (after Sun and McDonough, 1989) (b) of intrusive rock samples in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit
Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized trace element patterns (after Boynton, 1984) (a), and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (after Sun and McDonough, 1989) (b) of intrusive rock samples in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit花岗闪长岩稀土元素分模式为轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损的右倾型(图 6a),稀土总量为∑ REE= 141.61×10-6~294.81×10-6,平均值为188.57×10-6,轻重稀土分馏程度中等,LREE/HREE=7.22~10.15,(La/Yb)N=7.52~10.67,重稀土元素相对平坦,(Gd/ Yb)N=1.47~1.59,具有较强的铕负异常(δEu=0.46~ 0.56),基本无铈异常(δCe=0.94~1.04)。微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中(图 6b)岩石样品富集大离子亲石元素(如:Rb、Ba、K、Sr)和化学性质活泼的不相容元素(如:U、Th),相对亏损高场强元素(如:Ta、Nb、P、Ti)和重稀土元素。
磁铁矿石样品的稀土元素配分模式为轻稀土亏损,重稀土富集的左倾型(图 6a),稀土总量较低(∑ REE=11.91×10-6~21.60×10-6),轻重稀土分馏程度中等,LREE/HREE=0.69~0.76,(La/Yb)N=0.27~ 0.32,具微弱的铕负异常(δEu= 0.62~0.68),基本无铈异常(δCe=0.73~0.80)。微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中(图 6b)岩石样品富集Rb、U、Sm、Y、Yb、Lu,相对亏损Sr、Zr、Ti等元素。
6. 讨论
6.1 成岩(矿)时代
中生代以来,东北地区爆发了大规模的成岩、成矿事件。随着多个矿床的发现,该地区逐渐成为地质学者们研究的重点区域,并积累了大量的年代学资料(程瑞玉等,2006;Wu et al., 2011;Zhang et al., 2013;许文良等,2013;于介江等,2103;张国宾,2014;王庆磊等,2015;王庆双等,2015;韦延兰等,2015;邵军等,2015)。对已发表的中生代岩浆岩年代学资料(SHRIMP和LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄)的统计分析发现,东北地区的岩浆活动主要集中在早—中侏罗世(170~200 Ma)和早白垩世(100~130 Ma)。位于东北地区东部的完达山地块,其岩浆活动主要集中在早白垩世(109~135 Ma),如程瑞玉等(2006)采用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测得蛤蚂河花岗闪长岩体成岩时代为114.0~116.6 Ma和124.0 Ma,太平村花岗岩成岩时代为110.0~114.0 Ma;Zhang et al(2013)获得完达山四平山金矿床的赋矿围岩四平山组流纹岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb年龄为(122.1±1.0) Ma;张国宾(2014)将完达山地区中酸性岩浆活动划分为早(128.0~135.2 Ma)、中(122.1~124.0 Ma)、晚(110.0~117.1 Ma)三期;王庆磊等(2015)测得完达山358高地花岗斑岩的成岩年代为(128.0±1.0)Ma,王庆双等(2015)测得先锋北山金矿硅化流纹岩和石英闪长玢岩的成岩年代为(117.0±0.5)Ma、(108.5±1.0)Ma;韦延兰等(2015)跃进山铜金矿花岗斑岩成岩年龄为(109.2±0.9)Ma。
本次所测花岗斑岩样品(YJS-1-N)和花岗闪长岩样品(YJS-2-N)均为自形-半自形,长柱状,岩浆震荡环带明显,Th/U比值大于0.1,具有岩浆结晶成因锆石的典型特征。因此,岩石样品的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值(115.8±1.0)Ma和(126.9±1.7)Ma分别代表跃进山铜金矿床花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩的成岩年龄。通过野外地质调查与室内综合研究发现,跃进山铜金矿体主要赋存于矽卡岩内,其次产于花岗斑岩和矽卡岩的构造裂隙中,大面积出露的花岗闪长岩内部及其与地层的接触带附近基本无铜金矿化。从花岗斑岩、花岗闪长岩产出特征及其与矽卡岩的侵入接触关系可知,矿区矽卡岩形成与花岗斑岩密切相关,铜金矿化时代应略晚于花岗斑岩成岩时代,即跃进山铜金矿化时代略晚于(115.8±1.0)Ma。
6.2 岩石成因
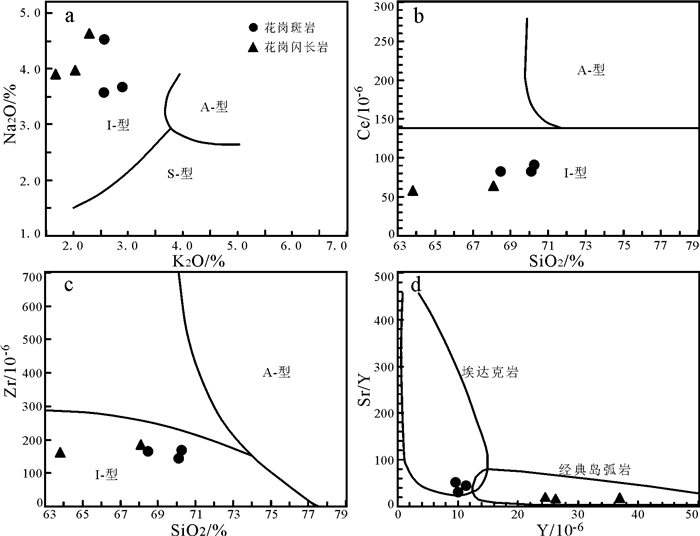
花岗岩是大陆地壳的重要组成部分,其成因类型分类方案尚未统一,目前最常用的分类方案为I、S、M和A型方案,其中M型较为少见,自然界中主要以A型、I型和S型为主(赵辛敏等,2014;任亮等,2015)。对于花岗岩的成因类型,不同学者曾从不同角度提出过多种判别方法(Whalen et al., 1987;Chappell and White, 1974, 2001;Chappell, 1999;Frost and Frost, 2011),如以铝饱和指数1.1作为I型和S型的分界(Chappell and White, 1974),此外,一系列地球化学图解(Whalen et al., 1987;Sylvester, 1989)在判别这三类花岗岩中也得到广泛应用,如K2O-Na2O、SiO2-Zr、SiO2-Ce等图解。本文花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩样品在K2O-Na2O图解(图 7a)、SiO2-Ce图解(图 7b)和SiO2-Zr图解(图 7c)中均落入了I型花岗岩范围内。
埃达克岩(adakite)是初由Defant and Drummond(1990)在研究阿留申群岛火山岩时提出来的,是指具有特定化学性质的中酸性火山岩或侵入岩,其地球化学标志是:SiO2≥56%,高铝(Al2O3≥ 15%)、MgO < 3%,贫Y和Yb(Y≤18×10-6,Yb≤1.9× 10-6),高Sr(Sr > 400×10-6),LREE富集,无Eu负异常(或轻微的负Eu异常)(Defant and Drummond, 1990;郭志军等,2012;吴鸣谦等,2014;康磊等,2015;王冬兵等,2016)。花岗斑岩样品为亚碱性弱过铝质钙碱性岩石系列,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损,具微弱铕负异常,无铈异常,在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 6)中,相对富集Rb、Ba、K、Th、U等元素,亏损Ta、Nb、P、Sr、Ti等元素。花岗斑岩样品具有富硅(68.50% ~70.30%)、富铝(A2O3=14.65% ~ 15.35%)、贫Y(10.30×10-6~11.10×10-6)和Yb(2.60× 10-6~3.95 × 10-6),高Sr(402.12 × 10-6~422.00 × 10-6),LREE富集,微弱Eu负异常,表现出典型的埃达克岩地球化学特征,在Y-Sr/Y图解(图 7d)中,花岗斑岩均落入埃达克岩区域。岩石样品中Ta、Nb和Ti元素具“TNT”负异常。一般认为,引起“TNT”负异常有3个可能性:①岩浆受到地壳物质的混染;②岩浆源区部分熔融过程中有金红石、钛铁矿等矿物残留;③与俯冲流体交代有关(Sun and McDonough, 1989;Mckenzie, 1989)。花岗斑岩的Rb/Sr比值(0.24~ 0.27)介于上地幔值(0.034)与地壳值(0.35)之间(Taylor and McLennan, 1995),Zr/Hf比值(33.02~35.21)介于地幔均值(30.74)与地壳均值(44.68)之间(Weaver and Tarney, 1984),Nb/Ta比值(6.08~14.13)低于地幔均值(17.5)而与地壳均值(12.3)接近(Sun and McDonough, 1989),反映花岗斑岩岩浆具有壳源和幔源的双重特征。极度富集Pb而亏损Nb、Ta的特征,表明样品具有大陆地壳的性质(McDonough and Sun, 1995;牛耀龄,2010;高山等,2009)。δ Eu的变化范围为0.67~0.88,(La/Yb)N值为26.29~31.35。在δ Eu-(La/Yb)N变异图解(图略)上,所有样品点均落入壳-幔型花岗岩范围内。综述可知,研究区花岗斑岩岩浆来源于地壳和地幔物质混合源区。
花岗闪长岩样品为富铝、高碱、低钙磷钛,亚碱性过铝质钙碱性岩石系列,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素相对亏损,具强铕负异常,无铈异常,在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图中,相对富集Rb、Ba、K、Th、U等元素,亏损Ta、Nb、P、Sr、Ti等元素,这些地球化学特征与壳源岩浆源区地球化学特征相似(Clemens, 2003)。花岗闪长岩样品的Rb/Sr、Nb/Ta、Zr/Hf比值分别为0.18~0.34、11.54~17.25和34.91~ 35.84,明显高于地幔均值而与地壳均值接近(Sun and McDonough, 1989;Taylor and McLennan, 1995),反映花岗闪长岩岩浆物质来源明显不同于典型的幔源或壳源物质,可能为壳幔混合来源。
6.3 成岩(矿)地球动力学背景
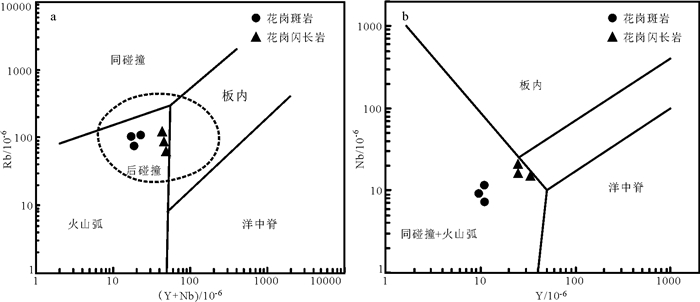
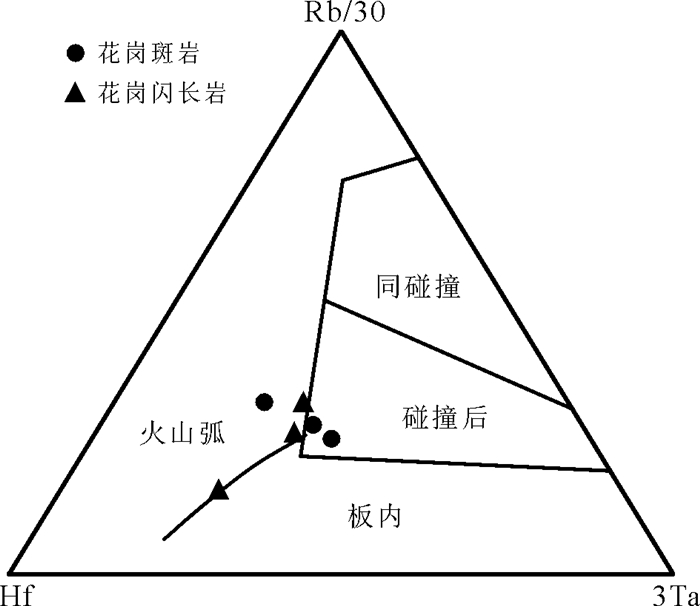
LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年结果显示花岗斑岩(样品YJS-1-N)和花岗闪长岩(样品YJS-2-N)的206Pb/ 238U加权平均年龄分别为(115.8±1.0)Ma和(126.9± 1.7)Ma,表明其成岩时代均为早白垩世。在(Y+ Nb)-Rb图解(图 8a)和Nb-Y图解(图 8b)中花岗闪长岩与花岗斑岩均落入后碰撞及火山弧花岗岩区域,在Rb/30-Hf-3Ta图解(图 9)中花岗闪长岩主要落入火山弧花岗岩区域,花岗斑岩主要落入碰撞后花岗岩区域。综上可知,花岗闪长岩和花岗斑岩形成于碰撞后构造环境。
中国东北地区处于西伯利亚板块、华北板块和太平洋板块交汇处,构造部位处于中亚造山带东端。中生代以来受太平洋板块俯冲的影响,发生了多次的改造和叠加增生。晚侏罗世—早白垩世太平洋板块的俯冲方向发生改变(Maruyama er al., 1997),东北地区的构造环境由挤压转变为伸展,岩石圈减薄使得东北地区形成了大面积的花岗岩(张兴洲等,2006;陈衍景等,2008;Zhang et al., 2013)。完达山地块是环太平洋活动带的重要组成部分,为太平洋板块俯冲拼贴的增生杂岩体(水谷伸治郎等,1989;周建波等,2005)。中—晚侏罗世完达山地块就位于佳木斯地块东缘(邵济安等, 1991, 1992;Zhang et al., 2013;葛肖虹等,2014),早白垩世早期完成拼贴,地球动力学背景开始由碰撞阶段的挤压增生体制转变为碰撞(俯冲)后的伸展减薄体制,加厚岩石圈地幔发生拆沉,软流圈物质上涌,形成大面积的中酸性岩浆岩(Sagong and Kwon, 2005;Zhang et al., 2010)。结合花岗闪长岩和花岗斑岩的成岩时代、岩石成因、岩浆来源及其构造环境特征,笔者认为跃进山铜金矿床成岩成矿作用与太平洋板块强烈俯冲作用后的伸展体制密切相关。
7. 结论
(1) 跃进山铜金矿床花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩的成岩年龄分别为(115.8±1.0)Ma和(126.9±1.7)Ma,铜金矿化时代与花岗斑岩成岩时代基本一致,为早白垩世晚期。
(2) 跃进山铜金矿床花岗闪长岩和花岗斑岩为富铝、高碱、低钙磷钛,为亚碱性过铝质钙碱性系列岩石,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损,属I型花岗岩范围,形成于壳源混合物质源区。
(3) 跃进山铜金矿花岗闪长岩和花岗斑岩形成于碰撞后构造环境,与太平洋板块强烈俯冲作用后的伸展体制密切相关。
致谢: 感谢黑龙江省第一地质勘察院李光辉高工、黄永卫高工在野外地质调查过程中给予的帮助和论文撰写过程中提供的宝贵意见,感谢匿名审稿人和责任编辑老师对本文提供的宝贵修改意见。 -
图 5 跃进山铜金矿床SiO2-K2O(实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976;虚线据Middlemost, 1985)(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)(b)
Figure 5. K2O versus SiO2(full line after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; imaginary line after Middlemost, 1985) (a), and A/NK versus A/ CNK (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) (b) diagrams in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit
图 6 跃进山铜金矿侵入岩岩石样品球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分图(据Boynton, 1984)(a)及原始地幔标准化的微量元素蛛网图(据Sun and McDonough, 1989)(b)
Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized trace element patterns (after Boynton, 1984) (a), and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (after Sun and McDonough, 1989) (b) of intrusive rock samples in the Yuejinshan Cu-Au deposit
表 1 跃进山铜金矿区花岗斑岩和花岗闪长岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS data for the granite porphyry and granodiorite in the the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit

表 2 跃进山铜金矿侵入岩岩石地球化学分析结果
Table 2 Geochemical data of intrusive rocks in the Yuejinshan copper-gold deposit

-
Boynton W V. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P(ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[J]. Elsevier, 63-114.
Chappell B W, White A J R. 1974. Two contrasting granite types[J]. Pacific Geology, 8:173-174. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027419645/
Chappell BW and White AJR. 2001. Two contrasting granite type:25years late[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Science, 48(4):489-499. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00882.x
Chappell BW. 1999. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 46(3):535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
Chen Yanjing, Xiao Wenjiao, Zhang Jinjiang. 2008. Ore-system as a geodynamic probe[J]. Geology in China, 35(6):1059-1073(in Chinese and English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200806006.htm
Cheng Ruiyu, Wu Fuyuan, Ge Wenchun, Sun Deyou, Liu Xiaoming, Yang Jinhui. 2006. Emplacement age of the Raohe Complex in eastern Heilongjiang Province and the tectonic evolution of the eastern part of northeastern China[J]. Acta Prtrologica Sinica, 22(2):353-376(in Chinese and English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB200602009.htm
Clemens J D. 2003. S-type granitic magmas-petrogenetic issues, models andevidence[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 61(1-2):1-18. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00107-1
Defant M J, Drummond M S. 1990. Derivation of some modern are magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 347(6294):662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Frost C D, Frost B R. 2011. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids:Their compositional variability and modes of origin[J]. Journal of Petrology, 52(1):39-53. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egq070
Gao Shan, Zhang Junfeng, Xu Wenliang, Liu Yongshen. 2009. Delamination and North China Craton destruction[J]. Science in China, 54(1):1962-1973(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz201104001
Ge Xiaohong, Liu Junlai, Ren Shoumai, Yuan Sihua. 2014. The formation and evolution of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic continental tectonics in eastern China[J]. Geology in China, 41(1):19-38(in Chinese and English abstract).
Guo Zhijun, Zhou Zhenhua, Li Guitao, Li Jinwen, Wu Xinli, Ouyang Hegen, Wang Aishun, Xiang Anping, Dong Xuzhou. 2012. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and petrogeochemistral characteristics of the intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the Aoergai copper deposit of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 39(6):1486-1500(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hoskin P W O, Black L P. 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18:423-39. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x/full
Hoskin P W O, Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews of Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1):27-62. doi: 10.2113/0530027
Kang Lei, Xiao Peixi, Gao Xiaofeng, Xi Rengang, Yang Zaichao. 2015. Neopaleozoic and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism and tectonic evolution of the western West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geology in China, 03:533-552(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201503011.htm
Kirillova G L. 2003. Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary basins of active continental margin of Southeast Russia:Paleogeography, tectonics, and coal-oil-gas presence[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 20:385-397. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00046-1
Kirillova G L. 2005. The late Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary basins at the continental margin of southeastern Russia:Geodynamic evolution and coal and petroleum potential[J]. Geotectonics, 39(5):389-407.
Kojima S, Mizutani S. 1987. Triassic and Jurassic radiolarian from the Nadanhada range, northeast China[J]. Trans. Proc. Palaeont Soc. Japan (NS), 148:256-276.
Kojima S. 1989. Mesozoic terrane accretion in Northeast China, Sikhote-Alinand Japan regions[J]. Paleos, 69:213-232. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003101828990165X
Li guanghui. 2011. Metallogenetic Series and Exploration Prediction inthe Taipingling-Wandashan Menerogenetic Zone of Heilongjiang Province[D]. Beijing: Ph.D. Thesis of China University of Geosciences(Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Maruyama S, Isozaki Y, Kimura G, Terabayashi M. 1997. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands:Plate tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 6(1):121-142. doi: 10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1
McDonough W F, Sun S S. 1995. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 120:223-253. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
Mckenzie D. 1989. Some remarks on the movement of small melt fractions in the mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 95(2):53-72. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X89901672
Middlemost E A K. 1985. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks: An Introduction to Igneous Petrology[M]. London and UK, Longman, 1-266.
Mizutani S, Shao ji'an, Zhang qinglong. 1989. The Nadanhada terrane in relation to Mesozoic tectonics on continental margins of East Asia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 63(3):204-216(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86253X/199001/3001362666.html
Niu Yaoling. 2010. Some Fundamentals and Existing problems in oceanic island basalt(OIB) origins of the plate[J]. Science in China, 55(2):103-114(in Chinese).
Peccerillo A, Taylor T S. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks form Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 56:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Ren Liang, Sun Jinggui, Tang Chen, Meng Lanjing, Li Yixing, Cui Peilong. 2015. Petrogenic and metallogenic geochronology and its geological implications of Lianzhushan gold deposit, Jiayin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(8):2435-2449(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201508021
Sagong H, Kwon S T. 2005. Mesozoic episodic magmatism in South Korea and its tectonic implication[J]. Tectonics, 24(5):1-18. doi: 10.1029-2004TC001720/
Shao Ji'an, Tang Kedong, Wang Chengyuan, Zang Pijia. 1991. The teclonic characleristics and evolution of Nadanhada Terrane[J]. Science in China(Series B), (7):744-750(in Chinese and English abstract).
Shao Ji'an, Wang Chengyuan, Tang Kedong. 1992. A new approach to the teclonics in the Ussuri (Wusuli) Region[J]. Geological Review, 38(1):33-39(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_OA000003154.aspx
Shao Jun, Li Yongfei, Zhou Yongheng, Wang Hongbo, Zhang Jing. 2015. Neo-Archaean magmatic event in erguna massif of northeast China:Evidence from the zircon LA-ICP-MS dating of the gneissic monzogranite from the drill[J]. Journal of Jilin university (Earth Science Edition), 45(2):364-373(in Chinese and English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201502003.htm
Sun S S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implication mantle composition and processes[J]. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Sylvester P J. 1989. Post-collisional alkaline granites[J]. Journal of Geology, 97(3):261-281. doi: 10.1086/629302
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2):241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
Tian Dongjiang, Zhou Jianbo, Zheng Changqing, Liu Jianhui. 2006. Geochemical characteristics and tectonics mechanism of the metabasic rocks for ophiolite complex in Wandashan orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 26(3):64-70(in Chinese and English abstract).
Wang Dongbin, Luo Liang, Tang Yuan, Yin Fuguang, Wang Baodi, Wang Liquan. 2016. Zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of Early Paleozoic adakites from the Niujingshan ophiolitic melange in the ChangningMenglian suture zone and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8):2317-2329(in Chinese and English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608006.htm
Wang Qinglei, Yang Yanchen, Li Qian, Ma Xiaoyang, Tan Yan, Zhang Guobin. 2015. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of graniteporphyry from 358 Upland rock gold deposit in Wanda Mountain area, Heilongjiang Province and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(12):2171-2180(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Qingshuang, Yang Yanchen, Han Shijiong, Zhang Guobin, Wei Yanlan, Huang Yongwei, Quan Chuanshun. 2015. Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of Xianfengbeishan gold deposit in Heilongjiang Province and their geological significanc[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(4):675-691(in Chinese with English abstract).
Weaver B L, Tarney J. 1984. Empirical approach to estimating the composition of the continental crust[J]. Nature, 310 (5978):575-577. doi: 10.1038/310575a0
Wei Yanlan, Yang Yanchen, Liu Na, Han Shijion, Wang Pingshuang. 2015. The dating of ore-bearing granite porphyry in the Yuejinshan skarn Cu-Au deposit, Heilongjiang Province, and its tectonic significance[J]. Geology in China, 42(1):169-179(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201501/663991042.html
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. 1987. A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4):407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, Zhang Y B, Grant M L, Wilde S A, Jahn B M. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(2011):1-30. doi: 10.1016-j.jseaes.2010.11.014/
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, Zhang Y B, Grant M L, Wilde S A, Jahn B M. Geochronology of the phanerozoic granitoids in Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Wu Mingqian, Zhao Guochun, Gao Jianwei, Wang Haitong. 2014. Geochemical characteristics of the Dushan complex and their geological significance[J]. Geology in China, 41(1):108-121(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Pei Fuping, Meng En, Tang Jie, Xu Meijun. 2013. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China:Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(2):339-353(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201302001
Yu Jiejiang, Hou Xuegang, Ge Wenchun, Zhang Yanlong, Liu Jiacheng. 2013. Magma mixing genesis of the Early Permian Liulian pluton at the northeastern margin of the Jiamusi massif in NE China:Evidences from petrography, geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9):2971-2986(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201309002
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, Li H M, Gunther D L, Wu F Y. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinantions of zircon by laser ablation-inducticely coupled plasma mass spectronmetry[J]. Geoanalytical and Geostandard Research, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3
Zeng Zhen, Zhang Xingzhou, Zhou Jianbo. 2017. The zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry and its geological significance of the Permian gabbro in the Yuejin complexs[J]. Geological Review, 63(supplementary issue):267-268.
Zhang Guobin, Yang Yanchen, Wang Jian, Wang Keyong, Ye Songqing. 2013. Geology, geochemistry, and genesis of the hot-spring-type Sipingshan gold deposit, eastern Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[J]. International Geology Review, 55(4):482-495. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2012.727572
Zhang Guobin. 2014. Study on Metallogenic Cystem of Wandashan Massif, Eastern Heilongjiang Province[D]. Changchun: Doctoral dissertation of Jilin University(in Chinese and English abstract).
Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, Wu F Y, Yang J H, Wilde S A, Li M. 2010. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subductioninduced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 276:144-165. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.05.013
Zhang Xingzhou, Yang Baojun, Wu Fuyuan, Liu Guoxing. 2006. The lithosphere Structure in the Hingmong-Jihei (Hinggan-MongoliaJilin-Heilongjiang)region, northeastern China[J]. Geology in China, 33(4):816-823(in Chinese and English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=22794816
Zhao Xinmin, Zhang Zuoheng, Liu Min, Li Yusheng, Guo Shaofeng. 2014. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the granites from the Xiaoliugou deposit in the western of the North Qilian[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(1):16-34(in Chinese and English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201401002
Zheng Z, Kono M, Shao J A. 1990. The amalgamative history of eastern Asia inferred from Paleomagnetism of North China[J]. Rock Magnetism and Paleogephysics, 17:1-18. http://eurekamag.com/research/020/288/020288674.php
Zhou Jianbo, Liu Jianhui, Zheng Changqing, Liu Pengju, Sun Jiapeng. 2005. Eastward extension of Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt and the suture zone of the plates:determination of Tanlu-Yalujiang-Yanji faults[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(1):92-104(in Chinese and English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXDX200501007.htm
陈衍景, 肖文交, 张进江. 2008.成矿系统:地球动力学的有效探针[J].中国地质, 35(6):1059-1073. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.06.004 程瑞玉, 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 柳小明, 杨进辉. 2006.黑龙江省东部饶河杂岩的就位时代与东北东部中生代构造演化[J].岩石学报, 22(2):353-376. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200602009 高山, 章军锋, 许文良, 刘勇胜. 2009.拆沉作用与华北克拉通破坏[J].科学通报, 54(1):1962-1973. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200914004.htm 葛肖虹, 刘俊来, 任收麦, 袁四化. 2014.中国东部中-新生代大陆构造的形成与演化[J].中国地质, 41(1):19-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.002 郭志军, 周振华, 李贵涛, 李进文, 武新丽, 欧阳荷根, 王挨顺, 向安平, 董旭舟. 2012.内蒙古敖尔盖铜矿中-酸性侵入岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年与岩石地球化学特征研究[J].中国地质, 39(6):1486-1500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.003 康磊, 校培喜, 高晓峰, 奚仁刚, 杨再朝. 2015.西昆仑西段晚古生代-中生代花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化过程[J].中国地质, 42(3):533-552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.011 李光辉. 2011.黑龙江完达山-太平岭成矿带成矿系列与找矿预测[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1011077631.htm 牛耀龄. 2010.板内洋岛玄武岩(OIB)成因的一些基本概念和存在的问题[J].科学通报, 55(2):103-114. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=KXTB201002002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 任亮, 孙景贵, 唐臣, 门兰静, 李怡欣, 崔培龙. 2015.黑龙江嘉荫连珠山金矿床成岩成矿年代学及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 31(8):2435-2449. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201508021 邵济安, 唐克东, 王成源, 臧启家, 张允平. 1991.那丹哈达地体的构造特征及演化[J].中国科学(B辑), (7):744-750. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2006110550.htm 邵济安, 王成源, 唐克东. 1992.乌苏里地区构造新探索[J].地质论评, 38(1):33-39. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1992.01.004 邵军, 李永飞, 周永恒, 王宏博, 张璟. 2015.中国东北额尔古纳地块新太古代岩浆事件:钻孔片麻状二长花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS测年证据[J].吉林大学学报:(地球科学版), 45(2):354-373. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201502004 水谷伸治郎, 邵济安, 张庆龙. 1989.那丹哈达地体与东亚大陆边缘中生代构造的关系[J].地质学报, 63(3):204-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1989.03.005 田东江, 周建波, 郑常青, 刘建辉. 2006.完达山造山带蛇绿混杂岩中变质基性岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].矿物岩石, 26(3):64-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2006.03.011 王冬兵, 罗亮, 唐渊, 尹福光, 王保弟, 王立全. 2016.昌宁-孟连结合带牛井山早古生代埃达克岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石成因及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 32(8):2317-2329. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201608006 王庆磊, 杨言辰, 李骞, 马晓阳, 谈艳, 张国宾. 2015.黑龙江完达山地区358高地岩金矿床花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 34(12):2171-2180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.004 王庆双, 杨言辰, 韩世炯, 张国宾, 韦延兰, 黄永卫, 全传顺. 2015.黑龙江先锋北山金矿床火山岩地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].矿床地质, 34(4):675-691. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201504002 韦延兰, 杨言辰, 刘娜, 韩世炯, 王庆双. 2015.黑龙江省跃进山铜金矿床花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].中国地质, 42(1):169-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.013 吴鸣谦, 赵国春, 高建伟, 王海涛. 2014.河北都山杂岩体地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 41(1):108-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.008 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 孟恩, 唐杰, 徐美君, 王伟. 2013.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 29(2):339-353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201302001 于介江, 侯雪刚, 葛文春, 张彦龙, 柳佳成. 2013.佳木斯地块东北缘早二叠世六连岩体的岩浆混合成因:岩相学、年代学和地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 29(9):2971-2986. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201309002 曾振, 张兴洲, 周建波. 2017.跃进山杂岩中二叠纪辉长岩的锆石UPb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 63(增刊):267-268. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZLP2017S1129&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张国宾. 2014.黑龙江省东部完达山地块区域成矿系统研究[D].长春: 吉林大学博士学位论文. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10183-1015513581.htm 张兴洲, 杨宝俊, 吴福元, 刘国兴. 2006.中国兴蒙-吉黑地区岩石圈结构基本特征[J].中国地质, 33(4):816-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.04.011 赵辛敏, 张作衡, 刘敏, 李育森, 郭少丰. 2014.北祁连西段小柳沟矿区花岗质岩石锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及成因研究[J].岩石学报, 30(1):16-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201401002 周建波, 刘建辉, 郑常青, 刘鹏举, 孙加鹏. 2005.大别-苏鲁造山带的东延及板块缝合线:郯庐-鸭绿江-延吉断裂的厘定[J].高校地质学报, 11(1):92-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.01.008 -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 何云龙,张国宾,杨言辰,冯玥,孔金贵,陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约. 现代地质. 2024(01): 128-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张国宾,何云龙,杨言辰,孔金贵,冯玥,陈兴凯. 黑龙江东部那丹哈达地体燕山期金铜成矿系统——中生代岩浆作用与成矿背景. 地质论评. 2023(05): 1763-1794 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李随民,李玉成,赵淑梅,张良良,王俊革,韩腾飞,孙志伟,韩玉丑,李樋. 河北邯郸洪山铜矿Ar-Ar和U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时代的限定. 中国地质. 2022(02): 575-585 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 于喜洹,石国明,符安宗,李新鹏,孙江军,尹国良,林泽付. 黑龙江省多宝山地区中奥陶世侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄及构造环境. 地质与资源. 2022(05): 588-596 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王崇一,郝宇杰,商青青,史雨凡,高煜,任云生. 黑龙江跃进山矽卡岩型铜金矿床花岗闪长岩的年代学和地球化学特征. 世界地质. 2021(01): 29-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 赵越,刘敬党,张国宾,张艳飞. 张广才岭南部帽儿山岩体二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2021(04): 1098-1118 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 黄鑫. 胶东大柳行金矿矿床特征及成因探讨. 西北地质. 2021(04): 129-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨雪叶,尹继元,肖文交,陈文,陈岳龙,孙敬博,张斌,王雅美. 东北那丹哈达岭中—新生代构造-热演化史:来自(U-Th)/He和裂变径迹热年代学的证据. 地质学报. 2021(12): 3660-3675 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 任云生,郝宇杰,王崇一,全传顺,李京谋,高煜,史雨凡. 黑龙江省完达山地区金铜成矿作用时代、构造背景及物质源区. 岩石学报. 2020(03): 644-664 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王嘉玮,朱裕生. 界面成矿探讨. 中国地质. 2019(01): 77-86 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 于跃江,黄辰旭. 黑龙江鸡东狼洞山地区找矿前景. 世界地质. 2019(04): 962-975 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: