Exploration of Mineral Water Resources in City Clusters Along the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze and Discoveries ― A Case Study of the Dataset of the Hydrogeological Survey in the 1∶50 000 Tingsiqiao Map-sheet, Xianning City
-
摘要:
长江中游城市群承东启西、连接南北,在我国经济均衡发展、和谐发展中占有重要地位,咸宁地区矿泉水资源的发现,将助力绿色经济发展。咸宁汀泗桥幅数据依托中国地质调查局“武汉都市圈京广高铁沿线汀泗桥幅地质环境综合调查”项目,在充分收集地质、遥感、物探及水文地质等资料基础上,开展汀泗桥幅1∶50 000水文地质调查。本数据集包含钻孔基本信息(12个钻孔)、钻孔地层描述信息(12个钻孔)、机民井点调查结果(77个机民井)、泉点调查结果(46个泉点)、地下水动态监测信息(2处)、无机水样测试结果(61件)和有机水样测试结果(9件),数据量约为4.77 MB。数据集充分反映了1∶50 000水文地质调查中典型水文地质现象、灰岩地层的岩溶发育特点及岩溶地下水的水化学特征。通过水化学分析,在咸宁市汀泗桥镇白羊畈−赤壁官塘驿镇大贵畈−中伙铺镇一线发现富锶型饮用天然矿泉水,赤壁中伙铺琅桥一带为富锶、富锌复合型饮用天然矿泉水,对该区的矿泉水资源勘查具有重要参考意义。实施探采结合井,服务地方用水需求。
Abstract:The city clusters along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, which connect the western parts with the eastern parts and the southern parts with the northern parts of China, play an important role in the balanced and harmonious development of the economy in China. The discovery of mineral water resources in Xianning City will contribute to the development of a green economy. Relying on the project initiated by China Geological Survey with the title Comprehensive Geological Environmental Survey of the Tingsiqiao Map-sheet in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area Along the Beijing-Guangzhou High-speed Railway, the dataset of the Tingsiqiao Map-sheet (also referred to as the Dataset) was developed through the hydrogeological survey in the Tingsiqiao Map-sheet, on a scale of 1∶50 000, as well as a full collection of existing geological survey data, remote sensing, geophysical prospecting and a hydrogeological survey. It consists of basic information on boreholes (12 boreholes), descriptions of strata revealed by boreholes (12 boreholes), results from the survey points of pumping/domestic wells (77 pumping/domestic wells), spring points survey results (46 spring points), dynamic monitoring information of groundwater (2 places) and test results from inorganic water samples (61 samples) and organic water samples (9 samples); with a data size of about 4.77 MB. From this dataset, the typical hydrogeological phenomena, the development features of karst in limestone strata and the hydrochemical features of karst groundwater obtained from the hydrogeological survey were fully reflected. According to hydrochemical analysis, Sr-rich potable natural mineral water is discovered along Baiyangfan, Tingsiqiao Town, Xianning City – Daguifan, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City – Zhonghuopu Town and Chibi City. Sr-rich and Zn-rich composite potable natural mineral water is also discovered in the Langqiao area, Zhonghuopu Town and Chibi City, providing important references for the exploration of mineral water resources in the area. Exploration-production wells were drilled with an aim to meet the local demand for water.
-
1. 引言
长江中游城市群在我国区位条件优越、资源种类丰富、生态环境优美、发展潜力巨大,是肩负促进“中部崛起”重任的特大型城市群之一,是长江经济带的重要组成部分(姜月华等,2017)。2016年,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心瞄准需求,开展“武汉都市圈京广高铁沿线汀泗桥幅地质环境综合调查”项目(“长江中游城市群咸宁−岳阳和南昌−怀化段高铁沿线1∶50 000水文地质调查”二级项目子项目,项目编号:DD20160248),旨在为城市群的规划建设提供基础地质依据。本项目的主要任务是查明区内水文地质条件和环境地质问题,重点查清区内岩溶分布、地下水强径流途径及盖层结构。
咸宁市汀泗桥幅位于幕阜山脉北缘地带与江汉平原南缘相接处,总体地势为南东高、北西低。长江干流位于工作区的北西侧,自南西向北东流。区内地貌类型多样,分为平原、丘陵、中低山三种类型。地处亚热带季风气候区,四季分明,具有冬季寒冷,夏天炎热,春秋多雨的特征。多年平均气温15~17℃,年平均日照时间为1 754.5 h,年平均降雨量约为1 577.4 mm。区内出露地层较简单,主要有新生界第四系的全新统和更新统,中生界白垩系、下三叠统大冶组;古生界上二叠统吴家坪组、大隆组、龙潭组,下二叠统茅口组、栖霞组和梁山组,中石炭统黄龙组和大浦组,上志留统茅山组和中志留统坟头组(杨艳林等,2018)。
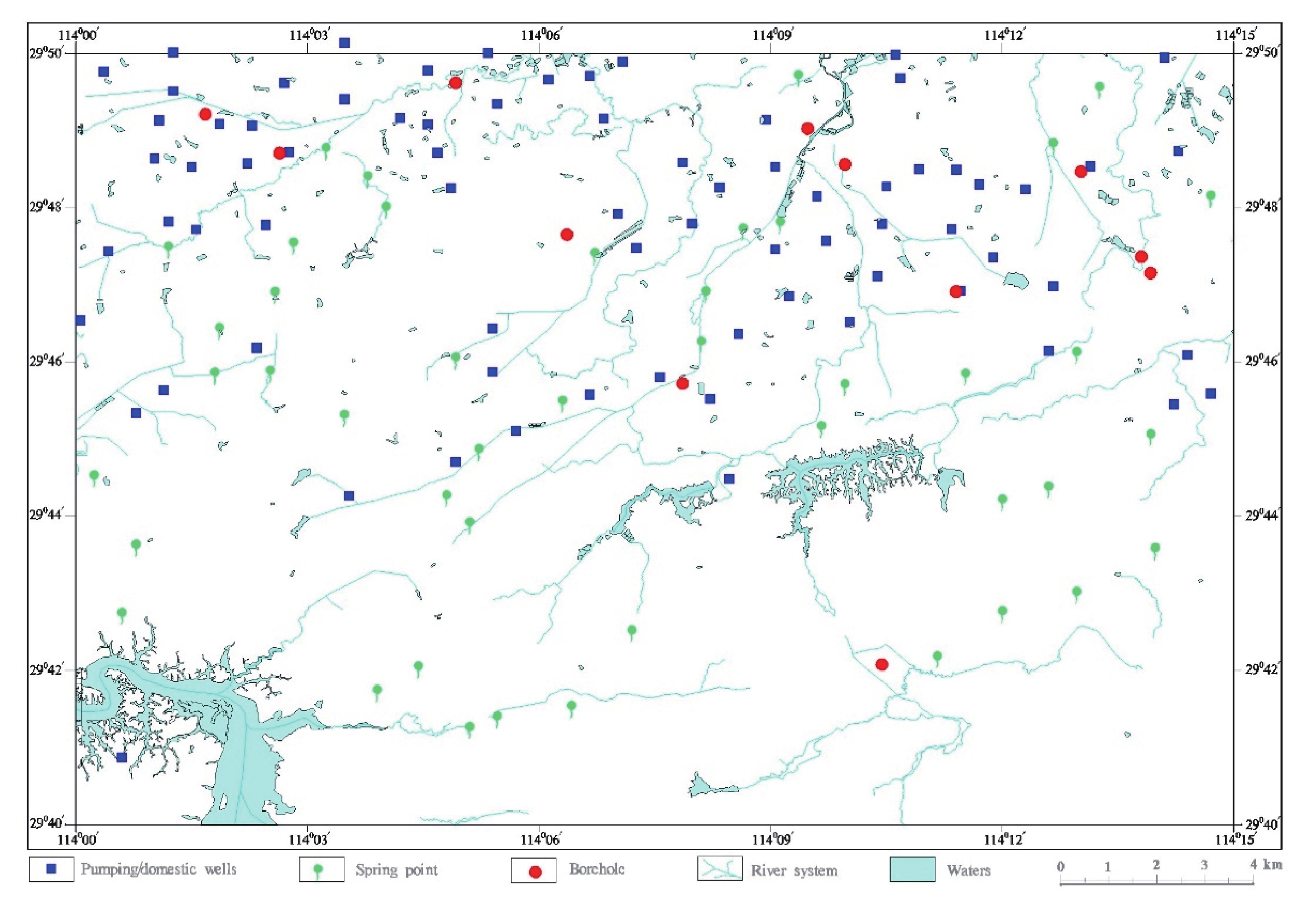
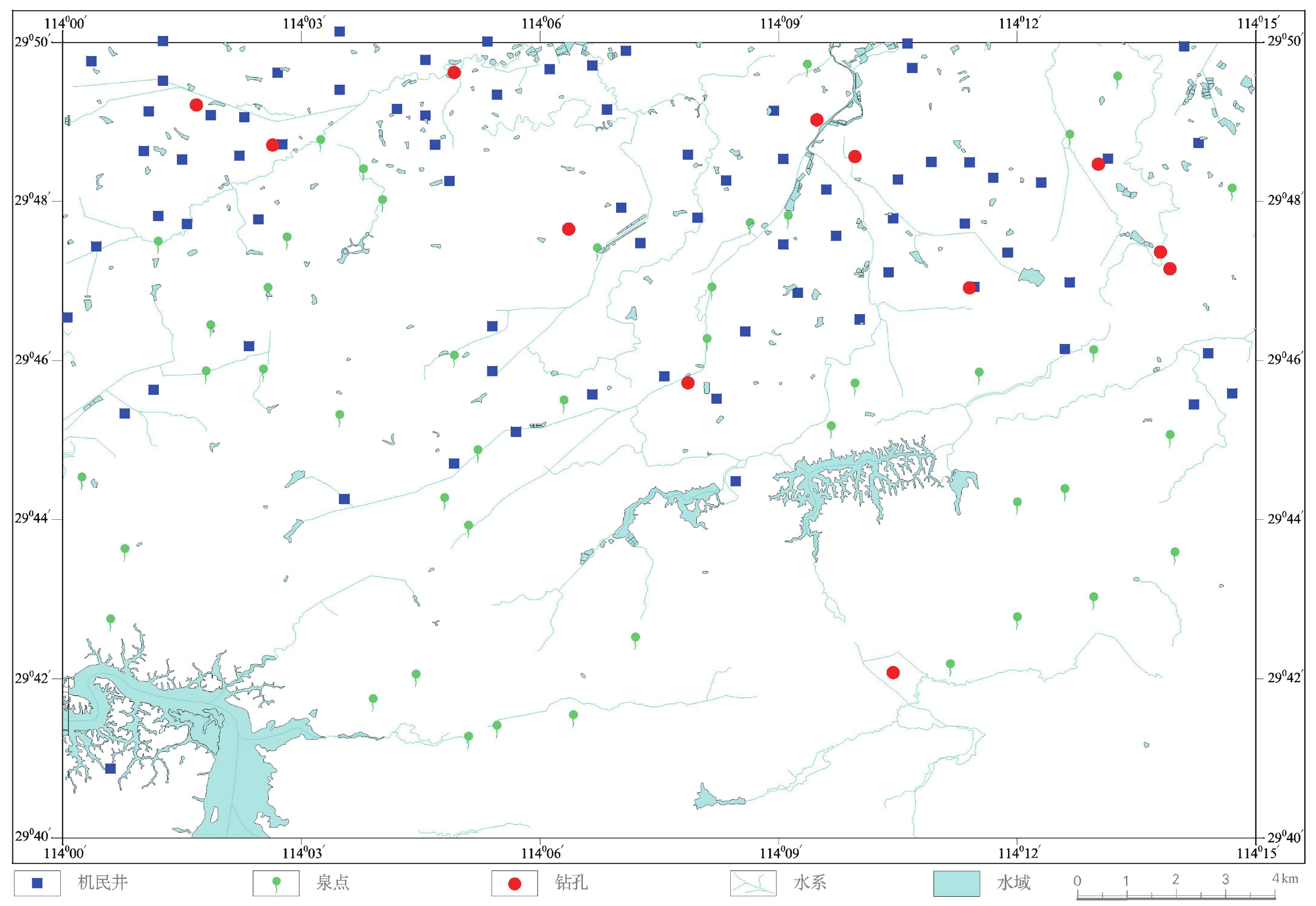
本项目从2016年1月至2016年12月,累计完成汀泗桥幅450 km2范围的1∶50 000水文地质调查,取得钻孔基础数据(12个钻孔)、钻孔地层描述信息(12个钻孔)、水文地质调查成果(77个机民井点和46个泉点)、地下水位动态监测信息(2处)、无机水样测试结果(61件)和有机水样测试结果(9件)等7组数据。野外现场调查点分布如图1所示。咸宁市汀泗桥幅1∶50 000水文地质调查数据集的元数据如表 1所示。
表 1 数据库(集)元数据简表条目 描述 数据库(集)名称 1∶50 000咸宁市汀泗桥幅水文地质调查数据集 数据库(集)作者 杨艳林,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
陈立德,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
邵长生,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
路韬,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
张傲,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心数据时间范围 2016年1月—2016年12月 地理区域 咸宁市咸安区汀泗桥镇,面积约450 km2;地理坐标:东经114°00′~114°15′,北纬29°40′~29°50′ 数据格式 *.xls 数据量 4.77 MB 数据服务系统网址 http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn 基金项目 中国地质调查局地质调查项目(DD20160248)资助 语种 中文 数据库(集)组成 钻孔基础数据.xls、钻孔地层描述信息.xls、机民井点调查表.xls、泉点调查表.xls、地下水位动态监测表.xls、有机水样测试结果.xls、无机水样测试结果.xls 2. 数据采集和处理方法
2.1 钻孔数据采集
本次工作过程中,所实施钻孔均依据《水文地质调查规范(1∶50 000)》(DZ/T 0282–2015)、《水文水井地质钻探规程》(DZ/T 0148−2014 )、《地下水监测井建设规范》(DZ/T 0270−2014)、《水质采样 样品的保存和管理技术规定》(HJ 493−2009)等相关要求开展钻探施工、岩心编录、钻孔成井、抽水试验、水样采集等,经过对钻孔重要信息的整理集成,形成了钻孔基本信息表和钻孔地层描述表。
抽水试验过程流量采用流量表(LXS-20F)和三角堰箱进行双重观测校核确定,水位埋深采用SWJ-80型钢尺水位计进行测量。在抽水试验接近尾声时,采集水样,并利用Manta2多参数测试仪现场测试常规指标,参数有水温、pH、电导率(EC)、溶解氧(DO)、氧化还原电位(Eh)等,其他参数经实验室检测获得。
2.2 水文地质调查数据采集
在野外调查过程中,对区内的机民井和泉点等水文地质点进行了详细访问、测量和记录。对机民井点,主要调查了井口直径、井口高程、井深、地下水位埋深、井壁结构和常规水质指标等。对泉点,主要调查了泉出露的水文地质条件、常规水质指标和泉流量及其年际变化情况等。泉流量测定方法主要采用流速仪法(LS300-A型便携式流速测算仪)、容积法和三角堰法。常规水质指标采用Manta2多参数测试仪测定。综合分析地形地貌、岩性构造、水文地质单元和机民井、泉的水化学异常及周围环境等条件,布置取样点。
2.3 水样采集与数据处理
本次工作根据《水质采样 样品的保存和管理技术规定》(HJ 493−2009)、《水质采样技术指导》(HJ 494−2009 )和《生活饮用水标准检验方法水样的采集和保存》(GB/T 5750.2−2006)等规范要求,进行水样采集、保存和送样。本数据包含无机水样61个(其中调查井水样34件、泉水样12件、钻孔水样12件和地表水样3件)和有机水样9个(全为钻孔水样)。无机水样的检测依据是《地下水污染调查评价规范》(DD 2008–01)。有机水样的检测依据是《地下水污染调查评价规范》(DD 2008–01),US.EPA 8081A,US.EPA 8310,US.EPA 524等。
2.4 地下水位动态监测
为了进一步查明研究区内水文地质条件,特别是地下水的补给、径流、排泄条件,掌握地下水动态规律,为地下水资源评价、科学管理及环境地质问题的研究提供科学依据,项目组在野外调查工作中,依据 《地下水动态监测规程》(DZ/T 0133–1994)要求,在典型的民井和钻孔建立了两处动态监测点。监测仪器采用电子自动测量水位探头(型号为Solinst 3001 LTC),测量参数有水温、水位和电导率。采样间隔为20 min、30 min;监测周期为一个水文年(2018年1月—2019年1月)。
3. 数据内容描述
咸宁市汀泗桥幅水文地质调查数据集为Excel表格型数据,包括7个数据文件,分别为钻孔基本信息表.xls、钻孔地层描述表.xls、机民井点调查表.xls、泉点调查表.xls、无机水样测试结果表.xls、有机水样测试结果表.xls和地下水位动态监测表.xls。
钻孔基本信息表.xls数据文件(表2),描述本次工作中施工12眼水文孔的基本信息,记录有钻孔编号、X、Y坐标(CGCS2000坐标系,以下同)、地理位置、地面高程、开孔孔径、孔径、终孔深度、初见水位、静水位埋深、滤水管段、主要含水层段、极大降深-涌水量、取样情况和备注等信息。每个水文孔为一行,共12行数据。
表 2 钻孔基本信息序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 钻孔编号 字符串 SZK01 2 X 浮点型 20230908 3 Y 浮点型 3302058 4 地理位置 字符串 湖北省咸宁市汀泗桥镇彭碑村六组 5 地面高程 m 浮点型 38.00 6 开孔孔径 m 浮点型 130.00 7 孔径 字符串 0~11.8 m,r=80 mm;11.8~39 m,r=73 mm;39.0~101.0 m,r=61 mm 8 终孔深度 m 浮点型 101.00 9 初见水位 m 浮点型 1.00 10 静水位埋深 m 浮点型 1.00 11 滤水管段 字符串 13.00~101.00 m 12 主要含水层段 字符串 20.0~21.3 m;42.0~44.6 m;65.0~67.4 m 13 极大降深−涌水量 字符串 7.90 ~118.90 m3/d 14 取样情况 字符串 水样:有机样与无机样 15 备注 字符串 未见溶洞 钻孔地层描述表.xls数据文件(表3),描述本次工作中施工的12眼水文孔揭露的地层结构及岩性信息,主要包括钻孔编号、层号、地层时代、层底高程、层底埋深、层厚、地层岩性描述等信息。
表 3 钻孔地层描述序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 钻孔编号 字符串 SZK01 2 层号 整数型 1 3 地层时代 字符串 Qh 4 层底高程 m 浮点型 36 5 层底埋深 m 浮点型 2 6 层厚 m 浮点型 2 7 地层岩性描述 字符串 红褐色—灰褐色耕植土,岩芯呈短柱状,切面较粗糙,略潮湿,局部可见少量植物根系 机民井点调查表.xls数据文件(表4),主要描述本次工作中调查的机民井点基本信息,包含野外编号、X、Y、地理位置、井口高程、井口直径、水位埋深、井深、井壁结构、取水层位、含水层岩性、开采量、水温、pH、味、气温、气味、溶解氧、电导率、氧化还原电位和调查时间等信息。每个调查点为一行,共77行。
表 4 机民井点普查调查表序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 野外编号 字符串 D533 2 X 浮点型 20218231 3 Y 浮点型 3298611 4 地理位置 字符串 湖北省赤壁市官塘驿镇官塘村七组 5 井口高程 m 浮点型 49.1 6 井口直径 mm 浮点型 650.0 7 水位埋深 m 浮点型 1.64 8 井深 m 浮点型 12 9 井壁结构 字符串 砖彻 10 取水层位 字符串 孔隙潜水 11 含水层岩性 字符串 砂土 12 水温 ℃ 浮点型 19.73 13 开采量 m3/h 浮点型 0.008 3 14 pH 浮点型 6.96 15 味 字符串 无 16 气温 ℃ 浮点型 30 17 气味 字符串 无 18 溶解氧 mg/L 浮点型 6.21 19 电导率 μs/cm 浮点型 291 20 氧化还原电位 mV 浮点型 356 21 调查时间 日期型 2016-8-15 泉点调查表.xls数据文件(表5),主要描述本次工作中调查的泉点基本信息,包含野外编号、X、Y、地理位置、泉水类型、地面高程、含水层岩性、泉水成因、主要用途、气温、流量测定方法、泉水流量、泉水温度、色度、味、气味、透明度、pH、氧化还原电位、溶解氧、电导率和调查时间等信息。每个调查点为一行,共46行。
表 5 泉点普查调查表序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 野外编号 字符串 D531 2 X 浮点型 20218487 3 Y 浮点型 3297583 4 地理位置 字符串 赤壁市官塘驿镇官塘村十组 5 泉水类型 字符串 下降泉 6 地面高程 m 浮点型 62.0 7 含水层岩性 字符串 T1d4白云质灰岩 8 泉水成因 图片 
9 主要用途 字符串 生活、灌溉用水 10 气温 ℃ 浮点型 29.0 11 流量测定方法 字符串 流速仪 12 泉水流量 L/s 浮点型 2.3 13 泉水温度 ℃ 浮点型 19.64 14 色度 字符串 无 15 味 字符串 无 16 气味 字符串 无 17 透明度 字符串 清澈透明 18 pH 浮点型 7.44 19 氧化还原电位 mV 浮点型 339 20 溶解氧 mg/L 浮点型 6.63 21 电导率 μs/cm 浮点型 995.4 22 调查时间 日期型 2016-8-15 无机水样测试结果表.xls数据文件(表略,参见数据集),主要记录了样品采样及测试结果信息,主要包括:送样编号、X、Y、水样类型、溶解性总固体、总硬度、总碱度、总酸度、可溶性SiO2、硝酸根、亚硝酸根、铵离子、硫酸根、碳酸根、重碳酸根、氯离子、氟离子、磷酸根离子、钠、钾、钙、镁、铁离子、亚铁离子、游离二氧化碳、pH、溴化物、碘化物、铝、锂、锶、锌、硒、铜、汞、镉、钡、六价铬、铅、钴、钒、钼、锰、镍、砷、银、偏硼酸、耗氧量等信息。其中测试指标有44项,每个样品1行,共计61行。
有机水样测试结果表.xls数据文件(表略,参见数据集),主要记录了采样信息和测试结果信息,主要包括基本信息3项(样品编号、检测编号、样品记述)和检测项目(卤代烃、氯代苯、单环芳烃类25项、有机氯农药11项、苯并(a)芘等共计37项)等信息。每个样品1行,共计9行。
4. 数据质量控制和评估
4.1 钻探数据质量
水文地质钻孔数据的质量控制包括钻孔的孔径、岩芯采取率、孔深与孔斜、水文观测、抽水试验、成井工艺、固井与封孔、原始记录与技术档案等环节,按照《水文地质调查规范(1∶50 000)》(DZ/T 0282−2015)、《水文水井地质钻探规程》(DZ/T 0148−2014)、《钻孔抽水试验规程》(DL/T 5213–2005)等标准进行检查验收,并对记录数据的完整性、规范性和准确性进行了仔细核查,确保钻探过程和数据记录的质量。
4.2 调查数据质量
严格按照《水文地质调查规范(1∶50 000)》(DZ/T 0282–2015)等规范、规程开展地面调查,共完成 1∶50 000水文地质调查面积450 km2。观察点采用GPS(佳明Montana 680)结合地形地物定位,GPS全部进行了校正,误差小于50 m。野外记录统一采用调查卡片的形式进行记录描述,内容齐全,描述准确;并遵照三级管理体系的要求,对调查点(如机民井、泉点)的调查数据,包括人工填写和电子记录等,进行了检查和核查。
4.3 水质样品测试数据质量
无机与有机水样的测试工作均由国土资源部长沙矿产资源监督检测中心(湖南省地质测试研究院)承担。其中无机样使用的主要仪器有:ICP–MS和ICAP–6300 ICP等离子全谱仪、722S可见光分光光度计、AFS-830a双道原子荧光光谱仪等。检测环境:温度20℃,湿度60%。有机样使用的主要仪器有:气相色谱-质谱联用仪(带吹扫捕集)、气相色谱仪、高效液相色谱仪等;检测环境:温度21.8℃,湿度52%。按《地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范》(DZ/T 0130.6−2006 )标准开展水样测试,对每批次样品,实验室进行了空白试验与平行试验,保证测试结果的准确性。测试选择分析方法的检出限均达到或优于相关规范的要求。
4.4 地下水动态监测数据质量
地下水动态监测工作由电子测量探头进行,项目组不定期到监测点,核查监测设施是否完好,设备运行是否正常;并采用水位计测量水位,与探头采集数据进行比对。经多次检测、核查,监测数据真实可靠。
5. 数据价值
数据集的建立为该区提供了一套基础性的数据资源。通过野外调查、水质测试结果和实施的探采结合井,取得了以下主要认识:
(1)查清了区内岩溶水文地质条件。覆盖型岩溶区,岩溶发育,在垂向上发育多重溶洞结构,岩溶地下水与浅层地下水联系密切。裸露型岩溶区,岩溶发育,常见各种岩溶地貌。岩溶泉多,水量大,受降雨影响明显。
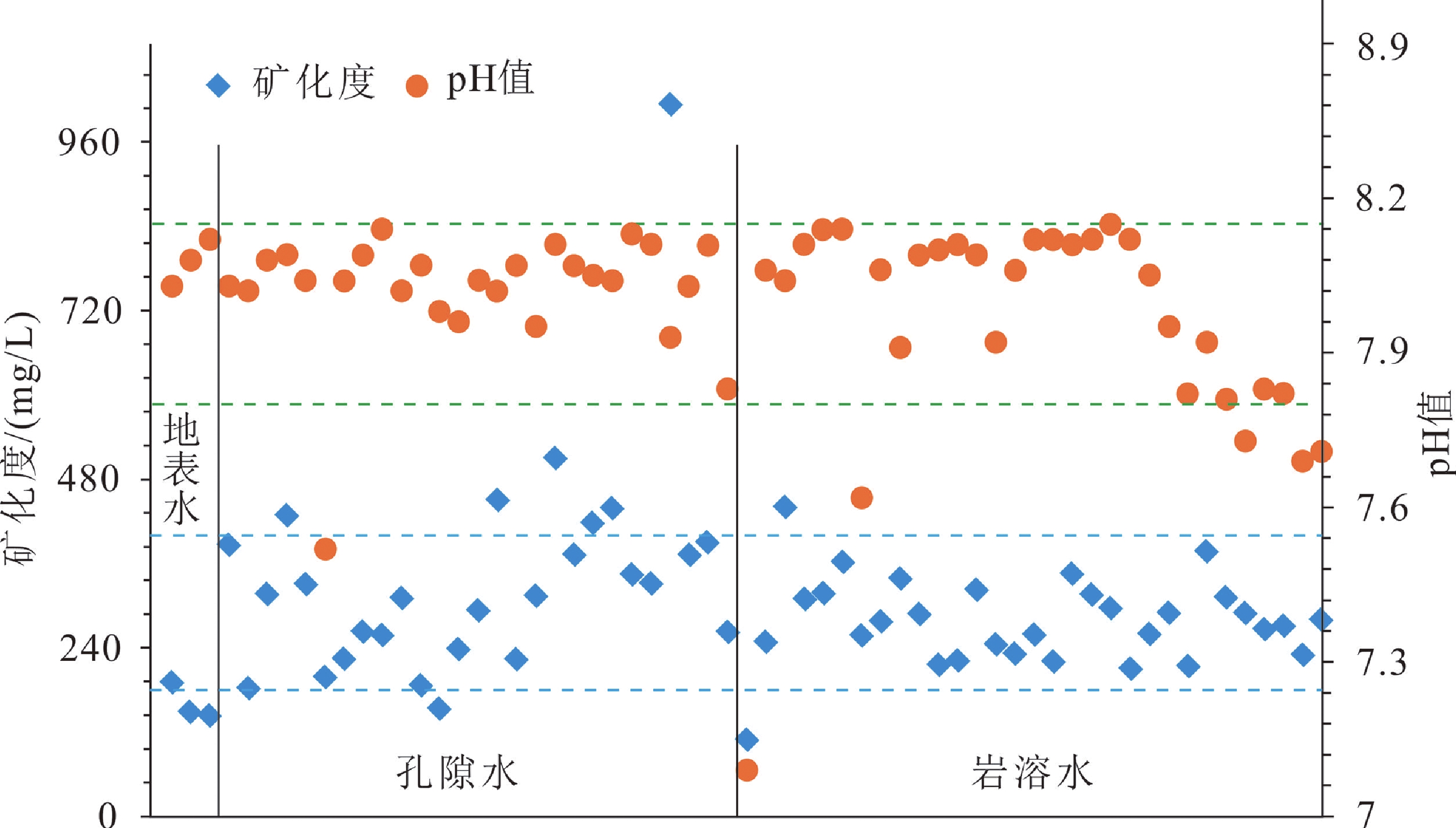
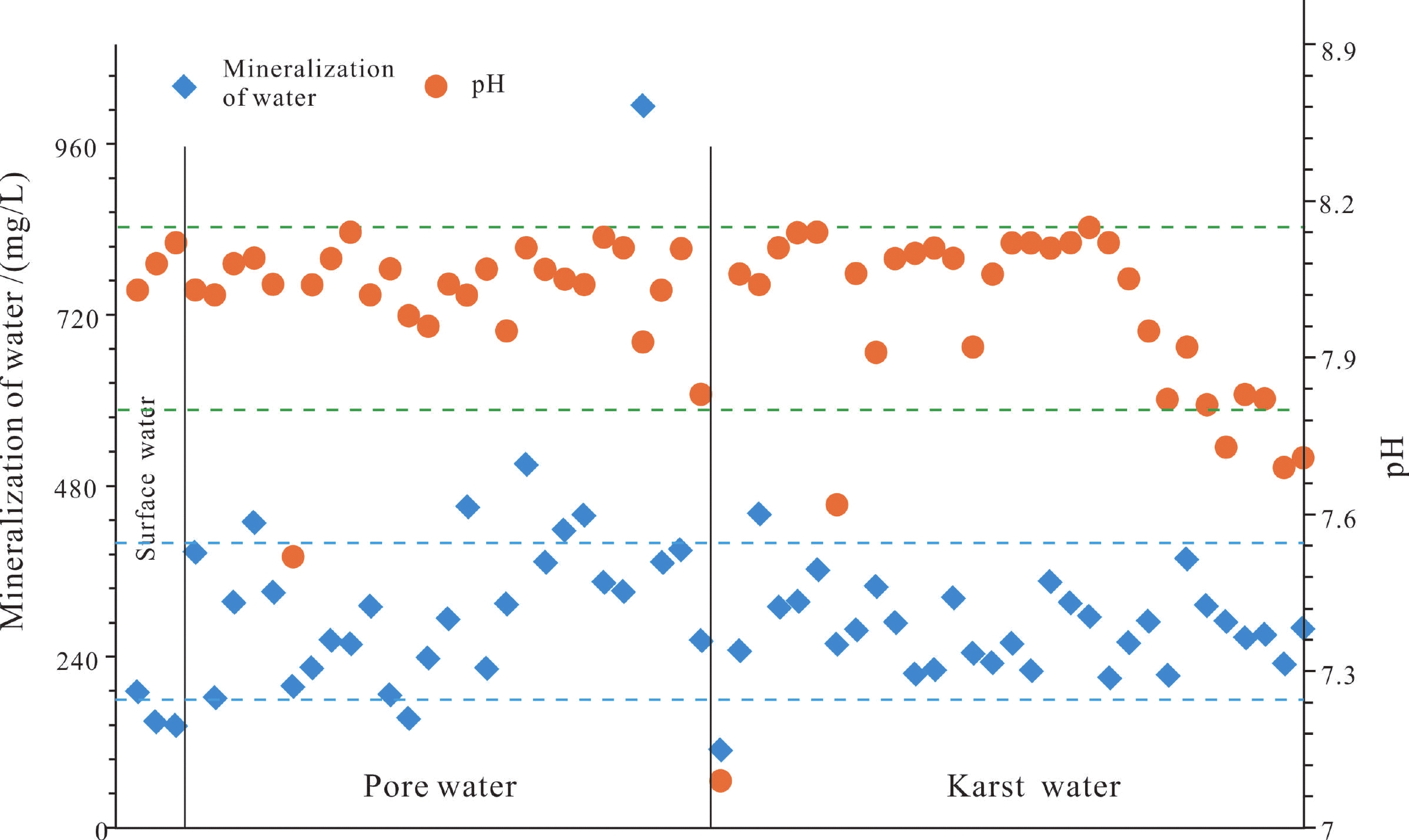
(2)掌握了区内地下水水化学特征。区内的地下水化学类型以重碳酸钙型为主,如图2所示,矿化度一般为0.18~0.40 g/L,基本为淡水。pH主要为7.80~8.15,水呈弱碱性。总硬度在100~300 mg/L,属于软水。
(3)查明了区内地下水污染状况及分布。区内浅层地下水污染主要表现为硝酸盐和氯离子超标。硝酸盐超标主要分布在农民居住区及农田周边,受人类活动影响较大。而深部岩溶地下水由于受人类活动影响小,水质较好。
(4)发现了大量优质天然矿泉水资源。经地下水微量元素特征分析,锶含量0.035~12.78 mg/L,锌含量0.001~3.418 mg/L。同时,地下水中还含有碘、锂等微量元素。经分析在咸宁汀泗桥镇白羊畈—赤壁官塘驿镇大贵畈—中伙铺镇一线发现富锶型饮用天然矿泉水,赤壁中伙铺琅桥一带为富锶、富锌复合型饮用天然矿泉水。初步估测年可开采矿泉水700 000 t以上,资源丰富。
(5)服务地方用水需求探采结合找水。本项目实施的探采结合井,除了查明区内水文地质条件,同时也具有一定的供水能力,如SZK01孔,降深7.9 m时,涌水量可达118.9 m3/d,已移交当地村委会,有效缓解了当地群众枯旱季缺水以及应急用水的需求。
6. 结论
该数据集形成于咸宁市开展1∶50 000汀泗桥幅水文地质调查工作中,项目成果及时服务于长江中游城市群国土空间规划和生态文明建设。通过地面调查,基本查明了区内地下水类型、补径排条件、含水岩组及其富水性等水文地质条件。钻探数据表明覆盖区存在多重岩溶空洞结构,应减少此区内的大规模无序开采而驱动岩溶地面塌陷,避免高层建筑群的规划建设和加强高层建筑或其它重大工程的地基处理。根据水化学测试结果,掌握了区内地下水的水化学特征及污染因子,并且发现区内存在资源丰富的富锶、锌型矿泉水,资源量丰富,适宜作优质饮用天然矿泉水开发。项目成果及应用,支撑服务当地经济绿色发展,改善民生,为长江中游城市群的可持续发展“添砖加瓦”。
致谢:咸宁市汀泗桥幅水文地质调查数据集是一项系统性工作,是项目组全体成员辛勤工作和慷慨付出的成果。另外,在数据集建设过程中,项目组得到了本单位技术委员会专家的指导和建议。稿件修改过程中,得到了审稿专家及编辑部的宝贵建设性意见,在此对他们表示诚挚的谢意。
1. Introduction
The city clusters along the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, boast a superior location with diverse resources, a beautiful ecological environment and considerable potential for development, constituting it as one of the ultra-large city clusters in China that shoulders the mission of boosting the rise of Central China. It is also an important component part of the Yangtze River Economic Belt(Jiang YH et al., 2017). In view of this, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey launched the project, in 2016, titled Comprehensive Geological Environmental Survey of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area Along the Beijing-Guangzhou High-speed Railway (a sub-project of the second-level project titled Hydrogeological Survey, on a Scale of 1∶50 000, in the City Cluster in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Along Xianning–Yueyang and Nanchang–Huaihua High-speed Railway, project No.: DD20160248), with the aim to provide a basic geological foundation for the suitability of planning and construction of city clusters. The hydrogeological survey of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, on a scale of 1∶50 000, is mainly to ascertain hydrogeological conditions and environmental geological problems in Xianning City; in particular, to determine karst distribution, paths of strong groundwater runoff and their cap rock structure in the city.
The Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, Xianning City, is located at the joint between the northern margin of Mufu Mountain and the southern margin of the Jianghan Plain. Overall topography is high in southeast and low in northwest. The trunk stream of the Yangtze River lies in the northwest side of the map sheet area and flows from southwest to northeast. The Tingsiqiao Map Sheet features diverse landforms consisting of plains, hills and mid-low mountains. It lies in a region of a subtropical monsoon climate and features four distinct seasons. It is cold in winter, hot in summer and mostly rains in spring and autumn. The average annual temperature, sunshine duration and annual precipitation in the area are 15–17°C, 1 754.5 h and around 1 577.4 mm respectively. Simple outcrops are distributed in the area, mainly consisting of Holocene and Pleistocene strata of Cenozoic Quaternary; Mesozoic strata, including Daye Formation of Lower Triassic and Cretaceous strata; Paleozoic strata, including Wujiaping Formation, Dalong Formation, and Longtan Formation of Upper Permian and Maokou Formation, Qixia Formation and Liangshan Formation of Lower Permian; Carboniferous strata, including Huanglong Formation and Dapu Formation, Maoshan Formation of Upper Silurian and Fentou Formation of Middle Silurian(Yang YL et al., 2018).
The hydrogeological survey of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet on a scale of 1∶50 000, lasted from January to December 2016, covering an accumulative area of 450 km2. Seven sets of data were obtained from the hydrogeological survey, including basic information from boreholes (12 boreholes), descriptions of strata revealed by boreholes (12 boreholes), results of the hydrogeological survey (77 pumping/domestic wells and 46 spring points), dynamic monitoring information of groundwater (2 places), the test results from inorganic water samples (61 samples) and organic water samples (9 samples). Distribution of field survey points is shown in Fig.1 and the metadata information of the Dataset is shown in Table 1.
1. Metadata Table of the Database (Dataset)Items Description Database (dataset) name Dataset of Hydrogeological Survey, on a Scale of 1∶50 000, in Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, Xianning City Database (dataset) authors Yang Yanlin, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Chen Lide, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Shao Changsheng, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Lu Tao, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Zhang Ao, Wuhan Center, China Geological SurveyData acquisition time January – December in 2016 Geographical area Tingsiqiao Town, Xian’an District, Xianning City, covering an area of about 450 km2; geographical coordinates: E 114°00′–114°15′, N 29°40′ –29°50′ Data format *.xls Data size 4.77 MB Data service system URL http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn Fund project A geological survey project initiated by China Geological Survey (DD20160248) Language Chinese Database (dataset) composition Basic data of boreholes.xls, description of strata revealed by boreholes.xls, survey points of pumping/domestic wells.xls, survey points of springs.xls, dynamic monitoring information of groundwater level.xls, test results from organic water samples.xls and test results from inorganic water samples.xls 2. Methods for Data Acquisition and Processing
2.1 Methods for Data Acquisition of Boreholes
The operations regarding boreholes such as borehole drilling, core logging, well drilling and completion, pumping tests and water sampling were all performed in accordance with DZ/T 0282−2015 Specification for the Hydrogeological Survey (1∶50 000) , DZ/T 0148−2014 Specification for Hydrological Well Drilling , DZ/T 0270−2014 Regulation of Groundwater Monitoring Well Construction and HJ 493−2009 Water Quality Sampling–Technical Regulation of the Preservation and Handling of Samples, among others . The data tables of basic data of boreholes and descriptions of strata revealed by boreholes were achieved by the collation and integration of important information on the boreholes.
During pumping tests, the water flow was determined by dual observation, checked with flowmeters (LXS-20F) and triangle weir tanks; the burial depth of the water level was measured with steel-tape water level gauges of the SWJ-80 type. Water samples were taken towards the end of the pumping tests. The multi-parameter tester, Manta2, was used to determine regular indices of water samples in the field such as water temperature, pH value, electrical conductivity (EC), dissolved oxygen (DO) and oxidation-reduction potential (Eh). Other parameters of the water samples were tested in the lab.
2.2 Data Acquisition of Hydrogeological Survey
Hydrogeological points of pumping/domestic wells and springs were carefully visited, measured and recorded during field surveys. The investigation of the pumping/domestic well points concentrated on the following parameters: wellhead diameter, well elevation and depth, groundwater-level burial depth, well wall structure and regular indices of water quality. The survey of the spring points concentrated on the hydrogeological conditions of spring outcrops, spring flow and regular indices of water quality, as well as its interannual changes. Spring flow was mainly measured by the velocity meter method (with the portable velocity meter, LS300-A), the volumetric method and the triangle weir method. Regular indices were measured with the multi-parameter tester, Manta2. Sampling points were deployed by comprehensive analysis of topography, landform, lithologic structure, hydrogeological units, hydrochemical anomalies of pumping/domestic wells and springs as well as the surrounding environment.
2.3 Collection and Data Processing of Water Samples
Water samples were taken, preserved and presented for testing in accordance with HJ 493−2009 Water Quality Sampling – Technical Regulation of the Preservation and Handling of Samples , HJ 494−2009 Water Quality–Guidance on Sampling Techniques and GB/T 5750.2−2006 Standard Examination Methods for Drinking Water – Collection and Preservation of Water Samples . The data contain 61 inorganic water samples (including 34 from wells, 12 from springs, 12 from boreholes and 3 from surface water) and 9 organic water samples (all from boreholes). The inorganic water samples were tested mainly in accordance with DD 2008−01 Specifications for Investigation and Assessment of Groundwater Pollution and the organic water samples, for the most part, were tested according to DD 2008−01 Specifications for Investigation and Assessment of Groundwater Pollution, US.EPA 8081A, US.EPA 8310 and US.EPA 524.
2.4 Dynamic Monitoring of Groundwater Level
Two dynamic monitoring points of typical domestic wells and boreholes were set up in accordance with DZ/T 0133 Regulation of Dynamical Monitoring of Groundwater in field surveys to further ascertain the hydrogeological conditions of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet area, especially the recharge, runoff and discharge conditions of groundwater, and to reveal the dynamic laws of groundwater. This will consequently provide a scientific basis for the assessment and scientific management of groundwater resources as well as the research, prevention and control of environmental geological problems. An automatic electronic water-level probe (Solinst 3001 LTC) was used to measure temperature, water level and electrical conductivity of the groundwater. The sampling intervals were 20 min and 30 min and the monitoring cycle was a hydrological year (Jan. 2018—Jan. 2019).
3. Description of Data Contents
The Dataset, presented by Excel, consists of seven data files, i.e., basic data of boreholes.xls, descriptions of strata revealed by boreholes.xls, survey points of pumping/domestic wells.xls, survey points of springs.xls, test results from organic water samples.xls, test results from inorganic water samples.xls and dynamic monitoring information of groundwater level.xls.
The data file “basic data of boreholes.xls” (Table 2) is used to describe the basic information of 12 hydrological boreholes. The data items of this file are: No., X coordinate and Y coordinate (CGCS2000 Coordinate System, the same hereinafter), geographical location, ground elevation, borehole head diameter, diameter, final depth, initial water level, burial depth of static water level, screen pipe section, main aquifer segment, maximal drawdown – water yield, sampling information and remarks. There are 12 lines of data in total, with each hydrological borehole being described on a single line.
2. Basic Data of BoreholesNo. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 No. string SZK01 2 X coordinate float 20230908 3 Y coordinate float 3302058 4 Geographical location string Group 6, Pengbei Village, Tingsiqiao Town, Xianning City, Hubei Province 5 Ground elevation m float 38.00 6 Borehole head diameter m float 130.00 7 Radius string 0–11.8 m, r=80 mm; 11.8–39 m, r=73 mm; 39.0–101.0 m, r=61 mm 8 Final depth m float 101.00 9 Initial water level m float 1.00 10 Burial depth of static water level m float 1.00 11 Screen section string 13.00–101.00 m 12 Main aquifer segment string 20.0–21.3 m; 42.0–44.6 m; 65.0–67.4 m 13 Max. drawdown – water yield string 7.90 –118.90 m3/d 14 Sampling information string Water sample: organic samples and inorganic samples 15 Remarks string No karst caves discovered The data file “descriptions of strata revealed by boreholes.xls” (Table 3) is used to describe the information on stratigraphic structures and the lithology revealed by the 12 hydrological boreholes. The data items in this file are: borehole No., stratum No., stratum age, elevation of stratum bottom, burial depth of stratum bottom, stratum thickness and description of stratum lithology.
3. Description of Strata Revealed by BoreholesNo. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Borehole no. string SZK01 2 Stratum no. int 1 3 Stratum age string Qh 4 Elevation of stratum bottom m float 36 5 Depth of stratum bottom m float 2 6 Stratum thickness m float 2 7 Description of stratum lithology string Rufous – dust-color arable soil, short-column-shaped core, rough section, slightly humid, a small amount of plant root system visible locally The data file “survey points of pumping/domestic wells.xls” (Table 4) is principally used to describe the basic information on survey points of pumping/domestic wells. The data items in this file are: field No., X coordinate, Y coordinate, geographical location, wellhead elevation, wellhead diameter, burial depth of water level, well depth, well wall structure, water intake horizon, lithology of aquifer, allowable yield, water temperature, pH value, taste, air temperature, odor, dissolved oxygen, EC, Eh and survey date. Each survey point is described on a single line, totaling 77 lines.
4. Reconnaissance Survey of Pumping (Domestic) WellsNo. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Field No. string D533 2 X coordinate float 20218231 3 Y coordinate float 3298611 4 Geographical location string Group 7, Guantang Village, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City, Hubei Province 5 Wellhead elevation m float 49.1 6 Wellhead diameter mm float 650.0 7 Burial depth of water level m float 1.64 8 Well depth m float 12 9 Well wall structure string Bricked 10 Water intake horizon string Pore phreatic water 11 Lithology of aquifer string Sandy soil 12 Water temperature ℃ float 19.73 13 Allowable yield m3/h float 0.0083 14 pH value float 6.96 15 Taste string No 16 Air temperature ℃ float 30 17 Odor string No 18 Dissolved oxygen mg/L float 6.21 19 EC µs/cm float 291 20 Eh mV float 356 21 Survey date Date 15-8-2016 The data file “survey points of springs.xls” (Table 5) is predominantly used to describe the basic information on spring survey points. The data items in this file are: field No., X coordinate, Y coordinate, geological location, spring type, ground elevation, lithology of aquifer, origin of spring, main purpose, air temperature, method of measuring water flow, water flow, water temperature, chroma, taste, odor, transparency, pH value, Eh, dissolved oxygen, EC and survey date. Each survey point is described on a single line, totaling 46 lines.
5. Reconnaissance Survey of SpringsNo. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Field No. string D531 2 X coordinate float 20218487 3 Y coordinate float 3297583 4 Geographical location string Group 10, Guantang Village, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City 5 Spring type string Gravity spring 6 Ground elevation m float 62.0 7 Lithology of aquifer string T1d4dolomitic limestone 8 Origin of spring Image 
9 Main purpose string Living and irrigation 10 Air temperature ℃ float 29.0 11 Method of measuring water flow string Flowmeter 12 Water flow L/s float 2.3 13 Water temperature ℃ float 19.64 14 Chroma string No 15 Taste string No 16 Odor string No 17 Transparency string Clear and transparent 18 pH value float 7.44 19 Eh mV float 339 20 Dissolved oxygen mg/L float 6.63 21 EC µs/cm float 995.4 22 Survey date Date 15-8-2016 The data file “test results from inorganic water samples.xls” (please refer to the Dataset for the data table) is mainly used to record the information on the collection and test results from inorganic water samples. The data items in this file are: sample presentation No., X coordinate, Y coordinate, water sample type, total dissolved solids, total hardness, total alkalinity, total acidity, soluble SiO2, NO3−, NO2−, NH4+, SO42−, CO32−, HCO32−, Cl−, F−, PO43−, Na, K, Ca, Mg, Fe3+, Fe2+, free CO2, pH value, bromide, iodide, Al, Li, Sr, Zn, Cu, Hg, Cd, Ba, Cr6+, Pb, Co, V, Mo, Mn, Ni, As, Ag, HBO2 and oxygen consumption. There are 44 testing indices. Each sample is recorded in a single line, totaling 61 lines.
The data file “test results from organic water samples.xls” (please refer to the Dataset for the data table) is primarily used to record the information on the collection and test results from organic water samples. The information in this file contains three items of basic information (sample No., testing No. and sample description) and test items (including 25 items of halohydrocarbon, chlorobenzene and mononuclear aromatics, 11 items of organic chlorine pesticides and 1 item of benzo(a)pyrene, totaling 37 items). Each sample is recorded on a line, totaling 9 lines.
4. Data Quality Control and Assessment
4.1 Drilling Data
The data quality control of hydrogeological boreholes includes quality control over the data such as borehole diameter, core recovery percentage, borehole depth, borehole deviation, hydrological observation, pumping test, well completion technique, well cementation, borehole sealing, original records and technical archives. Inspection and acceptance were carried out for these data in accordance with DZ/T 0282−2015 Specification for Hydrogeological Survey (1∶50 000) , DZ/T 0148−2014 Specification for Hydrological Well Drilling and DL/T 5213−2005 Code of Pumping Test in Boreholes for Hydropower and Water Conservancy Engineering . Meanwhile, the integrity, regularity and accuracy of the data were carefully checked in order to ensure the quality of drilling and data records.
4.2 Data Obtained From Surveys
A ground survey was conducted in strict accordance with applicable regulations and specifications such as DZ/T 0282−2015 Specification for Hydrogeological Survey (1∶50 000) , covering an area of the hydrogeological survey, on a scale of 1∶50 000, of 450 km2. The points for hydrogeological observation were positioned using GPS (Garmin Montana 680) in combination with terrain and surface features. All GPS data were calibrated, with errors less than 50 m. All records obtained from field surveys were kept in the form of a survey card, ensuring the integrity of the contents and accuracy of the descriptions. A three-level management system was adopted to check and verify the data of the survey points (such as the ones from pumping/domestic wells and springs), including the data filled manually and the electronic records.
4.3 Test Results of Water-Quality Samples
All of the inorganic and organic water samples were tested in the Changsha Supervision and Inspection Center of Mineral Resources, the Ministry of Land and Resources (Hunan Province Geological Testing Institute). The inorganic water samples were tested under an ambient temperature of 20°C and an ambient humidity of 60% with inductive-coupled plasma optical emission spectrometers; ICP–MS and ICAP–6 300 ICP, visible spectrophotometer 722 S and dual-channel atomic fluorescence spectrometer AFS-830a. The organic water samples were tested under an ambient temperature of 21.8°C and an ambient humidity of 52% with a gas chromatograph−mass spectrometer (with purge and trap), a gas chromatograph and a high-performance liquid chromatograph. All of the water samples were tested in accordance with DZ/T 0130.6–2006 Specification of Testing Quality Management for Geological Laboratories – Part 6 Water Analysis . Meanwhile, blank and parallel tests were carried out in the lab for each batch of the water samples, thus ensuring that the test results are accurate. Furthermore, the detection limits of the analysis methods selected all reached or exceeded the requirements specified in the relevant specifications.
4.4 Dynamic Monitoring Data of Groundwater
The dynamic monitoring of groundwater was performed with electronic measuring probes. The monitoring facilities and devices at monitoring points were irregularly checked to ensure that they were in good condition and operated normally. Moreover, water level gauges were adopted to measure water levels, which were then compared with the data obtained with the probes. According to repeated inspection and verification, the dynamic monitoring data are true and credible.
5. Value of the Data
The Dataset provides a set of fundamental data resources of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet area. The following results of the area were mainly achieved based on the field surveys, water quality testing and the exploration-production wells.
(1) The hydrogeological conditions of karst in the area were ascertained. In the karst-covered area, karst is well developed, multi-kast-cave structures developed vertically and karst groundwater comes into contact with shallow water. In the bare karst area, karst is well developed and various karst terrains are frequently visible. This area boasts many karst springs, which features a large water yield and is significantly affected by rainfall.
(2) The hydrochemical features of the groundwater in the area were understood. The groundwater is mainly of the bicarbonate type (Fig. 2), with a general mineralization degree of 0.18–0.40 g/L. It is basically fresh water and weakly alkaline, with a pH value ranging from 7.80–8.15. Additionally, it is soft water with a total hardness ranging from 100–300 mg/L.
(3) The status quo and distribution of groundwater pollution in the area were determined. The shallow groundwater pollution is mainly caused by nitrate(s) and Cl-exceeding their limits. The pollution caused by nitrate(s) exceeding its limits is significantly influenced by human activities and is mainly prevalent in the residential areas of farmers and the surrounding farmland areas. However, deep karst groundwater enjoys high water quality since it is only marginally affected by human activities.
(4) A large volume of high-quality natural mineral water resources was discovered. According to the analysis of characteristics of trace elements in the groundwater, the Sr content is 0.035–12.78 mg/L and Zn content is 0.001–3.418 mg/L in the groundwater. Meanwhile, there are other trace elements in the groundwater such as I and Li. According to hydrochemical analysis, Sr-rich potable natural mineral water was discovered along Baiyangfan, Tingsiqiao Town, Xianning City–Daguifan, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City–Zhonghuopu Town and Chibi City. Sr-rich and Zn-rich composite potable natural mineral water was discovered in the Langqiao area, Zhonghuopu Town and Chibi City. It is initially estimated that an annual allowable yield of the mineral water is 700 000 t. Therefore, the area boasts rich mineral water resources.
(5) Exploration-production wells were drilled to meet the local demand for water. The exploration-production wells drilled cannot only be used to ascertain hydrogeological conditions but also have a certain capacity to supply water, such as borehole SZK01, which has been handed over to the local village committees. The water yield of SZK01 reaches up to 118.9 m3/d at a drawdown of 7.9 m, effectively alleviating local demand for water during the dry seasons and in a case of emergency.
6. Conclusion
The Dataset was established through the hydrogeological survey, on a scale of 1∶50 000, of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, Xianning, aiming to timely serve the land space planning and ecological civilization building of the city clusters along the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. The hydrogeological conditions in the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet area such as the types, recharge, runoff and discharge of the groundwater and water-bearing rock formations and their water-yield property were ascertained through a ground survey. The drilling data revealed that multi-karst-cave structures exist in the covered karst area. Therefore, large-scale disordered exploitation that will drive the karst ground to collapse shall be reduced, the planning and construction of high-rise building clusters shall be avoided and the foundations of high-rise buildings or other critical projects will be strengthened. The hydrochemical features and pollutants of groundwater were grasped according to the results of the hydrochemical testing. Meanwhile, a large amount of Sr-rich and Zn-rich mineral water was discovered in the area, which were suitable to be developed as high-quality potable natural mineral water. The results of the hydrogeological survey and their application will support and serve the green development of the local economy, improve people’s livelihood and make contributions to the sustainable development of the city cluster in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River.
Acknowledgments: We would like to extend our sincere appreciation to all members participating in the systematical hydrogeological survey, on a scale of 1∶50 000, of the Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, Xianning for their hard work and generous devotion. Our sincere appreciation also goes to the experts from the technical committee of the Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey for their guidance and recommendations offered during the development of the Dataset. Lastly, our thanks go to the peer reviewers and the editors for their valuable opinions on the revision of this paper.
-
表 1 数据库(集)元数据简表
条目 描述 数据库(集)名称 1∶50 000咸宁市汀泗桥幅水文地质调查数据集 数据库(集)作者 杨艳林,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
陈立德,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
邵长生,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
路韬,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
张傲,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心数据时间范围 2016年1月—2016年12月 地理区域 咸宁市咸安区汀泗桥镇,面积约450 km2;地理坐标:东经114°00′~114°15′,北纬29°40′~29°50′ 数据格式 *.xls 数据量 4.77 MB 数据服务系统网址 http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn 基金项目 中国地质调查局地质调查项目(DD20160248)资助 语种 中文 数据库(集)组成 钻孔基础数据.xls、钻孔地层描述信息.xls、机民井点调查表.xls、泉点调查表.xls、地下水位动态监测表.xls、有机水样测试结果.xls、无机水样测试结果.xls 表 2 钻孔基本信息
序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 钻孔编号 字符串 SZK01 2 X 浮点型 20230908 3 Y 浮点型 3302058 4 地理位置 字符串 湖北省咸宁市汀泗桥镇彭碑村六组 5 地面高程 m 浮点型 38.00 6 开孔孔径 m 浮点型 130.00 7 孔径 字符串 0~11.8 m,r=80 mm;11.8~39 m,r=73 mm;39.0~101.0 m,r=61 mm 8 终孔深度 m 浮点型 101.00 9 初见水位 m 浮点型 1.00 10 静水位埋深 m 浮点型 1.00 11 滤水管段 字符串 13.00~101.00 m 12 主要含水层段 字符串 20.0~21.3 m;42.0~44.6 m;65.0~67.4 m 13 极大降深−涌水量 字符串 7.90 ~118.90 m3/d 14 取样情况 字符串 水样:有机样与无机样 15 备注 字符串 未见溶洞 表 3 钻孔地层描述
序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 钻孔编号 字符串 SZK01 2 层号 整数型 1 3 地层时代 字符串 Qh 4 层底高程 m 浮点型 36 5 层底埋深 m 浮点型 2 6 层厚 m 浮点型 2 7 地层岩性描述 字符串 红褐色—灰褐色耕植土,岩芯呈短柱状,切面较粗糙,略潮湿,局部可见少量植物根系 表 4 机民井点普查调查表
序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 野外编号 字符串 D533 2 X 浮点型 20218231 3 Y 浮点型 3298611 4 地理位置 字符串 湖北省赤壁市官塘驿镇官塘村七组 5 井口高程 m 浮点型 49.1 6 井口直径 mm 浮点型 650.0 7 水位埋深 m 浮点型 1.64 8 井深 m 浮点型 12 9 井壁结构 字符串 砖彻 10 取水层位 字符串 孔隙潜水 11 含水层岩性 字符串 砂土 12 水温 ℃ 浮点型 19.73 13 开采量 m3/h 浮点型 0.008 3 14 pH 浮点型 6.96 15 味 字符串 无 16 气温 ℃ 浮点型 30 17 气味 字符串 无 18 溶解氧 mg/L 浮点型 6.21 19 电导率 μs/cm 浮点型 291 20 氧化还原电位 mV 浮点型 356 21 调查时间 日期型 2016-8-15 表 5 泉点普查调查表
序号 数据项名称 单位 数据类型 实例 1 野外编号 字符串 D531 2 X 浮点型 20218487 3 Y 浮点型 3297583 4 地理位置 字符串 赤壁市官塘驿镇官塘村十组 5 泉水类型 字符串 下降泉 6 地面高程 m 浮点型 62.0 7 含水层岩性 字符串 T1d4白云质灰岩 8 泉水成因 图片 
9 主要用途 字符串 生活、灌溉用水 10 气温 ℃ 浮点型 29.0 11 流量测定方法 字符串 流速仪 12 泉水流量 L/s 浮点型 2.3 13 泉水温度 ℃ 浮点型 19.64 14 色度 字符串 无 15 味 字符串 无 16 气味 字符串 无 17 透明度 字符串 清澈透明 18 pH 浮点型 7.44 19 氧化还原电位 mV 浮点型 339 20 溶解氧 mg/L 浮点型 6.63 21 电导率 μs/cm 浮点型 995.4 22 调查时间 日期型 2016-8-15 1 Metadata Table of the Database (Dataset)
Items Description Database (dataset) name Dataset of Hydrogeological Survey, on a Scale of 1∶50 000, in Tingsiqiao Map Sheet, Xianning City Database (dataset) authors Yang Yanlin, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Chen Lide, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Shao Changsheng, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Lu Tao, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Zhang Ao, Wuhan Center, China Geological SurveyData acquisition time January – December in 2016 Geographical area Tingsiqiao Town, Xian’an District, Xianning City, covering an area of about 450 km2; geographical coordinates: E 114°00′–114°15′, N 29°40′ –29°50′ Data format *.xls Data size 4.77 MB Data service system URL http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn Fund project A geological survey project initiated by China Geological Survey (DD20160248) Language Chinese Database (dataset) composition Basic data of boreholes.xls, description of strata revealed by boreholes.xls, survey points of pumping/domestic wells.xls, survey points of springs.xls, dynamic monitoring information of groundwater level.xls, test results from organic water samples.xls and test results from inorganic water samples.xls 2 Basic Data of Boreholes
No. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 No. string SZK01 2 X coordinate float 20230908 3 Y coordinate float 3302058 4 Geographical location string Group 6, Pengbei Village, Tingsiqiao Town, Xianning City, Hubei Province 5 Ground elevation m float 38.00 6 Borehole head diameter m float 130.00 7 Radius string 0–11.8 m, r=80 mm; 11.8–39 m, r=73 mm; 39.0–101.0 m, r=61 mm 8 Final depth m float 101.00 9 Initial water level m float 1.00 10 Burial depth of static water level m float 1.00 11 Screen section string 13.00–101.00 m 12 Main aquifer segment string 20.0–21.3 m; 42.0–44.6 m; 65.0–67.4 m 13 Max. drawdown – water yield string 7.90 –118.90 m3/d 14 Sampling information string Water sample: organic samples and inorganic samples 15 Remarks string No karst caves discovered 3 Description of Strata Revealed by Boreholes
No. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Borehole no. string SZK01 2 Stratum no. int 1 3 Stratum age string Qh 4 Elevation of stratum bottom m float 36 5 Depth of stratum bottom m float 2 6 Stratum thickness m float 2 7 Description of stratum lithology string Rufous – dust-color arable soil, short-column-shaped core, rough section, slightly humid, a small amount of plant root system visible locally 4 Reconnaissance Survey of Pumping (Domestic) Wells
No. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Field No. string D533 2 X coordinate float 20218231 3 Y coordinate float 3298611 4 Geographical location string Group 7, Guantang Village, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City, Hubei Province 5 Wellhead elevation m float 49.1 6 Wellhead diameter mm float 650.0 7 Burial depth of water level m float 1.64 8 Well depth m float 12 9 Well wall structure string Bricked 10 Water intake horizon string Pore phreatic water 11 Lithology of aquifer string Sandy soil 12 Water temperature ℃ float 19.73 13 Allowable yield m3/h float 0.0083 14 pH value float 6.96 15 Taste string No 16 Air temperature ℃ float 30 17 Odor string No 18 Dissolved oxygen mg/L float 6.21 19 EC µs/cm float 291 20 Eh mV float 356 21 Survey date Date 15-8-2016 5 Reconnaissance Survey of Springs
No. Name of data item Unit Data type Example 1 Field No. string D531 2 X coordinate float 20218487 3 Y coordinate float 3297583 4 Geographical location string Group 10, Guantang Village, Guantangyi Town, Chibi City 5 Spring type string Gravity spring 6 Ground elevation m float 62.0 7 Lithology of aquifer string T1d4dolomitic limestone 8 Origin of spring Image 
9 Main purpose string Living and irrigation 10 Air temperature ℃ float 29.0 11 Method of measuring water flow string Flowmeter 12 Water flow L/s float 2.3 13 Water temperature ℃ float 19.64 14 Chroma string No 15 Taste string No 16 Odor string No 17 Transparency string Clear and transparent 18 pH value float 7.44 19 Eh mV float 339 20 Dissolved oxygen mg/L float 6.63 21 EC µs/cm float 995.4 22 Survey date Date 15-8-2016 -
[1] 环境保护部. 2009. 水质采样 样品的保存和管理技术规定: HJ 493−2009 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出出版社. [2] 环境保护部.2009. 水质采样技术指导: HJ 494−2009 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. [3] 姜月华, 林良俊, 陈立德, 倪化勇, 葛伟亚, 成杭新, 翟刚毅, 王贵玲, 班宜忠, 李媛, 雷明堂, 谭成轩, 苏晶文, 周权平, 张泰丽, 李云, 刘红樱, 彭柯, 王寒梅. 2017. 资源环境条件与重大地质问题[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1045−1061. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201706002 [4] 杨艳林, 邵长生, 靖晶. 2018. 系统聚类法在划分岩溶地下水化学类型中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 42(04): 738−744. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201804014 [5] 中华人民共和国地质矿产部. 1994. 地下水动态监测规程: DZ/T0133−1994 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. [6] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 2005. 钻孔抽水试验规程: DL/T 5213−2005 [S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社. [7] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2006. 地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范: DZ/T 0130−2006 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. [8] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2014. 水文水井地质钻探规程: DZT 0148−2014 [S].北京: 中国标准出版社. [9] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2014. 地下水监测井建设规范: DZ/T 0270−2014 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. [10] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2015. 水文地质调查规范: DZT 0282−2015(1∶50 000) [S]. 北京: 地质出版社. [11] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 2006. 生活饮用水标准检验方法水样的采集和保存: GB/T 5750.2−2006 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. [1] Jiang Yuehua, Lin Liangjun, Chen Lide, Ni Huayong, GeWeiya, Cheng Hangxin, Zhai Gangyi, Wang Guiling, Ban Yizhong, Li Yuan, Lei Mingtang, Tan Chengxuan, Su Jingwen, Zhou Quanping, Zhang Taili, Li Yun, Liu Hongying, Peng Ke, Wang Hanmei. 2017. Research on conditions of resources and environment and major geological problems in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1045−1061 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201706002
[2] Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. 2009. Water quality sampling-technical regulation of the preservation and handling of samples: HJ 493−2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press (in Chinese). [3] Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. 2009. Water quality-Guidance on sampling techniques: HJ 494−2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press (in Chinese). [4] Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of the People’s Republic of China.1994. Code for dynamic monitoring of groundwater: DZ/T 0133-1994[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). [5] National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. 2005. Code of pumping test in borehole for hydropower and water conservancy engineering: DL/T 5213-2005[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press (in Chinese). [6] Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2006. The specification of testing quality management for geological laboratories: DZ/T 0130−2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). [7] Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2014. The specification for hydrogeological well drilling: DZ/T 0148−2014[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). [8] Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2014. Regulation of groundwater monitoring well construction: DZ/T 0270-2014[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). [9] Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China.2015. Specification for hydrogeological survey(1∶50 000): DZ/T 0282−2015[S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese). [10] Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. 2006. Standard examination methods for drinking water-Collection and preservation of water samples: GB/T 5750.2−2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). [11] Yang Yanlin, Shao Changsheng, Jing Jing. 2018. The application of systematic clustering method to the classification of chemical types of karst groundwater[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 42(04): 738−744 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht201804014
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李敬杰,连晟,王明国,张智印,张涛. 藏东多曲河流域锶富集水化学特征及控制因素. 环境科学. 2024(04): 2067-2079 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙岐发,孙茁桉,贾林刚,田辉,郭晓东,都基众,李旭光,李霄,贾立国. 吉林省长春莲花山地区地下水中锶及偏硅酸的形成机理研究. 中国地质. 2023(01): 181-191 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 张志,徐洪苗,钱家忠,谢杰,陈皓龙,朱紫祥. 综合物探方法在矿泉水勘查中的应用——以泾县榔桥地区为例. 物探与化探. 2023(03): 690-699 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘思军. 水文地质问题对工程地质勘查的影响分析. 世界有色金属. 2021(09): 147-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: