Blueschists in Damenglong, Jinghong City, southwestern Yunnan, China: Petrology and metamorphism and their implications for the Paleo-Tethys
-
摘要:研究目的
蓝片岩为古洋壳的俯冲及洋-陆和陆-陆碰撞拼贴的产物,对深入探索洋壳或陆壳俯冲变质过程以及造山带的形成演化具有十分重要的意义。本文选择以滇西景洪大勐龙地区新发现的蓝片岩为研究对象,探讨其对昌宁—孟连古特提斯洋俯冲-造山背景的制约。
研究方法通过岩相学与矿物化学分析,根据矿物组合的不同,识别出研究区内两种不同类型的蓝片岩,初步建立变质演化P-T轨迹,并结合区域地质资料分析蓝片岩的成因机制与就位的动力学背景,约束昌宁—孟连古特提斯洋俯冲-造山演化。
研究结果获得白云母石榴蓝闪石英片岩峰期变质温压条件为T=450~490℃,P=0.90~1.45 GPa,绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩具有较低的峰期变质温压条件为T=430~470℃,P=0.69~0.73 GPa,并初步建立了两种不同类型蓝片岩变质演化P-T轨迹。
结论两类峰期变质条件的差异可能为俯冲隧道中不同俯冲深度的蓝片岩,这一研究成果为进一步探索昌宁—孟连古特提斯洋的俯冲消减-闭合的构造演化过程提供重要依据。
创新点:首次发现滇西景洪大勐龙地区高压蓝片岩,查明两类蓝片岩的变质峰期条件,建立变质演化P-T轨迹,约束昌宁—孟连古特提斯洋的俯冲消减-闭合的构造演化过程。
Abstract:This paper is the result of geological survey engineering.
ObjectiveBluesschist is the product of subduction of ancient oceanic crust and collage of ocean-continental and land-continental collisions. It is of great significance to further explore the subduction metamorphism of oceanic crust or continental crust and the formation and evolution of orogenic belts. In this paper, the newly discovered bluesschist in Damenglong area, Jinghong, western Yunnan, is selected as the research object, and its restriction on the Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Ocean subduction-orogenic setting is discussed.
MethodsThrough petrography and mineral chemistry analysis, two different types of bluesschist in the study area are identified according to different mineral combinations, and the P-T trajectory of metamorphic evolution is initially established. Combined with regional geological data, the genetic mechanism and dynamic background of bluesschist are analyzed to constrain the evolution of Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Ocean subduction and orogeny.
ResultsThe results show that the peak metamorphic temperature and pressure conditions of muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists are T =450-490℃, P=0.90-1.45 GPa, and chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schist with the low peak metamorphic temperature and pressure conditions are T = 430-470℃, P = 0.69-0.73 GPa. The P-T tracks of metamorphic evolution of two different types of bluesschist are preliminarily established.
ConclusionsThe metamorphic differences of the two types of blueschists occur might because the metamorphic rocks subducted to different depths were uplifted to the surface via subduction tunnels through the exhumation mechanism. The results of this study will provide an important basis for further exploring the subduction and closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Changning-Menglian suture zone.
-
1. 引言
地质学者们普遍认为蓝片岩的形成与大洋板块的俯冲作用有关,为古洋壳的俯冲及洋-陆和陆-陆碰撞拼贴所形成的缝合带的标志(Ernst, 1972, 1998;董申保,1989;Liou et al., 1989, 2003;魏春景,1994)。因此,对蓝片岩的形成、温压条件及变质作用演化等的研究能够为查明古板块的大陆动力学演化提供重要理论依据,对深入探索洋壳或陆壳俯冲变质过程以及造山带的形成演化具有十分重要的意义。
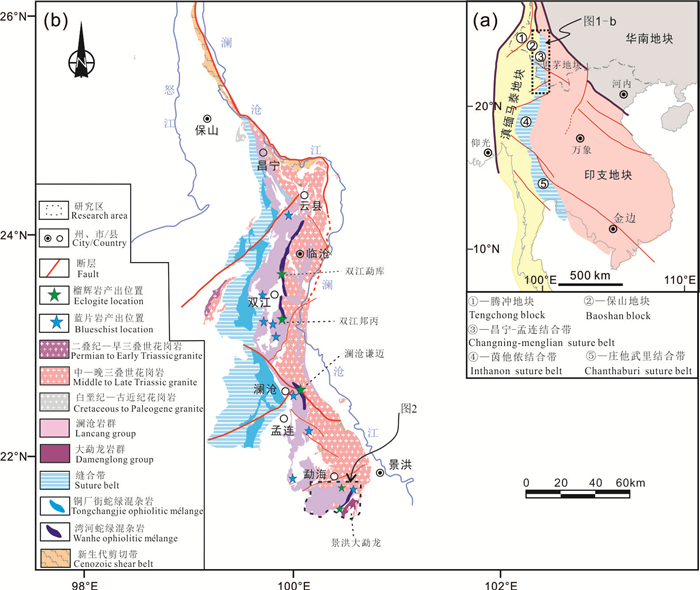
滇西昌宁—孟连结合带作为冈瓦纳大陆和欧亚陆块的分界,完整地记录了原特提斯洋的扩张、古特提斯洋的俯冲消减、洋盆闭合及闭合后陆-陆碰撞造山等一系列连续演化地质过程,为特提斯洋的地质演化历史和构造格架的研究提供了重要解剖窗口,因此一直是国内外特提斯研究的热点区域(刘本培等, 1993, 2002;钟大赉,1998;Feng et al., 2002;潘桂棠等,2003;段向东,2008;Jian et al., 2009a, b;李文昌等,2010;李静等,2015;邓军等,2016;王冬兵等,2016;孙载波等;2017;刘桂春等,2017;王保弟等,2018;Wang et al., 2019a)。关于该带内高压变质岩的研究近年来取得了一系列重要成果和进展,自云南省地质调查院通过1∶5万地质填图首次在双江县勐库地区发现并报道退变质榴辉岩以来(李静等,2015),迅速引起了地质学家的极大关注,与此同时,相关学者也对该地区榴辉岩的矿物组合、变质演化P-T-t轨迹、原岩地球化学特征及原岩形成时代等开展相关研究工作(徐桂香等,2016;陈光艳等,2017;李静等,2017;孙载波等, 2017, 2018;Wang et al., 2019a)。关于该带内的蓝片岩,自20世纪80年代彭兴阶等(1982)首次报道以来,有关研究者对其物质组成、变质作用与时代、岩石地球化学和原岩形成时代等进行研究(彭兴阶等,1983;张儒瑗等, 1989, 1990;Zhang et al., 2004;Fan et al., 2015;王舫等,2016;毕丽莎,2018;Wang et al., 2019b;王慧宁等,2019);目前该带内蓝片岩的研究也仅停留在双江粟义、澜沧上允和惠民等地。随着1∶5万地质填图进一步开展,自北向南相继在双江邦丙、澜沧谦迈、景洪大勐龙等地发现多处榴辉岩、蓝片岩等高压变质岩(孙载波等,2019;彭智敏等, 2019, 2022)(图 1)。故此,本文选择以景洪大勐龙地区新发现的蓝片岩为研究对象,通过详细岩石学、岩相学研究明确其变质演化过程,初步建立变质演化P-T轨迹,并结合区域地质资料分析蓝片岩的成因机制与就位的动力学背景,探讨其对滇西地区特提斯俯冲-造山与构造演化的制约。
![]() 图 1 东南亚主要板块构造带分布图(a,据Sone and Metcalfe, 2008)和三江南段昌宁—孟连结合带地质简图(b,据Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015修改)Figure 1. (a) Tectonic framework of Southeast Asia (modified from Sone and Metcalfe, 2008); (b) Geological sketch of the Changning-Menglian suture belt (modified from Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015)
图 1 东南亚主要板块构造带分布图(a,据Sone and Metcalfe, 2008)和三江南段昌宁—孟连结合带地质简图(b,据Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015修改)Figure 1. (a) Tectonic framework of Southeast Asia (modified from Sone and Metcalfe, 2008); (b) Geological sketch of the Changning-Menglian suture belt (modified from Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015)2. 区域地质背景
位于滇西地区的澜沧岩群,其地层时代、物质来源以及变质时代等的研究,一直是云南省基础地质研究中长期存在争议的一个地层单位。该套地层北起凤庆县,经云县、双江、澜沧县和西双版纳等地区,往南可延伸至缅甸境内,呈近南北向狭长条状分布(图 1)。云南区测队1965年创名于澜沧县❶,原始定义:绢-白云石英片岩、绢云微晶片岩、千枚岩及板岩等,有铁、磷、硅质岩的夹层,属寒武纪。云南区测队5分队、2分队(1979)❷❸进一步细分为8个组:阿克组、南勒组、巴夜组、南木岭组、勐井山组、曼来组、惠民组、南坑河组,分别归入元古代、晚元古代。云南省地质科学研究所(1984年专题研究)认为上列8个组中下部的3个组可能是上部层位的构造重复,建议只保留和使用上部的5个组,属晚元古代(6~10亿年)。云南省地质矿产局(1990)在《云南省区域地质志》中将其划分为南木岭组、惠民组、西定组,认为属中元古代。云南省地质矿产局(1996)在《云南省岩石地层》中采用云南省地质科学研究所(1984)专题研究的意见,将澜沧岩群划分5个组级单位,属晚元古代。云南省地质调查院(2019)❹根据岩石组合特征、大量同位素年学资料及变质变形特征等将其划分了5个岩组:青白口系南木岭岩组、南华系勐井山岩组、震旦系—寒武系曼来岩组、奥陶系惠民岩组和志留系南坑河岩组,各岩组之间脆韧性剪切带接触。从沉积作用的角度看,其为与湾河蛇绿混杂岩对应的西部被动大陆边缘沉积,时代主体上属早古生代,可能还包括了少量陆壳残片,从大地构造演化角度看,其是特提斯大洋关闭过程中形成的俯冲增生杂岩,经历了较为复杂的演化历史。
产于该套地层内低温高压变质岩主要分布于澜沧县上允、惠民和勐海县西定一带(周维全和林文信,1982;Zhang et al., 1993;钟大赉,1998),岩石类型包括蓝闪多硅白云母片岩、绿泥绿帘蓝闪钠长片岩和石榴多硅白云母片岩等(Zhang et al., 1993;赵靖等,1993;毕丽莎,2014)。通过对高压低温变质岩内多硅白云母和蓝闪石进行Ar-Ar定年分析获得294~214 Ma的变质年龄(赵靖等,1994;Heppe et al., 2007;毕丽莎,2018)。景洪大勐龙地区新发现的蓝片岩产于湾河蛇绿混杂岩南段(图 2),湾河蛇绿混杂岩最早由1∶25万临沧、滚龙幅❶发现并命名,主要出露于双江县湾河—银厂河一带,南北延伸约25 km,为临沧花岗岩基内的一个巨大捕虏体,并认为是铜厂街蛇绿混杂岩经构造改造、花岗岩浆顶托等作用形成的构造岩片。通过近年来的1∶5万地质填图,该蛇绿混杂岩北起云县头道水,经双江勐库银厂河、澜沧黑河、景洪大勐龙一带,向南延入缅甸,南北延伸超过200 km(图 1),其空间分布、物质组成、成矿作用和形成年代等方面都与西侧铜厂街蛇绿混杂岩存在一定差异(刘桂春等,2017),并在该结合带内发现高压—超高压变质岩—退变质榴辉岩(李静等,2015;孙载波等,2019)。该蛇绿混杂岩现存岩石有白云石英片岩、绿片岩、英云闪长岩-斜长岩、纹层状斜长角闪岩-变质(堆晶)辉长岩、辉石橄榄岩、蓝片岩、退变榴辉岩等。代表了蛇绿岩套的远洋沉积、洋底玄武岩、浅色岩系、镁铁质堆晶杂岩、变质橄榄岩、高压—超高压变质岩。除特殊标注外,本文矿物缩写代码据Whitney and Evans (2010)。
3. 岩石学特征
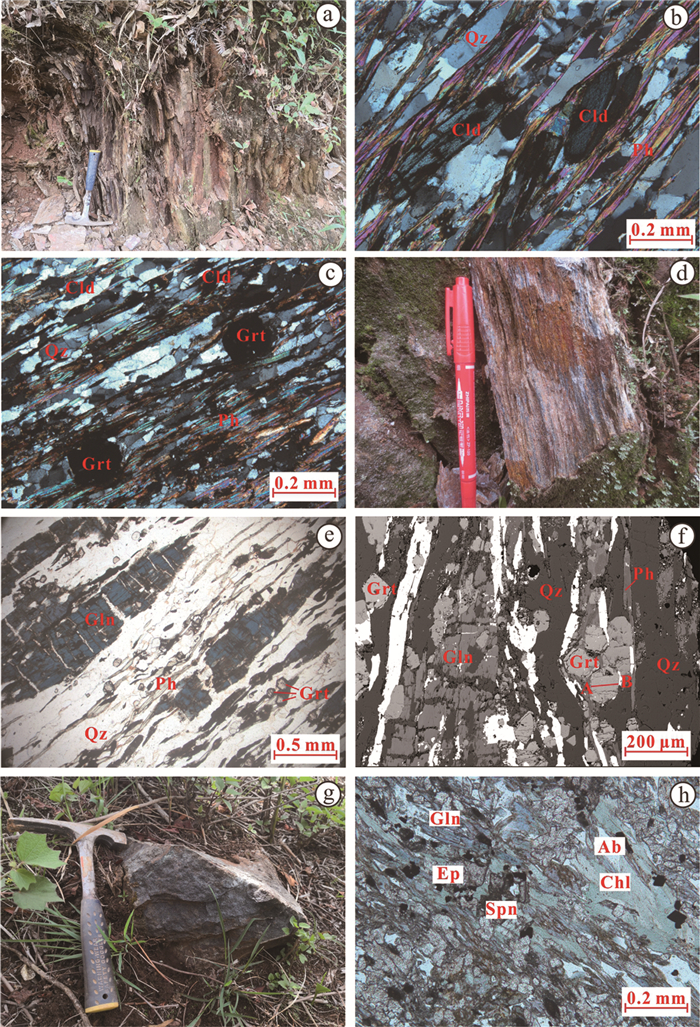
本文样品采自景洪大勐龙曼先坦和勐宋坝村子附近(图 2),前者岩石野外露头较好,为变质-火山沉积型,岩性为多硅白云母石榴蓝闪石英片岩(PM013-2-2)(图 3d),围岩为含石榴硬绿泥石多硅白云片岩(图 3a);后者野外露头较差,为变基性岩,主要岩性为浅灰绿色绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩(PM025-6-1)(图 3g),岩石经历了不同程度的变质作用改造,其矿物组合也不相同,多硅白云母石榴蓝闪石英片岩矿物组合为:石榴子石(Grt)+多硅白云母(Ph)+蓝闪石(Gln)+石英(Qz);绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩矿物组合为:蓝闪石(Gln) +绿泥石(Chl)+绿帘石(Ep)+阳起石(Act)+钠长石(Ab)。
![]() 图 3 景洪大勐龙地区蓝片岩野外露头及显微镜下照片a—含石榴硬绿泥白云母片岩(围岩)野外露头;b、c—白云母基质中残留少量浑圆他形筛状变斑状全铁泥化石榴子石、微透镜状弱铁泥化硬绿泥石;d—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩野外露头;e—细微粒自形石榴子石、定向透镜云母和半自形柱状蓝闪石分别呈微透镜-条痕-条带状富集;f—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴石成分剖面位置(BSE);g—绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩野外露头;h—岩石主要由定向分布的绿帘石、蓝闪石、绿泥石、阳起石、钠长石组成;Grt—石榴子石;Qz—石英;Ph—多硅白云母;Chl—绿泥石;Cld—硬绿泥石;Ep—绿帘石;Ab—钠长石;Spn—榍石Figure 3. Outcrops and photomicrographs of blueschists in the Damenglong area, Jinghong Citya-Outcrop of garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist (surrounding rock); b, c-A small amount of round, sieve-like, variegated, all-iron muddy garnet and microlens-like, weak-iron muddy chlorite remaining in the muscovite matrix; d-Outcrop of muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist; e-Fine-grained euhedral garnet, directional lenticular mica, and subhedral columnar glaucophane enriched in lentoid, streak and stripped shapes, respectively; f-The section position of chemical zoning of garnet in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophan-quartz schist (BSE); g-Outcrop of chlorite-epidote-actinolite- glaucophane schist; h-Rock consisting primarily of directionally distributed epidote, glaucophane, hlorite, actinolite, and albite; Grt-Garnet; Qz-Quartz; Ph-Phengite; Chl-Chlorite; Cld-Chloritold; Ep-Epidote; Ab-Albite; Spn-Sphene
图 3 景洪大勐龙地区蓝片岩野外露头及显微镜下照片a—含石榴硬绿泥白云母片岩(围岩)野外露头;b、c—白云母基质中残留少量浑圆他形筛状变斑状全铁泥化石榴子石、微透镜状弱铁泥化硬绿泥石;d—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩野外露头;e—细微粒自形石榴子石、定向透镜云母和半自形柱状蓝闪石分别呈微透镜-条痕-条带状富集;f—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴石成分剖面位置(BSE);g—绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩野外露头;h—岩石主要由定向分布的绿帘石、蓝闪石、绿泥石、阳起石、钠长石组成;Grt—石榴子石;Qz—石英;Ph—多硅白云母;Chl—绿泥石;Cld—硬绿泥石;Ep—绿帘石;Ab—钠长石;Spn—榍石Figure 3. Outcrops and photomicrographs of blueschists in the Damenglong area, Jinghong Citya-Outcrop of garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist (surrounding rock); b, c-A small amount of round, sieve-like, variegated, all-iron muddy garnet and microlens-like, weak-iron muddy chlorite remaining in the muscovite matrix; d-Outcrop of muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist; e-Fine-grained euhedral garnet, directional lenticular mica, and subhedral columnar glaucophane enriched in lentoid, streak and stripped shapes, respectively; f-The section position of chemical zoning of garnet in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophan-quartz schist (BSE); g-Outcrop of chlorite-epidote-actinolite- glaucophane schist; h-Rock consisting primarily of directionally distributed epidote, glaucophane, hlorite, actinolite, and albite; Grt-Garnet; Qz-Quartz; Ph-Phengite; Chl-Chlorite; Cld-Chloritold; Ep-Epidote; Ab-Albite; Spn-Sphene3.1 含石榴硬绿泥石白云母片岩
岩石呈浅灰色,具斑状变晶结构,基质为细粒鳞片粒状变晶结构,条痕片状构造。变斑晶为石榴子石(5%)、硬绿泥石(8%),基质为鳞片状多硅白云母(60%)、他形粒状石英(17%)和微量隐微晶片状绿泥石。镜下见各自富集定向细晶多硅白云母和石英基质中,残留少量微透镜状弱铁泥化硬绿泥石(图 3b)、浑圆他形变斑状全铁泥化石榴子石(图 3c);多硅白云母条纹条痕中可见褶曲状多硅白云母构成的条痕状剪切条带。
3.2 白云母石榴蓝闪石英片岩
岩石呈浅灰色,具斑状变晶结构,基质为细粒鳞片粒状变晶结构,片状构造。变斑晶为石榴子石(5%)、蓝闪石(20%),基质为细粒石榴子石(8%)、石英(51%)、多硅白云母(8%)、黑云母(2%)和微量绿帘石和铁泥质成分。镜下见蓝闪石变斑晶呈透镜半自形柱状,局部可见微细粒自形石榴子石包裹体;石榴石变斑晶呈不规则状镶嵌于石英颗粒之间(图 3e),其中细微粒自形石榴石、白云母和半自形柱状蓝闪石近定向分布构成主期片理(图 3f)。
3.3 绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩
岩石呈灰绿色,细微粒纤柱状变晶结构,片状构造,主要矿物物组成包括蓝闪石(35%)、阳起石(30%)、绿帘石(18%),次要矿物包括绿泥石(8%)、钠长石(3%)、多硅白云母(2%),少量副矿物榍石(3%)和金属矿物(1%)(图 3h)。镜下见蓝闪石呈半自形柱状,绿帘石呈他形细粒状,钠长石呈他形微细粒变晶状,阳起石呈他形长柱状,其内普遍见蓝闪石残余,由蓝闪石在温度升高条件下转变形成。
4. 矿物化学特征
电子探针矿物微区化学成分分析在自然资源部大陆动力学实验室完成,使用电子探针显微分析仪(EPMA)为日本电子JEOL公司的JXA-8100。测试条件为:加速电压15 kV,电流2×10-8 A,摄谱时间10 s,修正方法ZAF,标准样品为美国SPI组合标样,电子束斑5 μm,部分小的包体矿物用2 μm束斑测定。能谱仪(EDS)由英国OXFORD公司制造,加速电压20 kV,束流1.52×10-9 A。无水矿物成分以标准的a.p.f.u氧含量计算,而白云母以11个氧原子,角闪石以23个氧原子,绿帘石以12.5个氧原子,绿泥石以14个氧原子计算。具有代表性的矿物测试结果见表 1和表 2。
表 1 白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩及围岩(石榴硬绿泥白云片岩)的主要矿物成分数据(%)Table 1. Representative mineral components of the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists and their surrounding rocks (garnet-chloritoid-muscovite schist) (%) 表 2 绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩主要矿物成分数据(%)Table 2. Representative mineral components of chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists (%)
表 2 绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩主要矿物成分数据(%)Table 2. Representative mineral components of chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists (%)
4.1 闪石类矿物
角闪石化学分类参照Leake et al.(1997),角闪石占位模型采用Holland et al.(1979)的模型,Fe3+校正采用Si + Ti + Al + Cr + Mg + Mn + Fe + Ni = 13的方案。
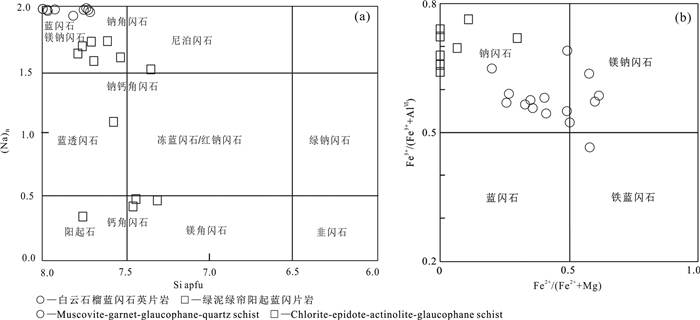
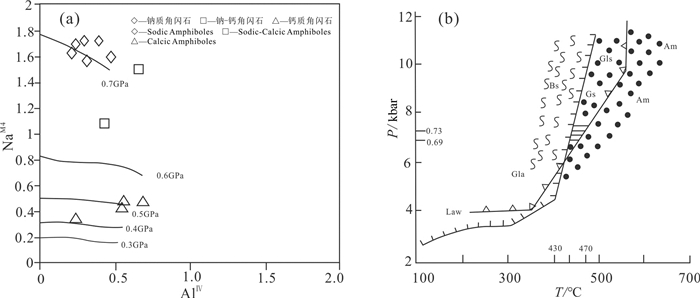
白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中的闪石类矿物主要为钠质角闪石,端元组分主要为镁钠闪石、钠闪石,个别点属铁蓝闪石(图 4a),未见典型蓝闪石(glaucophane)矿物(图 4b)。该地区钠质角闪石从核部至边部,NaB、AlⅥ和Fe3+/(Fe3+ + AlⅥ)变化不明显,NaB = 1.92~1.98 a.p.f.u,AlⅥ = 0.76~1.40 a.p.f.u,Fe3+/ (Fe3+ + AlⅥ) = 0.47~0.69。XMg从核部至边部表现为明显的升高趋势,XMg = 0.38~0.79,表明样品中蓝闪石可能记录了升温的进变质过程。
![]() 图 4 景洪大勐龙勐宋坝地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩和绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩中闪石族矿物成分图解(根据Leak et al., 1997)Figure 4. Mineral component diagrams of amphiboles in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists and chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City (after Leake et al., 1997)
图 4 景洪大勐龙勐宋坝地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩和绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩中闪石族矿物成分图解(根据Leak et al., 1997)Figure 4. Mineral component diagrams of amphiboles in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists and chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City (after Leake et al., 1997)绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩中的闪石类矿物主要为钠角闪石,含有少量的钙质角闪石和钠-钙质闪石,钠质闪石端元组分主要为钠闪石(图 4a),未见典型蓝闪石(glaucophane)矿物(图 4b),钠-钙质闪石成分主要为冻蓝闪石和蓝透闪石,钙质角闪石成分主要为镁角闪石,含少量的阳起石,应该为最晚期的闪石类型。显微镜下可见钠质角闪石类矿物特有的紫(Ng)-深蓝(Nm)-浅黄色(Np)多色性。环带构造不发育,但探针分析表明,其中心常见镁钠闪石,而边部则为冻蓝闪石,Al2O3化学成分略有增高。
4.2 石榴石
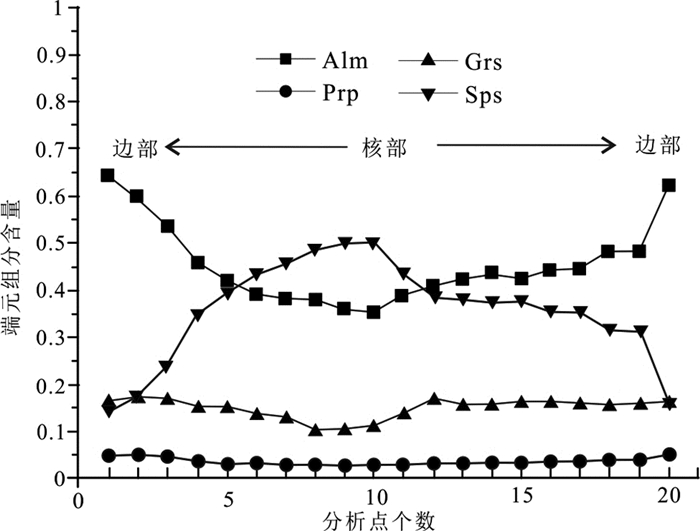
白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中微细粒自形石榴子石Al2O3含量为19.62%~20.34%,FeO为0.00%~1.44%,MnO为15.38%~28.46%,MgO为6.21%~21.81%,CaO为0.67%~1.29%。石榴子石具清晰的环带结构,核部包体较少,石榴子石端元组分变化范围为Alm35~64Py3~5Grs11~18Sps14~50,石榴子石的成分特征显示其核部富Mn,边部Mn逐渐减少,Fe和Ca的含量从核部到边部逐渐增加,Mg的含量在核部和边部相差不大(图 5),这表明石榴子石形成于一个进变质阶段。
![]() 图 5 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴子石变斑晶成分图解Alm—铁铝榴石;Grs—钙铝榴石;Prp—镁铝榴石;Sps—锰铝榴石;分析点位置见图 3fFigure 5. Compositional zoning diagram of garnet porphyroblasts in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong CityAlm-Almandine; Grs-Grossular; Prp-Pyrope; Sps-Spessartine; location of analysis points shown in Fig. 3f
图 5 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴子石变斑晶成分图解Alm—铁铝榴石;Grs—钙铝榴石;Prp—镁铝榴石;Sps—锰铝榴石;分析点位置见图 3fFigure 5. Compositional zoning diagram of garnet porphyroblasts in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong CityAlm-Almandine; Grs-Grossular; Prp-Pyrope; Sps-Spessartine; location of analysis points shown in Fig. 3f4.3 白云母
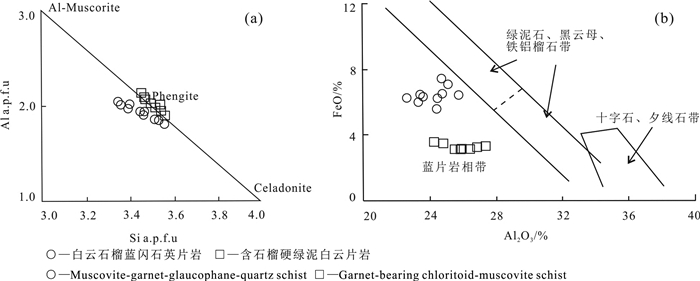
矿物成分分析表明,白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩及含石榴硬绿泥石白云母片岩(围岩)中白云母均属多硅白云母(表 1;图 6a)。前者Si值为3.35~3.56 a.p.f.u.,XMg(=Mg/(Mg+Fe)为0.37~0.57,XNa(=Na/(Na+K)值为0.02~0.07;后者Si值为3.45~3.56 a.p.f.u.,XMg为0.55~0.65,XNa值为0.01~0.04。前者Al2O3含量24.21%~27.28%,FeO含量3.11%~3.58%;后者Al2O3含量22.53%~25.76%,FeO含量5.58%~7.45%,在Al2O3-FeO图解中(图 6b),该地区多硅白云母变质程度达到了蓝片岩相,该变质相形成的温压条件一般为P=3×10-8~12×10-8 Pa,T=200~500℃(Miyashiro, 1979)。
![]() Figure 6. Si vs. Al diagram (a; after Wei Chunjing and Zhu Wenping, 2007) and Al2O3 vs. FeO diagram (b; after Miyashiro, 1979) of muscovite in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist and garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City
Figure 6. Si vs. Al diagram (a; after Wei Chunjing and Zhu Wenping, 2007) and Al2O3 vs. FeO diagram (b; after Miyashiro, 1979) of muscovite in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist and garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City4.4 绿帘石和绿泥石
绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩中,绿帘石的XPs值(Fe3+/(Fe3++Al))为0.27,绿泥石的XMg值为0.56。成分接近于镁铁绿泥石。
4.5 硬绿泥石
含石榴硬绿泥石白云片岩(围岩)中硬绿泥石含量见表 1,Al2O3含量为39.73%~40.27%,FeO为24.05%~24.73%,MnO为0.32%~0.66%,MgO为2.34%~2.53%,其中XMg的变化范围不大,为0.14~0.16。
5. 变质作用及温压条件
5.1 白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩
根据白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩的矿物组合和显微构造特征可以大致将研究区内的蓝片岩划分为三个大的变质阶段:
第一阶段以出现石榴子石为特征,主要为早期俯冲过程中的高压条件下形成。在这一阶段,先期石榴子石由于压力没有达到最大值,核部以锰铝榴石为主,而后随着俯冲的继续,压力升高,边部镁铝榴石的含量逐渐增高,形成了一个进变质的环带结构,这一时期可能的矿物共生组合为石榴子石(Grt)+ 多硅白云母(Phe)+ 金红石(Rt)+ 石英(Qtz)等。
第二阶段则是以蓝闪石矿物的出现为特征,此阶段随着压力的降低和温度的升高,核部早期的锰铝榴石为边部铁铝榴石取代,金红石也由于压力降低而向榍石转变,这一时期可能的矿物共生组合为石榴子石(Grt)+ 蓝闪石(Gln)+多硅白云母Phe + 榍石(Ttn)+ 石英(Qtz)等,推测此期可能为蓝片岩相的叠加变质作用。
第三阶段则是以出现黑云母等为特征,矿物组合为黑云母(Bt)+ 石英(Qtz)+榍石(Ttn)等。Veblen and Ribbe(1982)对角闪岩石学及实验相关的研究指出,蓝片岩和绿片岩的区别在于含钠质角闪石类矿物蓝闪石、青铝闪石,也可含硬柱石、硬玉或绿辉石,缺失黑云母。推测此期已进入到了绿片岩相变质作用。
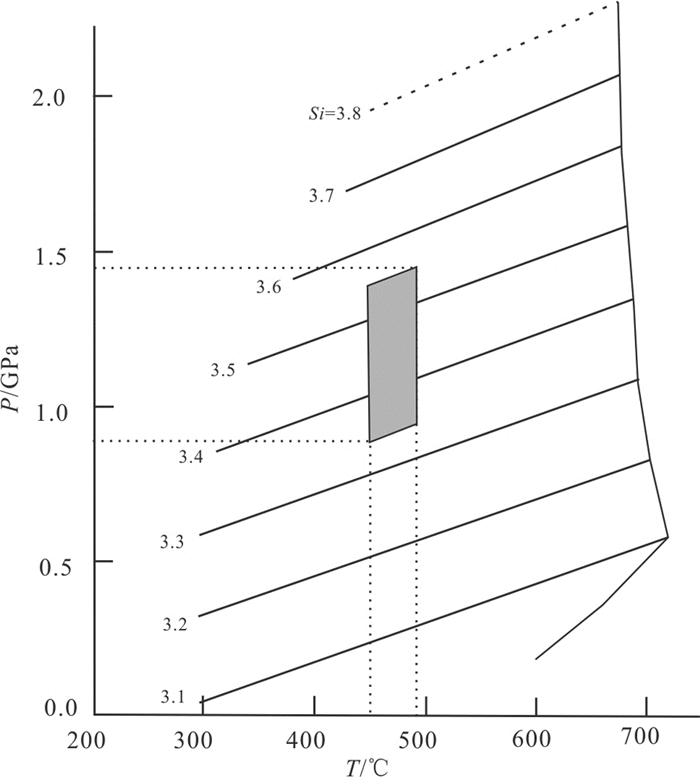
将白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中的蓝闪石化学成分投影到NaM4-AlⅣ图解上,求得压力值高于0.7 GPa(图 8a),将蓝片岩及围岩中多硅白云母的电子探针数据投图可知,这些岩石均达到了蓝片岩相变质。本文采用石榴子石-多硅白云母温度计(Green and Hellman, 1982),选择白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴子石核部成分与基质中自形且新鲜的多硅白云母进行配对估算变质温度,固定压力条件为0.8 GPa,获得压力峰期对应的变质温度为450~490℃。根据Massonne and Szpurka(1997)提出的多硅白云母压力计(图 7),结合本文所研究样品的多硅白云母中Si值(3.35~3.56),限定白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩的变质温压条件为T=450~490℃,P= 0.90~1.45 GPa。
![]() 图 7 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩的P-T条件估算(据Masone and Szpurka, 1997)Figure 7. P-T estimation for the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong City (after Masone and Szpurka, 1997)
图 7 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩的P-T条件估算(据Masone and Szpurka, 1997)Figure 7. P-T estimation for the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong City (after Masone and Szpurka, 1997)5.2 绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩
根据该岩石的矿物组成可知其原岩可能为变基性岩。结合岩石的矿物组合和显微构造特征,可将蓝片岩中矿物大致分为峰期和峰期后两个阶段:峰期主要共生矿物组合为蓝闪石(Gln)+绿帘石(Ep)+绿泥石(Chl),峰期后变质压力降低,主要矿物组合包括:绿泥石(Chl)+绿帘石(Ep)+钠长石(Ab)+阳起石(Act)/角闪石(Hb)±蓝透闪石(Wnc)。
蓝片岩仅产于较高压和中—低温变质条件,这一结论符合于全世界造山带中蓝片岩的变质作用(Maresch,1977)。由于该地区蓝片岩中闪石包括钠质角闪石、钠-钙质角闪石和钙质角闪石,角闪石的NaM4与AlⅣ压力之间的相关变化一直为人们所公认(Shido et al., 1959),NaM4含量随压力的增大而增高,故可作为有用的相对压力计(Brown,1977)。从AlⅣ-NaM4关系图(图 8a)可以看出,该地区钙质、钠-钙质和钠质3类闪石的压力随NaM4的增大而增大,其中钙质闪石形成压力在0.41~0.51 GPa,冻蓝闪石和蓝透闪石形成的压力在0.51~0.65 GPa,蓝闪石形成的压力在0.69~0.73 GPa,因此可知该地区蓝片岩的形成压力应该在0.69~0.73 GPa。根据蓝片岩的矿物组合及所估算的变质压力(0.69~0.73 GPa),借助于蓝片岩变质作用的P-T图解(图 8b),可估算其变质温度约为430~470℃。
![]() 图 8 景洪大勐龙地区绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩角闪石NaM4-AlⅣ相图(a,底图据Brown, 1977)蓝闪石变质作用的P-T图解(b,底图据Moody et al., 1983)Law—硬柱石稳定区域;Gla—蓝闪石温度区:据Maresch(1977);Bs—蓝片岩元;Gls, Gs—绿片岩单元的蓝闪绿片岩;Am—角闪岩及单元;黑点区—蓝闪绿片岩及角闪岩单元的P-T估算区间;横线区—勐宋坝蓝片岩估算的P-T区间Figure 8. AlⅣ- NaM4 diagram of amphibole(Brown, 1977)(a) and metamorphic P-T diagram of glaucophan(据Moody et al., 1983)(b) in the chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong CityLaw-Lawsonite stability area; Gla-Glaucophane stability area; after Maresch (1977); Bs-Blueschist unit; Gls, Gs-Glaucophane greenschist of greenschist unite; Am-Amphibolite unite; Blackspot area-The estimated P-T condition of glaucophane greenschist and amphibolite unit; Lineae transversae area-The estimated P-T condition of the Mengsongba blueschist
图 8 景洪大勐龙地区绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩角闪石NaM4-AlⅣ相图(a,底图据Brown, 1977)蓝闪石变质作用的P-T图解(b,底图据Moody et al., 1983)Law—硬柱石稳定区域;Gla—蓝闪石温度区:据Maresch(1977);Bs—蓝片岩元;Gls, Gs—绿片岩单元的蓝闪绿片岩;Am—角闪岩及单元;黑点区—蓝闪绿片岩及角闪岩单元的P-T估算区间;横线区—勐宋坝蓝片岩估算的P-T区间Figure 8. AlⅣ- NaM4 diagram of amphibole(Brown, 1977)(a) and metamorphic P-T diagram of glaucophan(据Moody et al., 1983)(b) in the chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong CityLaw-Lawsonite stability area; Gla-Glaucophane stability area; after Maresch (1977); Bs-Blueschist unit; Gls, Gs-Glaucophane greenschist of greenschist unite; Am-Amphibolite unite; Blackspot area-The estimated P-T condition of glaucophane greenschist and amphibolite unit; Lineae transversae area-The estimated P-T condition of the Mengsongba blueschist峰期后变质的温度和压力,目前还难以估计,特征矿物组合为阳起石、绿泥石、绿帘石、石英、榍石、磷灰石、铁氧化物等,因此阳起石的形成压力可能指示了本区绿片岩相的变质压力,根据NaM4-AlⅣ图解大致限定退变质阶段变质压力在0.4 GPa左右,温度大概在350~370℃。
6. 讨论
滇西昌宁—孟连缝合带是东特提斯缝合域中重要的构造带,代表了滇缅泰马和印支板块的分界线。该古特提斯洋缝合带保存了一系列岩石记录,包括蛇绿混杂岩、俯冲相关的镁铁质岩体、OIB-型洋岛玄武岩、低压—高压变质岩以及后碰撞花岗岩和双峰式火山岩(Jian et al., 2004, 2008;Heppe,2006;Dong et al., 2013)。东特提斯构造域受到新生代印度—欧亚大陆碰撞的影响,导致强烈的挤压变形和走滑,岩石记录难以保存,因此东特提斯构造域古特提斯主洋闭合的残余至今存在争议。前人通过变质基底性质与构成、古生物地理分区、古代沉积构造等判定昌宁—孟连缝合带为古特提斯闭合的主洋(刘本培等, 1993, 2002;李才等,2009;Wang et al., 2018)。自云南省地质调查院通过1∶5万地质填图以来,该带内高压变质岩的研究近年来取得了一系列重要成果和进展,自北向南相继在双江勐库和邦丙、澜沧谦迈和景洪大勐龙等地发现多处榴辉岩和蓝片岩等高压变质岩,填补了缝合带内变质岩研究的空白。在古特提斯缝合带中,三叠纪榴辉岩只在龙木措—双湖缝合带和昌宁—孟连缝合带被报道(Zhai et al., 2011;李静等,2017;Wang et al., 2019b)。龙木措—双湖缝合带榴辉岩峰期变质P-T条件:2.0~2.5 GPa,427~520℃,对应矿物组合:石榴子石+绿辉石+多硅白云母+金红石+硬柱石(Zhai et al., 2011)。昌宁—孟连缝合带榴辉岩峰期矿物组合:石榴子石+绿辉石+白云母+硬柱石+金红石,峰期P-T条件:2.4~2.6 GPa,420~530℃(Wang et al., 2019b)。同时两个缝合带内榴辉岩的地球化学性质具有OIB-型的亲和性,暗示了退变质榴辉岩的原岩为洋岛火山岩,典型的洋壳俯冲的榴辉岩。结合两处缝合带也发育高级蓝片岩,因此在变质岩组合上也支持昌宁—孟连缝合带是龙木措—双湖缝合带的南沿,共同组成了古特提斯主洋的残余。
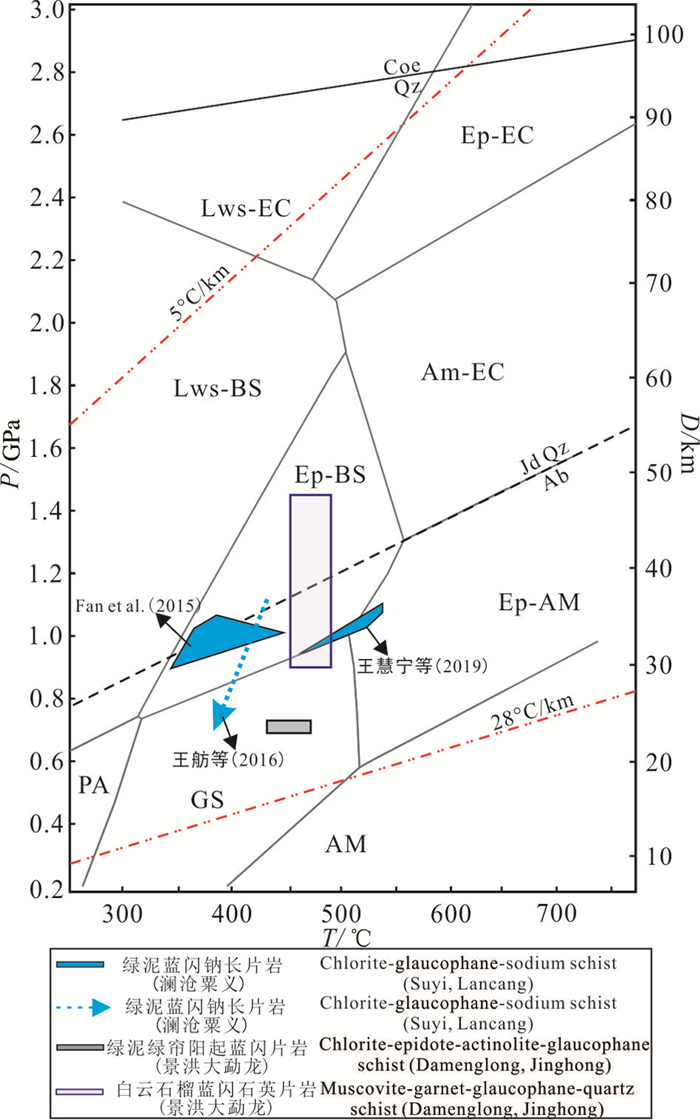
滇西昌宁—孟连缝合带发育大量的三叠纪后碰撞岩浆作用,例如临沧花岗岩和景洪双峰式火山岩,共同构建了古特提斯洋闭合的框架(Peng et al., 2013;Deng et al., 2018)。然而,缝合带内缺少二叠纪—早三叠世岩浆作用的记录, 尤其是俯冲相关的岩浆岩研究程度较低,导致古特提斯洋的消减作用缺少针对性的讨论。关于昌宁—孟连缝合带内蓝片岩的研究目前主要集中在双江粟义、澜沧上允一带,张儒瑗等(1990)采用K-Ar同位素测年获得南榔、粟义地区的蓝片岩中的青铝闪石变质年龄为193 Ma;赵靖等(1993, 1994)采用同位素测年获得多硅白云母40Ar/39Ar变质年龄238 Ma,蓝片岩中蓝闪石40Ar/39Ar年龄为279 Ma,经历了214 Ma蓝片岩相变质;Fan et al.(2015)采用LA-ICP-MS获得粟义蓝片岩锆石U-Pb年龄为260 Ma,蓝片岩中蓝闪石40Ar/39Ar年龄为242 Ma,前者为原岩年龄,后者为变质年龄,峰期的温压为:T=300~450℃,P=0.5~0.9 GPa;王舫等(2016)获得粟义蓝片岩峰期压力为0.95 GPa;毕丽莎等(2018)获得澜沧上允白云母石英片岩中多硅白云母40Ar/39Ar变质年龄为255.3 Ma,蓝闪石40Ar/39Ar变质年龄为248.5 Ma,峰期变质温压为:T=430~490 ℃,P=0.7~0.8 GPa;Wang et al.(2019b)获得粟义多硅白云母和蓝闪石40Ar/39Ar变质年龄分别为242.5 Ma和228.7 Ma。研究表明,粟义—惠民一带蓝片岩形成于二叠纪,经历了三叠纪蓝片岩相变质作用改造。通过对大勐龙地区不同类型蓝片岩的研究,获得白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩(T=450~490℃,P=0.90~1.45 GPa)、绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩(T=430~470℃,P=0.69~0.73 GPa)峰期变质作用的温压条件,并确定了各自变质级别:白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩温压条件略高于粟义—惠民一带蓝片岩;绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩主要经历了绿片岩相的变质,温压条件与粟义—惠民一带蓝片岩的温压相近。由于测年数据缺乏,对岩石折返过程尚未完全把握,根据各变质期次的温压条件初步建立了两种不同类型蓝片岩P-T轨迹(图 9)。
![]() Lws-BS—硬柱石蓝片岩相;Ep-Ec—绿帘石榴辉岩相;Ep-AM—绿帘角闪岩相;GS—绿片岩相;AM—角闪岩相;PA—绿千石钠长石相Figure 9. Metamorphic P-T estimations for blueschists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong area. The major metamorphic facies is after Evans(1990), Liou and Zhang (2003); Diagnostic reaction Core= Qz is after Oh and Liou(1998)Lws-BS-Lawsonite-blueschist facies; EP-BS-Epidote-blueschist facies; EP-EC-Epidote-eclogite facies; EP-AM- Epidote-amphibolite facies; GS-Greenschist facies; AM-Amphibolite facies; PA-Pumpellyite-albite facies
Lws-BS—硬柱石蓝片岩相;Ep-Ec—绿帘石榴辉岩相;Ep-AM—绿帘角闪岩相;GS—绿片岩相;AM—角闪岩相;PA—绿千石钠长石相Figure 9. Metamorphic P-T estimations for blueschists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong area. The major metamorphic facies is after Evans(1990), Liou and Zhang (2003); Diagnostic reaction Core= Qz is after Oh and Liou(1998)Lws-BS-Lawsonite-blueschist facies; EP-BS-Epidote-blueschist facies; EP-EC-Epidote-eclogite facies; EP-AM- Epidote-amphibolite facies; GS-Greenschist facies; AM-Amphibolite facies; PA-Pumpellyite-albite facies7. 结论
(1) 在景洪大勐龙地区新识别出一套经历高压变质作用形成的蓝片岩,岩石类型不相同,包括白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩和绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩。通过岩相学及矿物学研究,获得白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩(T=450~490℃,P=0.90~1.45 GPa)、绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩(T=430~470℃,P=0.69~0.73 GPa)峰期变质的温压条件。
(2) 初步建立了两种不同类型蓝片岩的变质演化P-T轨迹,推测其成因可能为不同变质程度的岩石俯冲到不同深度,通过俯冲隧道折返机制所形成,为滇西地区古特提斯洋的消减-闭合的构造演化过程及形成的构造背景提供重要素材。
注释
❶云南省地质矿产局. 1965. 1∶100万普洱幅区域地质调查报告[R].
❷云南省地质矿产局. 1979. 1∶20万勐海县幅区域地质调查报告[R].
❸云南省地质矿产局. 1979. 1∶20万景洪幅区域地质调查报告[R].
❹云南省地质调查院. 2019. 1∶5万曼各、小街、曼班、大勐龙、万纳兰、勐宋坝幅区域地质调查报告[R].
致谢: 云南省地质调查院张虎教授级高工认真审阅了本文并提出了详细修改意见;中国地质科学院地质研究所大陆动力学实验室电子探针实验室毛小红博士在实验测试过程中给予了指导和帮助;匿名审稿专家认真审阅全文,并提出了非常宝贵的修改意见,对文章学术理论的提升有极大的帮助,作者在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
图 1 东南亚主要板块构造带分布图(a,据Sone and Metcalfe, 2008)和三江南段昌宁—孟连结合带地质简图(b,据Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015修改)
Figure 1. (a) Tectonic framework of Southeast Asia (modified from Sone and Metcalfe, 2008); (b) Geological sketch of the Changning-Menglian suture belt (modified from Burchfiel and Chen, 2013; Li et al., 2015)
图 3 景洪大勐龙地区蓝片岩野外露头及显微镜下照片
a—含石榴硬绿泥白云母片岩(围岩)野外露头;b、c—白云母基质中残留少量浑圆他形筛状变斑状全铁泥化石榴子石、微透镜状弱铁泥化硬绿泥石;d—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩野外露头;e—细微粒自形石榴子石、定向透镜云母和半自形柱状蓝闪石分别呈微透镜-条痕-条带状富集;f—白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴石成分剖面位置(BSE);g—绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩野外露头;h—岩石主要由定向分布的绿帘石、蓝闪石、绿泥石、阳起石、钠长石组成;Grt—石榴子石;Qz—石英;Ph—多硅白云母;Chl—绿泥石;Cld—硬绿泥石;Ep—绿帘石;Ab—钠长石;Spn—榍石
Figure 3. Outcrops and photomicrographs of blueschists in the Damenglong area, Jinghong City
a-Outcrop of garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist (surrounding rock); b, c-A small amount of round, sieve-like, variegated, all-iron muddy garnet and microlens-like, weak-iron muddy chlorite remaining in the muscovite matrix; d-Outcrop of muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist; e-Fine-grained euhedral garnet, directional lenticular mica, and subhedral columnar glaucophane enriched in lentoid, streak and stripped shapes, respectively; f-The section position of chemical zoning of garnet in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophan-quartz schist (BSE); g-Outcrop of chlorite-epidote-actinolite- glaucophane schist; h-Rock consisting primarily of directionally distributed epidote, glaucophane, hlorite, actinolite, and albite; Grt-Garnet; Qz-Quartz; Ph-Phengite; Chl-Chlorite; Cld-Chloritold; Ep-Epidote; Ab-Albite; Spn-Sphene
图 4 景洪大勐龙勐宋坝地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩和绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩中闪石族矿物成分图解(根据Leak et al., 1997)
Figure 4. Mineral component diagrams of amphiboles in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists and chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City (after Leake et al., 1997)
图 5 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩中石榴子石变斑晶成分图解
Alm—铁铝榴石;Grs—钙铝榴石;Prp—镁铝榴石;Sps—锰铝榴石;分析点位置见图 3f
Figure 5. Compositional zoning diagram of garnet porphyroblasts in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong City
Alm-Almandine; Grs-Grossular; Prp-Pyrope; Sps-Spessartine; location of analysis points shown in Fig. 3f
图 6 景洪大勐龙勐宋坝地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩和含石榴硬绿泥石白云母片岩中白云母Al-Si图解(a, 魏春景和朱文萍,2007)和Al2O3-FeO图解(b, Miyashiro, 1979)
Figure 6. Si vs. Al diagram (a; after Wei Chunjing and Zhu Wenping, 2007) and Al2O3 vs. FeO diagram (b; after Miyashiro, 1979) of muscovite in the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist and garnet-bearing chloritoid-muscovite schist from the Damenglong-Mengsongba area, Jinghong City
图 7 景洪大勐龙地区白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩的P-T条件估算(据Masone and Szpurka, 1997)
Figure 7. P-T estimation for the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong City (after Masone and Szpurka, 1997)
图 8 景洪大勐龙地区绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩角闪石NaM4-AlⅣ相图(a,底图据Brown, 1977)蓝闪石变质作用的P-T图解(b,底图据Moody et al., 1983)
Law—硬柱石稳定区域;Gla—蓝闪石温度区:据Maresch(1977);Bs—蓝片岩元;Gls, Gs—绿片岩单元的蓝闪绿片岩;Am—角闪岩及单元;黑点区—蓝闪绿片岩及角闪岩单元的P-T估算区间;横线区—勐宋坝蓝片岩估算的P-T区间
Figure 8. AlⅣ- NaM4 diagram of amphibole(Brown, 1977)(a) and metamorphic P-T diagram of glaucophan(据Moody et al., 1983)(b) in the chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schist from the Damenglong area, Jinghong City
Law-Lawsonite stability area; Gla-Glaucophane stability area; after Maresch (1977); Bs-Blueschist unit; Gls, Gs-Glaucophane greenschist of greenschist unite; Am-Amphibolite unite; Blackspot area-The estimated P-T condition of glaucophane greenschist and amphibolite unit; Lineae transversae area-The estimated P-T condition of the Mengsongba blueschist
图 9 景洪大勐龙地区蓝闪片岩变质P-T条件估算变质相系参考Evans(1990)和Liou and Zhang (2003);变质反应Coe=Qz参考Oh and Liou(1998)
Lws-BS—硬柱石蓝片岩相;Ep-Ec—绿帘石榴辉岩相;Ep-AM—绿帘角闪岩相;GS—绿片岩相;AM—角闪岩相;PA—绿千石钠长石相
Figure 9. Metamorphic P-T estimations for blueschists from the Damenglong area, Jinghong area. The major metamorphic facies is after Evans(1990), Liou and Zhang (2003); Diagnostic reaction Core= Qz is after Oh and Liou(1998)
Lws-BS-Lawsonite-blueschist facies; EP-BS-Epidote-blueschist facies; EP-EC-Epidote-eclogite facies; EP-AM- Epidote-amphibolite facies; GS-Greenschist facies; AM-Amphibolite facies; PA-Pumpellyite-albite facies
表 1 白云石榴蓝闪石英片岩及围岩(石榴硬绿泥白云片岩)的主要矿物成分数据(%)
Table 1 Representative mineral components of the muscovite-garnet-glaucophane-quartz schists and their surrounding rocks (garnet-chloritoid-muscovite schist) (%)

表 2 绿泥绿帘阳起蓝闪片岩主要矿物成分数据(%)
Table 2 Representative mineral components of chlorite-epidote-actinolite-glaucophane schists (%)

-
Bi L S, Liang X, Wang G H, Zhang H D, Wang Q, Wu C Q. 2018. Metamorphism-deformation phases and Ar-Ar chronological constraints of the Lancang Group in the middle and southern sections of the Lancangjiang Tectonic Belt, Western Yunnan[J]. Earth Science, 43(9): 3252-3266(in Chinese with English abstract).
Bi L S. 2014. Metamorphism and Deformation Characteristics of Metamorphic Rocks in Shangyun-Huimin Section of Changning-Menglian Suture, Yunnan, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 15-51(in Chinese with English abstract).
Brown E H. 1977. The crossite content of Ca-amphibole as a guide to pressure of metamorphism[J]. Journal of Petrology, 18(1): 53-72. doi: 10.1093/petrology/18.1.53
Burchfiel B C, Chen Z L. 2013. Tectonics of the southeastern Tibetan plateau and its adjacent foreland[J]. Memoir of the Geological Society of American, 210: 1-164.
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Yunnan Province. 1990. Regional Geology of Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese).
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Yunnan Province. 1996. Stratigraphy(Lithostratic) of Yunnan Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press(in Chinese).
Chen G Y, Xu G X, Sun Z B, Tian S M, Zhang H, Huang L, Zhou K. 2017. Genetic study of amphiboles in retrograded eclogites from Mengku area, Shuangjiang County, Western Yunnnan Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 36(1): 36-47 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.01.003
Deng J, Wang C, Zi J, Xia R, Li Q. 2018. Constraining subduction-collision processes of the Paleo-Tethys along the Changning-Menglian suture: New zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotopes of the lincang batholith[J]. Gondwana Research, 62: 75-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.008
Deng J, Wang Q F, Li G J. 2016. Superimposed orogeny and composite metallogenic system: Case study from the Sanjiang Tethyan belt, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2225-2247(in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong G C, Mo X X, Zhao Z D, Zhu D C, Goodman R, Kong H L, Wang S. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and the petrological and geochemical constraints on Lincang granite in Western Yunnan, China: Implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 62: 282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.003
Dong S B. 1989. The general features and distributions of the glaucophane schist belts of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 13(1): 101-114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Duan X D. 2008. The Basin Evolution Sudies of the Changning-Menglian Zone in the Gengma Area, Southweatern Yunnan[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-186(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ernst W G. 1972. Occurrence and mineralogic evolution of blueschist belts with time[J]. American Journal of Science, 272(7): 657-668. doi: 10.2475/ajs.272.7.657
Ernst W G. 1988. Tectonic history of subduction zones inferred from retrograde blueschist P-T paths[J]. Geology, 16(12): 1081-1084. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<1081:THOSZI>2.3.CO;2
Evans B W. 1990. Phase relations of epidote-blueschists[J]. Lithos, (1/3): 3-23.
Fan W M, Wang Y J, Zhang Y H, Zhang Y Z, Jourdan Fred, Zi J W, Liu H C. 2015. Paleotethyan subduction process revealed from Triassic blueschists in the Lancang tectonic belt of Southwest China[J]. Tectonophysics, 662: 95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.12.021
Feng Q L. 2002. Stratigraphy of volcanic rocks in the Changning-Menglian Belt in southwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(6): 657-664. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00006-8
Green T H, Hellman P L. 1982. Fe-Mg partitioning between coexisting garnet and phengite at high pressure, and comments on a garnet-phengite geothermomster[J]. Lithos, 15(4): 253-266. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(82)90017-2
Grimmer J C, Ratschbacher L, McWilliams M, Franz L, Gaitasch I, Tichomirowa M, Hacker B R, Zhang Y Q. 2003. When did the Ultrahigh-Pressure rocks reach the surface? A 207Pb/206Pb Zircon, 40Ar/39Ar White Mica, Si-in-White Mica, Single-Grain Provenance study of Dabie Shan synorogenic foreland sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 197(1/4): 87-100.
Heep K, Helmcke Dand Wemmer K. 2007. The Lancang River Zone of southwestern Yunnan, China: A questionable location for the active continental margin of Paleotethys[J]. Journal of Asina Earth Sciences, 30(5/6): 706-720.
Heppe K. 2006. Plate tectonic evolution and mineral resource potential of the Lancang River zone, southwestern Yunnan, People's Republic of China[J]. Geologisches Jahrbuch S D, 7: 1-159.
Holland T, Blundy J. 1994. Non-ideal interactions in calcic amphiboles and their bearing on amphibole-plagioclase thermometry[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 116: 433-447. doi: 10.1007/BF00310910
Jian P, Liu D Y, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang Y Z, Sun X M, Zhang W. 2009a. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in Southwest China (Ⅰ): Geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 113(3/4): 748-766.
Jian P, Liu D Y, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang Y Z, Sun X M, Zhang W. 2009b. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in Southwest China (Ⅱ): Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province[J]. Lithos, 113(3/4): 767-784.
Jian P, Liu D Y, Sun X M, 2008. SHRIMP dating of the Permo-Carboniferous Jinshajiang ophiolite, southwestern China: Geochronological constraints for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32: 371-384. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.006
Jian P, Liu D Y, Sun X M. 2004. SHRIMP dating of Jicha Alaskan-type gabbro in western Yunnan Province: Evidence for the Early Permian subduction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78, 165-170.
Leake B E, Woolley A R, Arps C E S, Birch W D, Gilbert M C, Grice J D, Hawthorne F C, Kato A, Kisch H J, Krivovichev V G, Linthout K, Laird J, Mandarino J, Maresch W V, Nickel E H, Rock N M S, Schumacher J C, Smith D C, Stephenson N C N, Ungaretti L, Whittaker E J W, Guo Youzhi. 1997. Nomenclature of amphiboles: Report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on new minerals and mineral names[J]. American Mineralogist, 61: 295-321.
Li Cai, Xie Yaowu, Dong Yongsheng, Xu Feng, Qiangba Zhaxi, Jiang Guangwu. 2009. The North Langcangjiang suture: The boundary between Gondwana and Yangtze?[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1711-1719(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.004
Li Gongjian, Deng Jun, Wang Qingfei, Liang Kun. 2015. Metallogenic model for the Laochang Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit related to a Paleo-Tethys OIB-like volcanic center, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 578-594. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.01.012
Li Jing, Sun Zaibo, Huang Liang, Xu Guixiang, Tian Sumei, Deng Renhong, Zhou Kun. 2017. P-T-t path and geological significance of retrograded eclogites from Mengku Area in Western Yunnnan Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 2285-2301(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jing, Sun Zaibo, Xu Guixiang, Zhou Kun, Huang Liang, Tian Sumei, Zeng Wentao, Chen Guangyan, Liu Guichun. 2015. Firstly discovered retrograded eclogites from Mengku area, Shuangjiang County, Western Yunnnan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica. 35(4): 421-424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Wenchang, Pan Guitang, Hou Zengqian, Mo Xuanxue, Wang Liquan, Ding Jun, Xu Qiang. 2010. The Archipelagic Arc Basin-collision Orogeny Metallogenic Theory and Exploration Technology in Sanjiang Area of Western China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-490 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liou J G, Wang X M, Coleman R G, Zhang Z M, Maruyama S. 1989. Blueschists in major suture zones of China[J]. Tectonics, 8(3): 609-919. doi: 10.1029/TC008i003p00609
Liou J G, Zhang R Y. 2003. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphicrocks[C]//Meyers R A (ed.). Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology. 3rd Edition. San Diego: Academic Press, 227-244.
Liu Benpei, Feng Qinglai, Chonglakmani C, Helmcke D. 2002. Framework of Paleotethyan archipelago ocean of western Yunnan and its elongation towards north and South[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 9(3): 161-171(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.03.020
Liu Benpei, Feng Qinglai, Fang Nianqiao, Jia Jinhua, He Fuxiang. 1993. Tectonic evolution of palaeo-Tethys Poly-Island-Ocean in Changning-Menglian and Lancangjiang Belts, Southwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 18(5): 529-539(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Guichun, Sun Zaibo, Zeng Wentao, Feng Qinlai, Huang Liang, Zhang Hu. 2017. The age of Wanhe ophiolitic mélange from Mengku Area, Shuangjiang County, Western Yunnnan Province, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 36(2): 163-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.02.003
Maresch W V. 1977. Experimental studies on glaucophane: A analysis of present knowledge[J]. Tectonophysics, 43: 109-125. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(77)90008-7
Massonne H J, Szpurka Z. 1997. Thermodynamic properties of white micas on the basis of high-pressure experiments in the systems K2O-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O and K2O-FeO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O[J]. Lithos, 41(1): 229-250.
Miyashiiro. 1979. Metamorphism and Metamorphic Belts[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
Oh C W, Liou J G. 1998. A petrogenetic grid for eclogite and related facies under high-pressure metamorphism[J]. Island Arc, 7(1/2): 36-51.
Pan Guitang, Xu Qiang, Hou Zengqian, Wang Liquan, Du Dexun, Mo Xuanxue, Li Dingmou, Wang Mingjie, Li Xingzhen, Jiang Xingshen, Hu Yunzhong. 2003. Arckipelagic Orogenesis Metallogenic Systems and Assessment of the Mineral Resources along the Sanjiang Area in Southwestern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-420 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng T P, Wilde S A, Wang Y J, Fan W M, Peng B X. 2013. Mid-Triassic felsic igneous rocks from the southern Lancangjiang Zone, SW China: Petrogenesis and implications for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 168/169: 15-32. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.015
Peng Xingjie, Luo Wanlin. 1982. The discovery of glaucophane schist zone in the southern Lancangjiang in the Western Yunnan Province, China and its tectonic implication[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2: 69-75(in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng Xingjie, Luo Wanlin. 1983. A preliminary indentification of the paired metamorphic zones in the southern segment of Lancang Jiang[C]//Contribition to the Geology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau, 2: 21-30(in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng Zhimin, Wang Baodi, Hu Jinfeng, Fu Yuzhen, Wang Guozhi, Zhang Ji, Liu Yunhe, Zhang Zhang, Guan Junlei, Han Wenwen. 2022. Determination and oceanic crust subduction of Early Palaeozoic accretionary complexes in the western Yunnan Province—New cognition based on the geological survey of Wendong sheet (1: 50000)[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1656-1672(in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng Zhimin, Wang Guozhi, Wang Baodi, Wang Liquan, Fu Yuzhen, Guan Junlei, Hu Jinfeng, Zhang Ji. 2019. Discovery of glaucophane eclogites in Lancang group at Bangbing area from Yunnan[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 46(5): 639-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2019.05.14
Sheng Qihan, Geng Yuansheng. 2012. The tempo-spatial distribution, geological characteristics and gensis of bluechist belts in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(9): 1407-1446 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.09.007
Shido F, Miyashiro A. 1959. Hronblendes of basic metamorphic rocks[J]. Journal of the Faculty of Science, University of Tokyo. Section II, Geology, mineralogy, geography, geophysics, 12: 85-102.
Sone M, Metcalfe I. 2008. Parallel Tethyan Sutures in mainland SE Asia: New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 340(2/3): 166-179.
Sun Zaibo, Hu Shaobin, Zhou Kun, Zhou Tingquan, Zhao Jiangtai, Wang Yunxiao, Zhang Xingpei, Zhang Shengze, Wang Huining, Wang Wei. 2019. Petrology, mineralogy and metamorphic p-T path of eclogites from the Qianmai area, Lancang county, western Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(7): 1105-1115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Zaibo, Li Jing, Zhou Kun, Zeng Wentao, Wu Jialin, Hu Shaobin, Liu Guichun, Zhao Jiangtai. 2018. Zircon U-Pb age and geological significance of retrograded eclogites from Mengku area in western Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin Of China, 37(11): 2032-2043 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2018.11.009
Sun Zaibo, Zeng Wentao, Zhou Kun, Wu Jialin, Li Gongjian, Huan Liang, Zhao Jiangtai. 2017. Identification of Ordovician oceanic island basalt in the Changning-Menglian suture zone and its tectonic implications: Evidence from geochemical and geochronological data[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 36(10) : 1760-1771(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Baodi, Wang Liquan, Pan Guitang, Yin Fuguang, Wang Dongbing, Tang Yuan. 2013. U-Pb zircon dating of Early Paleozoic gabbro from the Nantinghe ophiolite in the Changning-Menglian suture zone and its geological implication[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(4): 344-354 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-4-344
Wang Baodi, Wang Liquan, Wang Dongbing, Yin Fuguang, He Juan, Peng Zhimin, Yan Guochuan. 2018. Tectonic evolution of the Changning-Menglian Proto-Paleo Tethys Ocean in the Sanjiang area, southwestern China[J]. Earth Science, 43(8): 2527-2550(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Dongbing, Luo Liang, Tang Yuan, Yin Fuguang, Wang Baodi, Wang Liquan. 2016. Zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of Early Paleozoic adakites from the Niujingshan ophiolitic mélange in the Changning-Menglian Suture zone and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 32(8): 2317-2329(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang F, Liu F L, Schert H P, Liu P H, Ji L, Cai J, Liu L S. 2019b. Paleo-Tethyan tectonic evolution of Lancangjiang metamorphic complex: Evidence from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and 40Ar/39Ar isotope geochronology of blueschists in Xiaoheijiang-Xiayun area, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 65: 142-155. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.08.007
Wang Fang, Liu Fulai, Ji Lei, Liu Pinghua, Cai Jia, Tian Zhonghua, Liu Lishuang. 2016. Petrogenesis and metamorphic evolution of blueschist from Xiaoheijiang-Shangyun area in Lancangjiang metamorphic complex[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 35: 804-820 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.05.005
Wang H N, Liu F L, Li J, Sun Z B, Ji L, Tian Z H, Liu L S, Santosh M. 2019a. Petrology, geochemistry and P-T-t path of lawsonite bearing ecloites in the Changning-Mengkian orogenic belt, southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 37(4): 439-478. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12462com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200709015.htm
Wang Huining, Liu Fulai, Ji Lei, Tian Zhonghua, Xu Wang, Liu Lishuang. 2019. Petrology, geochemistry and metamorphic evolution of Lancang Group in the Changning-Menglian complex belt and its implications on the tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(6): 1773-1799 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.06.09
Wei Chunjing, Zhu Wenping. 2007. Progress in the study of phengite geobarometry[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(9): 1123-1130 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.09.014
Wei Chunjing. 1994. Progress in the study of blueschists and related high pressure metamorphic belts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1(1/2): 140-144(in Chinese with English abstract).
Whitney, Evans B W. 2010. Abbreviations for names of rockforming minerals[J]. Ameican Mineralogist, 95(1): 185-187. doi: 10.2138/am.2010.3371
Xu Guixiang, Zeng Wentao, Sun Zaibo, Huang Liang, Chen Guangyan, Tian Sumei, Zhou Kun. 2016. Petrology and mineralogy of retrograded eclogites from Mengku area, Shuangjiang County, Western Yunnnan Province, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(7): 1035-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.07.001
Zhai Q G, Zhang R Y, Jahn B M, Li C, Song S G, Wang J. 2011. Triassic eclogites from Central Qiangtang, Northern Tibet, China: Petrology, geochronology and metamorphic P-T path[J]. Lithos, 125: 173-189. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.02.004
Zhang Ruyuan, Cong Bolin, Han Xiuling. 1990. Amphiboles of blueschist in west Yunnan region[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1: 43-53(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Ruyuan, Cong Bolin, Li Yonggang. 1989. Blueschists and their tectonic significance in western of Yunan Provience[J]. Science China (Series B), 12: 1317-1329(in Chinese).
Zhang Z B, Li J, Lü G X, Yu H, Wang F Z. 2004. Characteristics of blueschist in Shuangjiang tectonic melange zone, West Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 15(2): 224-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.02.016
Zhao Jing, Zhong Dalai, Wang Yi. 1994. Metamorphism of Lancang metamorphic belt, the western Yunnan and its relation to deformation[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 10(1): 27-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1994.01.003
Zhao Jing. 1993. A study of muscovites from the Lancang metamorphic belt in westrn Yunnan and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 12(3): 251-260 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhong Dalai. 1998. The Paleotethys Orogenic Belt in West of Sichuan and Yunnan[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1-230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
毕丽莎, 梁晓, 王根厚, 张海迪, 王泉, 吴春桥. 2018. 滇西澜沧江构造带中-南段澜沧岩群变质变形期次及Ar-Ar年代学约束[J]. 地球科学, 43(9): 3252-3266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201809023.htm 毕丽莎. 2014. 滇西昌宁—孟连缝合带南段上允—惠民一带变质杂岩的变质变形特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 15-51. 陈光艳, 徐桂香, 孙载波, 田素梅, 张虎, 黄亮, 周坤. 2017. 滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩中闪石类矿物的成因研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 36(1): 36-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.01.003 邓军, 王庆飞, 李龚健. 2016. 复合造山和复合成矿系统: 三江特提斯例析[J]. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2225-2247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608001.htm 董申保. 1989. 中国蓝闪石片岩带的一般特征及其分布[J]. 地质学报, 63(3): 273-284. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1989.03.003 段向东. 2008. 滇西南耿马地区昌宁—孟连带盆地演化研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 1-186. 李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜, 徐锋, 强巴扎西, 蒋光武. 2009. 北澜沧江带的性质: 是冈瓦纳板块与扬子板块的界线吗?[J]. 地质通报, 28(12): 1711-1719 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.004 李静, 孙载波, 黄亮, 徐桂香, 田素梅, 邓仁宏, 周坤. 2017. 滇西勐库退变质榴辉岩的P-T-t轨迹及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 33(7): 2285-2291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201707022.htm 李静, 孙载波, 徐桂香, 周坤, 黄亮, 田素梅, 曾文涛, 陈光艳, 刘桂春. 2015. 滇西双江县勐库地区榴闪岩的发现与厘定[J]. 矿物学报, 35(4): 421-424. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2015.04.001 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 候增谦, 莫宣学, 王立全, 丁俊, 徐强. 2010. 西南"三江"多岛弧盆-碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 92-104. 刘本培, 冯庆来, Chonglakmani C, Helmcke D. 2002. 滇西古特提斯多岛洋的结构及其南北延伸[J]. 地学前缘, 9(3): 161-171. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.03.020 刘本培, 冯庆来, 方念桥, 贾进华, 何馥香. 1993. 滇西昌宁—孟连和澜沧江带带古特提斯多岛洋构造演化[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 18(5): 529-539. 刘桂春, 孙载波, 曾文涛, 冯庆来, 黄亮, 张虎. 2017. 滇西双江县勐库地区湾河蛇绿混杂岩的厘定、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 36(2): 163-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.02.003 潘桂棠, 徐强, 候增谦, 王立全, 杜德勋, 莫宣学, 李定谋, 汪名杰, 李兴振, 江新胜, 胡云中. 2003. 西南"三江"多岛弧造山过程、成矿系统与资源评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 106-112. 彭兴阶, 罗万林. 1982. 滇西澜沧江南段蓝片岩带的发现及其大地构造意义[J]. 中国区域地质, 2: 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD198202007.htm 彭兴阶, 罗万林. 1983. 澜沧江南段双变质带的初步确定[C]//青藏高原地质论文集. 2: 21-30. 彭智敏, 王保弟, 胡金峰, 付玉真, 王国芝, 张辑, 刘云鹤, 张璋, 关俊雷, 韩文文. 2022. 云南滇西地区早古生代增生杂岩的厘定及其洋壳俯冲消减作用——基于1∶5万文东幅区域地质调查的新认识[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1656-1672. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20220519?st=search 彭智敏, 王国芝, 王保弟, 王立全, 付于真, 关俊雷, 胡金峰, 张辑. 2019. 云南邦丙澜沧岩群中发现蓝闪石榴辉岩[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 46(5): 0639-0640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201905014.htm 沈其韩, 耿元生. 2012. 中国蓝片岩带的时空分布、地质特征和成因[J]. 地质学报, 86(9): 1407-1446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.09.007 孙载波, 曾文涛, 周坤, 吴嘉林, 李龚健, 黄亮, 赵江泰. 2017. 昌宁—孟连结合带奥陶纪洋岛玄武岩的识别及其构造意义——来自地球化学和锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质通报, 36(10): 1760-1772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201710008.htm 孙载波, 胡绍斌, 周坤, 周听全, 赵江泰, 王云晓, 张星培, 张生泽, 王慧宁, 王巍. 2019. 滇西澜沧谦迈地区榴辉岩岩石学、矿物学特征及其变质演化p-T轨迹[J]. 地质通报, 38(7): 1105-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201907004.htm 孙载波, 李静, 周坤, 曾文涛, 段向东, 赵江泰, 徐桂香, 樊岳华. 2017. 滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 31(4): 746-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201704009.htm 孙载波, 李静, 周坤, 曾文涛, 吴嘉林, 胡绍斌, 刘桂春, 赵江泰. 2018. 滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 37(11): 2032-2043. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2018.11.009 王保弟, 王立全, 潘桂棠, 尹福光, 王冬兵, 唐渊. 2013. 昌宁—孟连结合带南汀河早古生代辉长岩锆石年代学及地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 58(4): 344-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201304009.htm 王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 尹福光, 贺娟, 彭智敏, 闫国川. 2018. 三江昌宁—孟连带原-古特提斯构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 43(8): 2527-2550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808001.htm 王冬兵, 罗亮, 唐渊, 尹福光, 王保弟, 王立全. 2016. 昌宁—孟连结合带牛井山早古生代埃达克岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2317-2329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608006.htm 王舫, 刘福来, 冀磊, 刘平华, 蔡佳, 田忠华, 刘利双. 2016. 澜沧江杂岩带小黑江-上允地区蓝片岩的成因及变质演化[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 35(5): 804-820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201605005.htm 王慧宁, 刘福来, 冀磊, 田忠华, 许王, 刘利双. 2019. 昌宁—孟连杂岩带澜沧岩群的岩石学、地球化学和变质演化及其对古特提斯构造演化的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 35(6): 1773-1799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201906009.htm 魏春景, 朱文萍. 2007. 多硅白云母地质压力计的研究进展[J]. 地球通报, 26(9): 1123-1130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200709015.htm 魏春景. 1994. 蓝片岩及其有关高压变质带研究的新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 1(1/2): 140-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY4Z1.024.htm 徐桂香, 曾文涛, 孙载波, 黄亮, 陈光艳, 田素梅, 周坤. 2016. 滇西双江县勐库地区(退变质)榴辉岩的岩石学、矿物学特征[J]. 地质通报, 35(7), 1036-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201607001.htm 云南省地质矿产局. 1990. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 云南省地质矿产局. 1996. 云南省岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. 张儒瑗, 从柏林, 韩秀伶. 1990. 滇西蓝片岩中的角闪石[J]. 地质科学, 1: 43-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199001004.htm 张儒瑗, 从柏林, 李永刚. 1989. 滇西蓝片岩及其构造意义[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 12: 1317-1329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK198912012.htm 赵靖, 钟大赉, 王毅. 1994. 滇西澜沧变质带变质作用和变形作用的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 10(1): 27-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199401002.htm 赵靖. 1993. 滇西澜沧变质带中白云母的研究及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 12(3): 251-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW199303006.htm 钟大赉. 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-231. 周维全, 林文信. 1982. 澜沧江变质带南段蓝闪石片岩特征[J]. 中国区域地质, (2): 76-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD198202008.htm



 下载:
下载: