Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic potential of ultrabasic rocks in North Altun area, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
北阿尔金地区经历了新元古代中期—早寒武世北阿尔金洋裂解形成及扩张、中寒武世—晚奥陶世北阿尔金洋双向俯冲-增生和早志留世—早泥盆世北阿尔金洋碰撞造山作用,在漫长的构造演化过程中保留了较多的基性-超基性岩体,地球化学研究显示,北阿尔金地区至少存在两种构造环境下的超基性岩。第一种超基性岩的微量元素特征显示其几乎没有受到地壳物质的混染,铂族元素含量低于原始地幔,推断其可能来源于原始地幔20%左右的部分熔融,形成于大陆裂谷的构造环境,为洋盆快速拉张时期幔源岩浆的快速上升侵位,代表了北阿尔金洋的初始裂解期间的岩浆活动。第二种超基性岩源区较为复杂,经历了较为强烈的地壳物质的混染,该组样品所在的蛇绿岩带具有俯冲带环境下蛇绿岩的特征,可能形成于汇聚背景下的弧后盆地环境,洋壳的俯冲携带大量的水及大陆边缘陆壳物质进入地幔岩浆源区,代表了北阿尔金地区在早古生代的古洋盆的俯冲消减过程。第一组样品的m/f值平均为1.64,为无矿的富铁质超基性岩,不具有Cu-Ni成矿潜力,铂族元素分析显示,其母岩浆可能为玄武质岩浆和超镁铁质岩浆混合的结果,为硫不饱和岩浆,经历过有限的硫化物熔离作用;第二组样品的铂族元素和Ni的含量较高,主要来源于地幔,未经历硫化物的熔离作用,m/f值平均17.95,为与铬铁矿有关的镁质超基性岩,具有形成铬铁矿的潜力,但形成铜镍硫化物矿床的潜力不大。
Abstract:North Alun area has experienced complicated tectonic evolution process and, as a result, quite many ultrabasic rocks were formed in a post-collision extension background throughout the area, and geochemical characteristics of these rocks show that ultrabasic rocks in the study area have two kinds of different magmatic sources, evolution processes and tectonic backgrounds. The trace element characteristics show that the first group samples are almost free from the contamination of crustal substances and that the PGE content is lower than that of the primitive mantle. It can be inferred that the first group samples might have come from about 20% partial melting of the primitive mantle and the samples might have been formed in the continental rift tectonic environment because of the rapid rise and emplacement of mantle-derived magma during the quick extension of the oceanic basin, representing the magmatic activity of North Altun Ocean during the initial cleavage period. The geochemical characteristics of the second group samples show that their source region was more complicated and experienced a relatively strong contamination of crustal substances. The research shows that ophiolite belt contained in the samples has the characteristics of ophiolite in a subduction zone environment; therefore, it can be inferred that it was probably formed in a back-arc basin environment under the convergence background, the subduction of oceanic crust that carried a large amount of water and continental crustal substances in the continental margin entered the mantle magma region, suggesting that the subduction process of the ancient oceanic basin of North Altun area occurred in the Early Paleozoic. The average m/f value of the first group samples is 1.64, indicating that the samples are barren iron-rich ultrabasic rocks having no metallogenic potential of Cu-Ni deposits. The analysis of platinum group elements shows that the parental magma might have resulted from the mixing of basaltic magma with ultramafic magma, which was sulfur-unsaturated magma, and the samples experienced limited sulfide liquation. The average m/f value of the second group samples is 17.95, indicating that the samples consist of magnesian ultrabasic rocks associated with chromite, and they have no metallogenic potential of chromite; the values of platinum group elements and Ni are comparatively high, and these elements were mainly from the mantle, and did not experience sulfide liquation. Therefore, the metallogenic potential of Cu-Ni sulfide deposits of the two groups of samples is quite low.
-
1. 引言
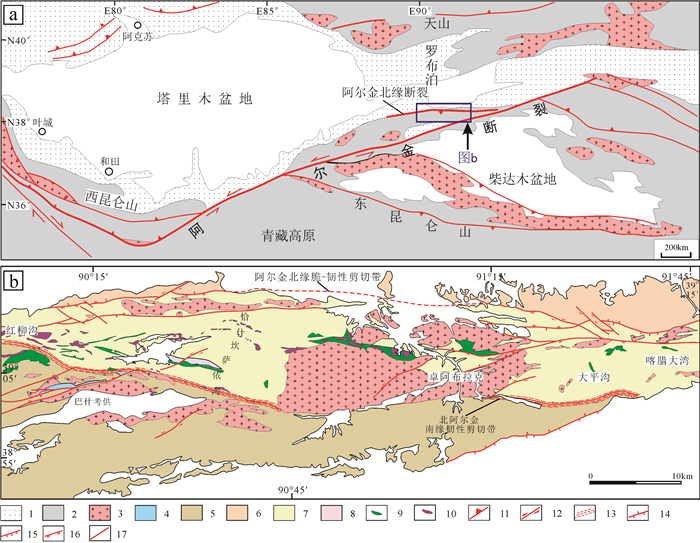
阿尔金造山带位于青藏高原北部边缘,分割了中国西部两个最大的盆地——塔里木盆地和柴达木盆地(图 1a),阿尔金造山带与西部的昆仑造山带、东部的祁连造山带和秦岭造山带共同构成了秦祁昆造山带,是中国最重要的多金属成矿区带之一(李文渊等,2011;董顺利等,2013)。近几十年来,北阿尔金地区的基础地质研究热点主要集中在阿尔金断裂的形成和演化(郭召杰等,1998;葛肖虹等,2002;李海兵等,2007;Liu et al., 2007;陈柏林等,2010;孟繁聪等,2010;吴磊等,2013)、早古生代岩浆活动与大地构造演化(陈宣华等,2003;戚学祥等,2005;吴才来等, 2005, 2007;陈正乐等,2006;Lu et al., 2008;Wu et al., 2009;韩凤斌等,2012;刘涵等, 2012, 2013;张占武等,2012;李松斌等,2013;孟令通等,2015;王立社等,2015;张建新等,2015;何江涛等,2016;吴玉等,2016;吴玉等,2019)、北阿尔金成矿带成矿作用(陈柏林等,2015;伍跃中等,2017)、超高压变质作用(刘良等,1999;杨经绥等,2003;Zhang et al., 2005, 2006;张建新等,2007;Liu et al., 2013;朱文斌等,2018;Pak et al., 2019)、蛇绿混杂岩带构造环境和年代学研究(吴俊等,2002;杨经绥等, 2003, 2008;Liu et al., 2007;修群业等,2007;张志诚等,2009;董连慧等,2010;杨子江等,2012)等方面,并取得了丰硕的成果。
![]() 图 1 北阿尔金地区地质构造简图(a)及研究区地质图(b)1—中生代—新生代沉积岩;2—早中生代岩体;3—古生代侵入岩;4—侏罗系;5—古—新元古界;6—太古宇—古元古界;7—北阿尔金构造杂岩带;8—早古生代高压变质岩;9—基性岩;10—超基性岩;11—断裂;12—走滑断裂;13—韧性剪切带;14—正断层;15—逆断层;16—压性断层;17—性质不明断层Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the North Altun area (a) and geological map of the study area (b)1- Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary rock; 2- Early Mesozoic intrusions; 3- Paleozoic intrusions; 4- Jurassic strata; 5- Paleocene-Neoproterozoic strata; 6- Paleocean-Paleocene strata; 7- North Altun tectonic complex zone; 8- Early Paleozoic high-pressure metamorphic rock; 9- Basic rocks; 10- Ultrabasic rocks; 11- Fracture; 12- Strike-slip fault; 13- Ductile shear zone; 14- Normal fault; 15 - Reverse fault; 16- Compressive fault; 17- Unknown fault
图 1 北阿尔金地区地质构造简图(a)及研究区地质图(b)1—中生代—新生代沉积岩;2—早中生代岩体;3—古生代侵入岩;4—侏罗系;5—古—新元古界;6—太古宇—古元古界;7—北阿尔金构造杂岩带;8—早古生代高压变质岩;9—基性岩;10—超基性岩;11—断裂;12—走滑断裂;13—韧性剪切带;14—正断层;15—逆断层;16—压性断层;17—性质不明断层Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the North Altun area (a) and geological map of the study area (b)1- Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary rock; 2- Early Mesozoic intrusions; 3- Paleozoic intrusions; 4- Jurassic strata; 5- Paleocene-Neoproterozoic strata; 6- Paleocean-Paleocene strata; 7- North Altun tectonic complex zone; 8- Early Paleozoic high-pressure metamorphic rock; 9- Basic rocks; 10- Ultrabasic rocks; 11- Fracture; 12- Strike-slip fault; 13- Ductile shear zone; 14- Normal fault; 15 - Reverse fault; 16- Compressive fault; 17- Unknown fault阿尔金造山带经历了复杂的构造演化历史以及多期多旋回的地质构造运动和岩浆热事件,为成矿作用提供了优越的地质条件。研究表明,晚燕山期以来,阿尔金断裂带左行走滑400 km(许志琴等,1999;Ritts and Biffi, 2000;Yue et al., 2001;黄立功等,2004;刘永江等,2007),北阿尔金地区是北祁连成矿带西段被阿尔金断裂错断的部分,两地的矿床成因类型、矿种组合关系都具有可比性(陈柏林等,2010),阿尔金造山带东段,尤其是北阿尔金地区具有良好的多金属矿床成矿潜力,实际的矿产资源勘查工作也证实了该观点,目前在整个阿尔金成矿带已发现150多个矿床和矿点,矿种包括金、银、铜、铅锌、铁等,大量的研究集中于铁、铅锌、金、银等矿床的成矿特征和分布规律(李月臣等,2007;陈柏林等, 2009, 2012, 2018;Gao et al., 2011)、成矿带的划分和找矿预测(毛德宝等,2006;杨万志等,2013)。
近年来,在中亚造山带西段的阿尔泰、东天山和中天山等地区陆续发现了喀拉通克、黄山、图拉尔根、白石泉、天宇等一系列产于镁铁质-超镁铁质小型侵入体中的岩浆硫化物矿床,引起了国内外研究者的关注(秦克章等,2002;三金柱等,2006;柴凤梅等,2007;Mao et al., 2008;钱壮志等,2009;Song et al., 2009;Tang et al., 2011, 2012, 2014)。北阿尔金地区显生宙以来经历了早古生代的碰撞造山作用(刘函等,2013;张建新等,2015;吴玉等,2016),分布有较多的超基性岩体,但到目前为止还没有发现与超基性岩有关的矿床,因此本文通过对研究区内主要的超基性岩体进行地球化学和铂族元素分析,探讨其成矿潜力。
2. 地质背景
在大地构造位置上,北阿尔金地区位于阿尔金走滑断裂北侧与东西向的阿尔金北缘断裂所夹持的区域,北接塔里木地块南缘,南与柴达木盆地毗邻(图 1a)。研究显示,研究区经历了新元古代中期—早寒武世北阿尔金洋裂解形成及扩张阶段、中寒武世—晚奥陶世北阿尔金洋双向俯冲-增生阶段至早志留世—早泥盆世北阿尔金洋碰撞造山(刘良等,1999;戚学祥等,2005;张建新等,2007;杨经绥等,2008;吴玉,2016)。晚中生代以来由于印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞造山的远程效应,阿尔金断裂带发生了大规模的左行走滑(崔军文等,1999;Liu et al., 2007;陈柏林等,2010)。
研究区地层属于塔里木地层区中塔南地层分区的阿尔金山地层小区,由老到新依次出露太古宇达格拉格布拉克组(Ardg),中元古界蓟县系金雁山组(Zjj),下古生界上寒武统卓阿布拉克组(Є3zh)、斯米尔布拉克组(Є3s),石炭系上统英格布拉克组(C3y),古近系渐新统下干柴沟组(E3g)、新近系中新统上干柴沟组(N1g)、中新统下油砂山组(N1y)和第四系(Q)。区内主要发育古生代侵入岩,少量新元古代花岗闪长岩,呈规模较小的岩株或岩脉状侵位于太古界达格拉格布拉克组(Ardg)之中。早古生代侵入岩岩石类型有闪长岩、石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、似斑状二长花岗岩和花岗岩,均侵位于下古生界上寒武统卓阿布拉克组(Є3zh)和斯米尔布拉克组(Є3s)之中。研究区内辉长岩岩体规模较小,沿白尖山断裂的南侧呈比较零散状分布,为蛇绿混杂岩带的组成部分,中酸性侵入岩呈规模较大岩枝或岩基状产出。
阿尔金地区分布有两条蛇绿岩套,分别为北部红柳沟—拉配泉蛇绿混杂岩带和阿尔金山南部阿帕—茫崖蛇绿混杂岩带。此次研究的基性—超基性岩主要分布在北部的红柳沟—拉配泉蛇绿混杂岩带中,该蛇绿岩带宽为8~15 km,呈北东东或近东西向带状分布,在蛇绿混杂岩带中分布有72个超镁铁-镁铁质岩体,总面积约80 km2,岩体形态各不相同,规模极不一致,最大者可达十几平方千米(图 1b)。岩体呈岩墙、岩瘤、岩枝、岩脉成群出现。岩体中岩石类型分布很不均匀。在西段红柳沟到恰什坎萨依沟(后文简称恰沟)一带,基性岩与超基性岩伴生产出(图 1b);中段恰沟至卓阿布拉克(泉)北一带,主要出露规模较大基性侵入岩;而东段的白尖山至塔什布拉克(泉)北侧,主要出露超基性侵入岩。其中超基性岩类由堆晶橄榄岩、异剥橄榄岩、方辉橄榄岩、蛇纹岩、二辉橄榄岩和辉石岩等组成。
3. 样品采集及分析方法
3.1 样品采集
此次研究主要采集了新疆北阿尔金地区红柳沟、贝克滩、恰什坎萨伊、沟口泉、拉配泉等地的主要超基性岩体样品,基本涵盖了北阿尔金地区主要的超基性岩体(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 北阿尔金地区主要超基性岩体a—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的二辉橄榄岩;b—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的橄榄岩;c—红柳沟产于基性火山岩中的超基性岩透镜体;d—恰什坎萨依沟北侧产于复理石沉积岩中的超基性岩;e—蛇纹石化的超基性岩Figure 2. Main ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaa- Lherzolite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; b- Peridotite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; c- Ultrabasic rocks lens body produced in basic volcanic rocks on Hongliu ditch; d- Ultrabasic rocks produced in falsite sedimentary rocks on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; e- Serpentinized ultrabasic rocks
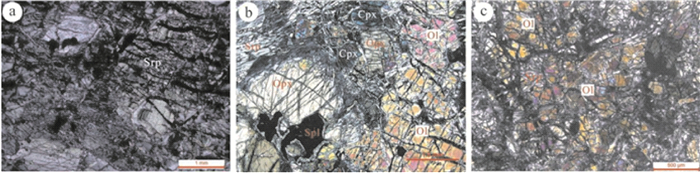
图 2 北阿尔金地区主要超基性岩体a—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的二辉橄榄岩;b—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的橄榄岩;c—红柳沟产于基性火山岩中的超基性岩透镜体;d—恰什坎萨依沟北侧产于复理石沉积岩中的超基性岩;e—蛇纹石化的超基性岩Figure 2. Main ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaa- Lherzolite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; b- Peridotite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; c- Ultrabasic rocks lens body produced in basic volcanic rocks on Hongliu ditch; d- Ultrabasic rocks produced in falsite sedimentary rocks on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; e- Serpentinized ultrabasic rocks北阿尔金蛇绿岩套中超基性岩野外露头呈灰绿或暗灰色(图 2),具网环/网格结构和变余斑状结构,主要由橄榄石(65%~70%)和辉石(30%±)组成,超基性岩中的橄榄石基本上已全部蛇纹石化(图 3,图 4a),但个别仍较为新鲜,在二辉橄榄岩中可见橄榄石颗粒较大,粒径在1~2.5 mm,部分已蚀变成蛇纹石,镜下还可见斜方辉石、单斜辉石以及少量的尖晶石(图 4b);在镜下可见橄榄岩主要由橄榄石组成,辉石少见或发生了蚀变,可见少量阳起石化,其中橄榄石颗粒相对较小,粒径为0.1~0.5 mm(图 4c)。基性岩主要为堆晶辉长岩,面积超过20 km2。岩石具中—细粒辉长结构,块状构造。主要由普通辉石(50%~60%)、基性斜长石(35%~45%)及少量石英(5%±)组成。副矿物有钛铁矿、磁铁矿、黄铁矿、锆石、磷灰石和金红石等。其中普通辉石常被绿泥石交代。
![]() 图 4 北阿尔金地区超基性岩显微镜下照片a—蛇纹石化橄榄石;b—二辉橄榄岩矿物组成;c—橄榄岩矿物组成;Ol—橄榄石; Cpx—单斜辉石; Opx—斜方辉石; Srp—蛇纹石; Spl—尖晶石Figure 4. Micrographs of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaa- Serpentinized olivine; b- Mineral composition of lherzolite; c- Mineral composition of Peridotite; Cpx- Clinopyxene; Opx- Orthopyroxene; Srp-Serpentine; Spl-Spinel
图 4 北阿尔金地区超基性岩显微镜下照片a—蛇纹石化橄榄石;b—二辉橄榄岩矿物组成;c—橄榄岩矿物组成;Ol—橄榄石; Cpx—单斜辉石; Opx—斜方辉石; Srp—蛇纹石; Spl—尖晶石Figure 4. Micrographs of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaa- Serpentinized olivine; b- Mineral composition of lherzolite; c- Mineral composition of Peridotite; Cpx- Clinopyxene; Opx- Orthopyroxene; Srp-Serpentine; Spl-Spinel3.2 地球化学分析
本次研究选择了16个较新鲜的岩石样品进行了地球化学分析,分析测试结果见表 1。
表 1 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩主量元素分析结果(%)Table 1. Major element analytical results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun Area (%)
地球化学分析是在国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素使用X-荧光光谱仪(3080E)进行测试,检测下限为0.05%,其中FeO采用容量滴定法,CO2用电导法,H2O-用重量法分析。微量元素分析使用等离子质谱仪ICP-MS(Excell)进行分析,稀土元素检测下限为0.05×10-6,部分元素检测下限为0.5×10-6。
3.3 铂族元素(PGE)分析
铂族元素(PGE)包括Os、Ir、Ru、Rh、Pt和Pd等6个元素,它们在地球表面所能发现的各类岩石中含量仅为10-9数量级,但特殊化学性质使它们具有明显不同于其他微量元素的地球化学行为,因此,在研究地球早期演化过程和机制、幔源岩浆起源和演化及相关岩浆矿床的成因中具有重要的示踪意义。本次研究选择了14个较新鲜的岩石样品进行了铂族元素分析,测试结果见表 2。
表 2 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩微量和稀土元素分析结果(10-6)Table 2. Trace and rare earth elements analytical results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Alun area (10-6)
铂素元素分析是在国家地质实验测试中心完成,首先将待测样品与碳酸钠、硼酸钠、硼砂、玻璃粉、硫磺、面粉混合,倒入坩埚中,然后加入适量锇稀释剂在1150℃高温炉内熔融,将熔体倒入铁模中冷却后取出锍扣,用HCl溶解锍扣滤出不溶物,在封闭溶样器中用王水溶解滤渣,最后在ICP-MS上测定Pt、Pd、Rh、Ir、Ru和Os,全流程空白值:Os、Ir、Ru、Pd为0.3 ng,Pt、Rh为0.06 ng。
4. 结果分析
4.1 主量元素地球化学特征
北阿尔金地区超基性岩主要分布在恰沟北段和红柳沟北部。主量元素分析结果剔除挥发组分H2O、CO2和LOI之后重新换算到100%。结果显示全岩SiO2含量为39.89%~49.75%,平均为46.16%。除SiO2之外,样品的A12O3、CaO、K2O、Na2O、MgO、P2O5、TiO2含量特征明显分为两组,第一组为洽沟和红柳沟北超基性岩,岩性主要为辉长岩;第二组为沟口泉、贝克滩和拉配泉地区的超基性岩,岩性主要为单辉辉橄岩、二辉辉橄岩、单辉辉石岩等,普遍蛇纹岩化。第一组样品上述氧化物含量分别为8.65%~14.91%、7.53%~11.11%、0.27%~4.88%、1.54~ 3.12%、4.15% ~13.01%、0.38% ~0.50%、3.33% ~ 4.05%;第二组样品上述氧化物含量分别为0.42%~ 1.86%、0.10%~6.30%、0.01%~0.02%、0.01%~0.08%、37.09%~46.56%、≤0.01%、0.01%~0.05%;2组样品的Na2O-K2O分别为2.04%~6.13%和0.01%~0.09%,m/f值(m/f=(Mg2--Ni2-)/(Fe2--Fe3--Mn2-))和Mg#分别为0.62~2.42、34~65和77~97,第一组样品的Mg#明显小于残留地幔岩的Mg#(89~92),而第二组样品的Mg#基本在地幔岩的Mg#范围内(平均值为90),说明第一组样品应为一种部分熔融程度相对较高的熔体。吴利仁(1963)根据m/f值将超基性岩分为镁质超基性岩(m/f>6.5)、铁质超基性岩(m/f=2~6.5)、富铁质超基性岩(m/f=0.5~2),据此,第一组样品为富铁质超基性岩(平均为1.64),第二组样品为镁质超基性岩(平均17.95)。
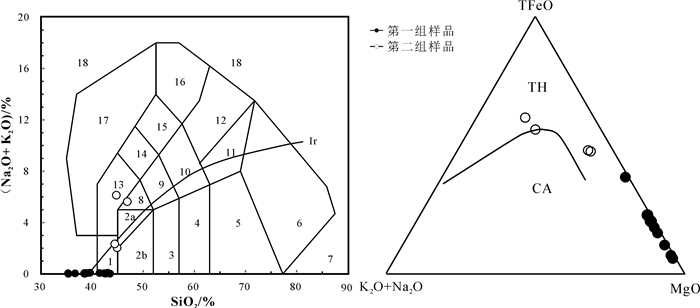
在TAS图解上(图 5),第一组样品主要落在了Ir分界线下方亚碱性辉长岩范围内,第二组样品落在了橄榄辉长岩到亚碱性辉长岩的范围内,第一组样品的Na2O-K2O含量更高一些,落在碱性-亚碱性过渡区内。在AFM图解[(Na2O-K2O)-TFeOMgO]上(图 5),第一组样品落在了拉斑系列范围内,第二组样品主要落在了钙碱性系列范围内,并靠近MgO端元。
![]() 图 5 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TAS和AFM图解Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性;1—橄榄辉长岩;2a—碱性辉长岩;2b—亚碱性辉长岩;TH—拉斑系列;CA—钙碱性系列Figure 5. TAS (a) and AFM diagrams (b) for the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaIr-Irvine boundary, The upper area is alkaline and the lower area is subalkaline; 1-Olivine gabbro; 2a-Basic gabbro; 2b-Subalkaline gabbro; THTholeiite series; CA-Calcium alkaline series
图 5 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TAS和AFM图解Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性;1—橄榄辉长岩;2a—碱性辉长岩;2b—亚碱性辉长岩;TH—拉斑系列;CA—钙碱性系列Figure 5. TAS (a) and AFM diagrams (b) for the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaIr-Irvine boundary, The upper area is alkaline and the lower area is subalkaline; 1-Olivine gabbro; 2a-Basic gabbro; 2b-Subalkaline gabbro; THTholeiite series; CA-Calcium alkaline series总的来说,第一组样品相对于第二组样品具有低的MgO含量和高的A12O3、CaO、K2O、TFeO、Na2O、P2O5和TiO2含量,因此也导致了其m/f和Mg#均低于第二组样品。
4.2 微量与稀土元素地球化学特征
微量元素含量及分布形式受控于岩浆体系,不同的构造环境发育不同的岩浆体系,因此可以通过对微量元素的特征进行对比,进而讨论岩体就位的构造环境,比如洋中脊拉斑玄武岩以亏损大离子亲石元素、富LREE为特征;岛弧拉斑玄武岩以低钾低钛、平坦型稀土配分为特征;而岛弧钙碱玄武岩则具有高钾低钛、高Sr含量、富LREE、亏损高场强元素的特征(Lassiter et al., 1997)。
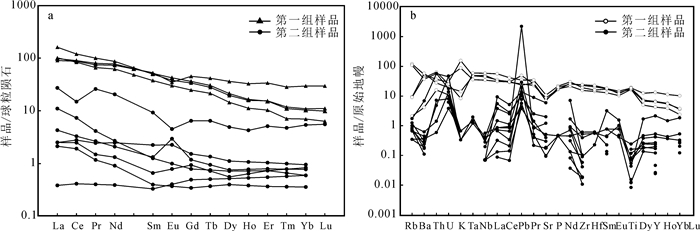
第一组样品稀土元素总含量(ΣREE)较高,为131~190×10-6,平均为158×10-6,轻重稀土分异明显(LREE/HREE=3.72~9.12),平均为7.09,(La/Yb)N为3.06~14.85,平均为10.51,δEu为0.71~0.97,显示轻微的Eu负异常,岩石中稀土元素Eu的富集与亏损主要取决于含钙造岩矿物的聚集和迁移,含钙的造岩矿物主要有偏基性的斜长石、磷灰石和含钙辉石,这类矿物中Ca2-离子半径与Eu2-、Eu3-相近,且与Eu2-电价相同,故晶体化学性质决定了Eu主要以类质同相的形式进入斜长石、磷灰石、单斜辉石等造岩矿物。由表 1可以看出,该组样品的CaO的含量较高,弱的Eu异常说明岩浆演化过程中未经历明显的分离结晶作用。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解上(图 6a),样品的配分模式为轻稀土富集的右倾式,类似于地幔橄榄岩底辟侵位过程中早期部分深熔作用分出的熔体,所有样品稀土配分模式十分一致,显示这些岩石来自相同的源区。样品与OIB配分曲线相似。在微量元素原始地幔标准化图解上,大离子亲石元素如Rb、K地球化学活动性强,受后期蚀变作用影响明显,分布形式不太一致(图 6b),除此之外的其他元素特征十分一致,均强烈亏损Sr元素,研究认为Sr的负异常可能是由于岩石的蚀变作用引起的,而样品Pb的正异常指示其成岩物质来自于富集型地幔E-MORB。
第二组样品的稀土元素总含量(ΣREE)很低,为0.28×10-6~34.26×10-6,平均为5.65×10-6,一些元素含量甚至低于检测限,在能完整显示球粒陨石标准化曲线的样品中,轻重稀土分异明显(LREE/HREE=1.36~74.20),平均为14.09,(La/Yb)N为0.65~ 30.91,平均为11.90。LREE和HREE的分异较大,结合岩体蚀变特征和研究区构造演化历史,认为其可能是由于经历了俯冲洋壳流体改造的原因,并受到一定的地幔交代作用(杨经绥等,2008)。样品的δEu值变化较大,为0.57~11.34,在计算出的δEu中,大部分为1左右,异常不明显。该组样品的微量元素含量很低,在原始地幔标准化图解上,大部分样品未能完整的显示出标准化曲线,但也可以看出,样品较富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba,由于蛇纹石化作用导致Rb、Ba、Th、K等元素相对富集,Zr、Hf、Ta等元素相对亏损(标准化图上没有数据点,说明含量低于检测值)。
微量元素标准化图解显示第二组样品亏损Nb、Ta等元素,可能和来自消减带物质的加入有关(张旗等,1999)。从表 3可以看出第一组样品与大陆裂谷拉斑玄武岩地球化学特征相似,第二组样品与图拉尔根含矿岩体,以及喀拉通克、岛弧钙碱玄武岩相似,具有类似岛弧钙碱玄武岩属性。
表 3 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩地球化学特征与各类玄武岩对比Table 3. Comparison of geochemical characteristics of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun area with various types of basalt
Th、Ta两元素均属强不相容元素,在软流圈地幔中具有相似的丰度,并在熔体与结晶矿物间具有基本相同的分配系数,岩浆与陆壳发生混染作用使得岩石的Th/Ta变大,因此Th/Ta是与俯冲有关的汇聚大地构造环境判别的重要指标(MeKenzie et al., 1991)。第一组样品的Th/Ta平均值为2.07,十分接近原始地幔的Th/Ta值2.2(Condie,1997),说明岩体在就位的过程中很少受到地壳物质的混染。第二组样品的Ta含量普遍较低,可测得的Ta含量的样品的Th/Ta值平均为7.91,明显高于原始地幔的Th/Ta值,说明其在就位的过程中受到了较多的地壳混染。La/Sm值也显示了相似的特征,通常认为高La/Sm(>4.5)值指示了地壳物质的混染(Lassiter et al., 1997),此次研究的第一组样品的La/Sm平均值为3.72,说明其没有受到地壳物质的混染,而第二组样品的La/Sm平均值为8.18,地壳物质的混染较为强烈。
4.3 铂族元素(PGE)特征
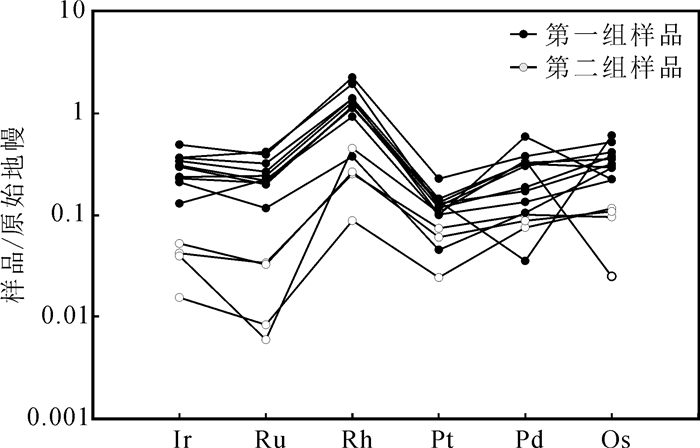
从表 4可以看出,第一组样品的铂族元素含量(∑PGE)较低,为4.23 × 10-9~12.04 × 10-9,平均为7.89×10-9,远低于原始上地幔的PGE含量(23.75× 10-9)(Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999),各元素含量差别较大,以Pt含量最高,为1.20×10-9~5.21×10-9,Rh含量最低,为0.08× 10-9~0.41×10-9,Pd/Ir=2.31~12.00,明显高于原始地幔的Pd/Ir值(1.18)(Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999),可能与Pd和Ir在部分熔融过程中的相容性有关,部分熔融程度越低,Pd/Ir值越大(Barnes et al., 1985)。
表 4 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩铂族元素分析结果(10-9)Table 4. Platinum group element analysis results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun area (10-9)
第二组样品的铂族元素含量较高,为13.03× 10-9~40.93×10-9,平均为25.68×10-9,大部分样品的PGE含量都高于原始上地幔的PGE含量(23.75× 10-9)(Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999),Pt和Rh含量较高,Pd/Ir=0.16~6.28,除一个样品外,其余样品Pd/Ir值平均为0.97,略低于原始地幔的Pd/Ir值(1.18)(Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999),PGE含量与岩石的SiO2含量并没有明显的相关性。国内的一些超基性岩Cu-Ni硫化物矿床如喀拉通克铜镍矿的镁铁质岩石PGE含量变化于0.2×10-9~44×10-9,平均为10× 10-9(钱壮志等,2009),白马寨矿床岩石的PGE含量为3×10-9~71×10-9,平均19×10-9(王生伟等,2006),白石泉PGE含量为2×10-9~78×10-9,平均为15×10-9(柴凤梅等,2007),东天山香山和图拉尔根矿区岩石PGE含量为1×10-9~5×10-9(孙赫等,2008),金川矿床超镁铁质岩石PGE平均含量为35×10-9(汤中立等,1995)。可以看出第一组样品的PGE含量普遍低于国内主要的超基性岩Cu-Ni硫化物矿床,而第二组样品PGE含量与金川矿床岩石中的PGE含量相近。
在铂族元素原始地幔标准化图解上(图 7),第一组样品显示比较明显的左倾配分形式,这与Ir在地幔部分熔融期间趋于相容,而Pd组趋于不相容有关,说明岩浆深部演化比较充分。而第二组样品显示略微的右倾模式,与俯冲带环境相吻合(Naldrett et al., 1979),这是因为流体相会造成Pt、Pd等相对易搬运的PGE元素迁移造成的。研究区两组样品的PGE分布的形式表明本区超基性侵入岩可能形成于不同的构造演化阶段。
![]() 图 7 北阿尔金地区超基性岩铂族元素原始地幔标准化图解(铂族元素原始地幔丰度数据引自Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999)Figure 7. Primitive mantle- normalized PGE diagrams of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun(abundance of PGE in mantle after Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1985; Barnes and Maier, 1999)
图 7 北阿尔金地区超基性岩铂族元素原始地幔标准化图解(铂族元素原始地幔丰度数据引自Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999)Figure 7. Primitive mantle- normalized PGE diagrams of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun(abundance of PGE in mantle after Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1985; Barnes and Maier, 1999)5. 讨论
5.1 岩浆源区特征与构造背景
北阿尔金地区的超基性岩主要分布在蛇绿岩带中,而蛇绿岩带被认为是识别古板块缝合线的重要标志,一般认为蛇绿岩中的超基性岩是大洋岩石圈向大陆消减时,洋壳下的上地幔物质随洋壳物质一起仰冲、拼贴到大陆边缘,因此常与洋壳物质共生。
此次研究的第一组样品的地球化学特征显示其源区几乎没有受到地壳物质的混染,但PGE含量低于原始地幔含量,一般幔源岩浆中PGE含量过低可能有两方面原因,一是原始地幔部分熔融程度较高时,原始岩浆中含有与原始地幔相当的PGE含量,但在深部发生了硫化物预先熔离,大大降低了岩浆中PGE的含量;二是当地幔部分熔融程度较低时,原始地幔中少量PGE随着部分熔融过程进入岩浆,绝大部分PGE仍然保存在残留的原始地幔中(Keays,1995),结果是部分熔融岩浆中PGE元素含量很低。孙赫等(2008)对东天山镁铁质—超镁铁质岩的铂族元素研究显示,来自上地幔高程度部分熔融(>25%)的岩浆中PGE含量与原始地幔的PGE含量相当,少量的硫化物熔离都可以引起PGE的严重亏损,而部分熔融程度较低的岩浆中有可能产生低PGE含量的岩体,根据其定量模拟结果,结合此次研究第一组样品的PGE含量,推断其可能来源于原始地幔20%左右的部分熔融。
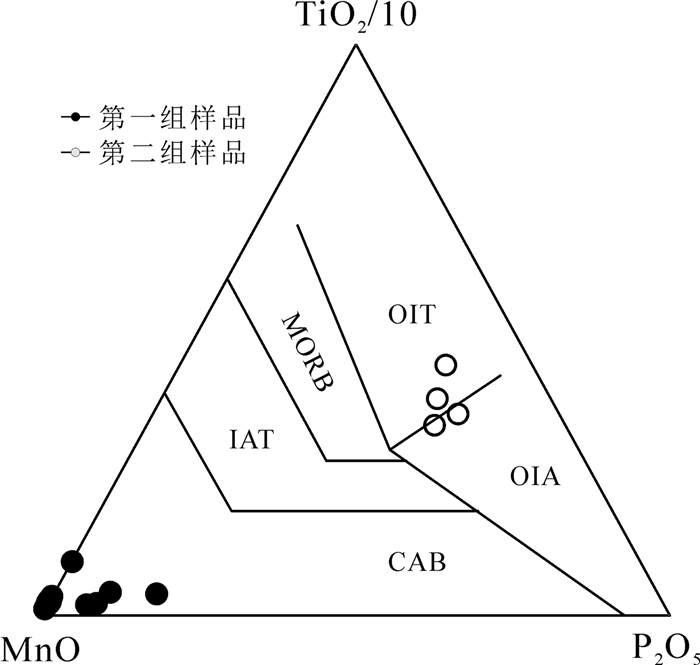
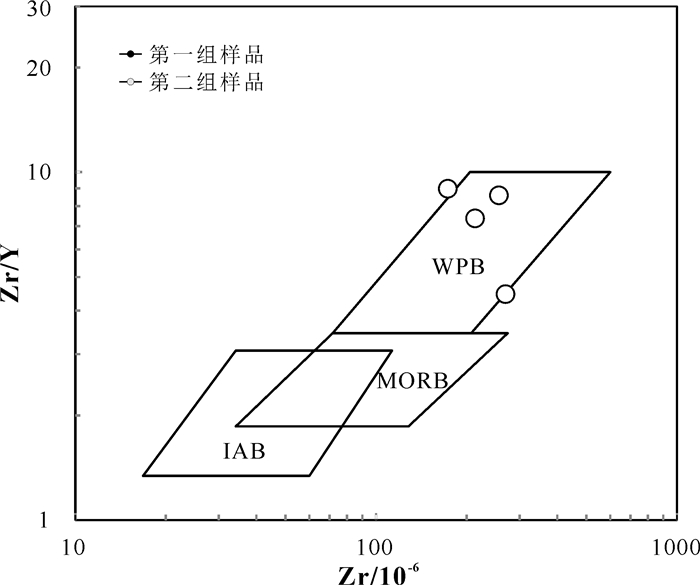
第一组样品在TiO2/10-P2O5-MnO图解上(图 8)落在了洋岛拉斑玄武岩范围内,幔源岩浆在侵位过程中最容易受到地壳物质的混入,但由于地壳混入对Zr、Y的含量影响不大,因此Zr-Zr/Y图解可以较真实的反应幔源岩浆的形成环境(夏林圻等,2007)。在Zr-Zr/Y图解上(图 9),由于第二组样品的Zr含量很低,没有落在构造判别区域内,第一组样品都落在了板内玄武岩区,其较高的Zr含量(平均为228×10-6)和Zr/Y值(>4.5)都体现了大陆玄武岩的特征。根据以上特征可以认为其形成于大陆裂谷环境,为洋盆快速拉张时期幔源岩浆的快速上升侵位。
![]() 图 8 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5OIT—大洋岛屿拉斑玄武岩;OIA—大洋岛屿碱性玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩Figure 8. TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5 diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaOIT—Oceanic island tholeiite basalt; OIA- Oceanic island alkalibasalt; MORB- Mid- oceanic ridge basalt; IAT- Island arc tholeiite basalt; CAB-Calc-alkaline basalt
图 8 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5OIT—大洋岛屿拉斑玄武岩;OIA—大洋岛屿碱性玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩Figure 8. TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5 diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun areaOIT—Oceanic island tholeiite basalt; OIA- Oceanic island alkalibasalt; MORB- Mid- oceanic ridge basalt; IAT- Island arc tholeiite basalt; CAB-Calc-alkaline basalt研究显示,阿尔金与北祁连地区发育相同的沟-弧-盆俯冲体系(杜远生等,2004;张建新等,2007;吴才来等,2007;杨经绥等,2008;刘晓煌等,2010),它们在中生代以前为同一个构造带。刘函等(2012)在阿尔金地区发现了750 Ma的双峰式火山记录,西安地质矿产研究所也报道过在该区索拉克一带玄武岩锆石中获得SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为(763±17)Ma和(754±17)Ma,代表了北阿尔金洋的初始裂解时间。同时,在北祁连地区也有同时期的洋盆初始裂解记录(曾建元等,2006;陆松年等,2009)。葛肖虹等(2000)认为阿尔金北缘地区发育的蛇绿岩带很可能是Rodinia大陆在中国境内的缝合带,而西域板块则是跨越上述缝合带的Rodinia大陆的一部分。因此第一组样品形成的地球动力学背景可能为Rodinia超大陆在新元古代(700~800 Ma)的裂解事件。
原始地幔Zr/Nb值可区分亏损地幔、过渡型地幔和富集型地幔,亏损地幔Zr/Nb值>18,过渡型地幔和富集型地幔Zr/Nb值< 18(Roex et al., 1983)。第一组样品的Zr/Nb平均值为7.19,说明其可能来源于富集型地幔;第二组样品的Zr/Nb值明显分为两组,分别为2.53~8.80和20.40~22.95,说明其源区较为复杂,可能为多种性质的地幔端元的混合,地球化学特征也显示其经历了较为强烈的地壳物质的混染。
Nb与Ta,Zr与Hf是地球化学性质相近的不相容元素对,在岩浆部分熔融及结晶过程中不发生分异,但在遭受来自俯冲消减板片脱水或熔融形成的流体或熔体改造的地幔,其Nb与Ta、Zr与Hf将发生明显的分异(Stolz et al., 1996)。第一组样品的Nb/Ta和Zr/Hf平均值分别为16.95和40.44,与原始地幔值(17.8和37)(McDonough and Sun, 1995)非常接近,而第二组样品为3.85和25.04,与原始地幔值和地壳相应值(11和33)(Taylor and Mclennan, 1985)都不同,表明其与俯冲作用有关。原始地幔、MORB以及OIB的Ce/Pb值都为25(Sun and McDonough, 1989),Ce/Pb值低于20就可以认为有俯冲板片来源的流体加入到软流圈地幔中(Seghedi et al., 2004)。第一组样品的Ce/Pb平均值为26.6,而第二组为2.45,因此推测第二组样品可能形成于汇聚背景下的弧后盆地环境,在这种环境下,洋壳的俯冲可以使大量的富水的洋壳物质及大陆边缘陆壳物质进入幔源岩浆区,第二组样品的微量元素的特征也显示出明显的地壳物质混染特征和多种岩浆源区混合的特征,主要与俯冲板片来源的流体或/和熔体交代作用有关。
北阿尔金蛇绿混杂岩带中广泛存在枕状玄武岩、堆晶辉长岩、辉绿岩墻群以及基性火山岩,前人研究表明其中的玄武岩具有MORB和OIB的组合特征(吴峻等,2002;修群业等,2007;孟繁聪等,2010;刘涵等,2013),为典型大洋环境的火山活动,基性—超基性堆晶岩的岩石地球化学特征表明该蛇绿岩带具有俯冲带环境(SSZ型)蛇绿岩的特征(杨经绥等,2008;张志诚等,2009)。
对北阿尔金地区蛇绿岩及基性火山岩年代学研究显示,北阿尔金地区古洋盆的俯冲消减作用可能发生在早—中奥陶世(517~455 Ma),而大洋的闭合和陆-陆碰撞作用可能发生在中晚奥陶世末460 Ma左右(修群业等,2007;杨经绥等,2008;张志诚等,2009;杨子江等,2012;刘涵等,2013;郝瑞祥等,2013)。
因此,第二组样品可能形成于早古生代发生的古洋盆的俯冲消减过程中。
5.2 超基性岩Cu-Ni硫化物矿床成矿潜力
Naldrett(1999)总结了世界上大型Cu-Ni硫化物矿床具有的共同特征:能够结晶大量橄榄石的岩浆;发育明显的地壳缝合带(切穿地壳的深大断裂);围岩中的硫含量较高;相关的岩浆具有明显的亲铜元素亏损;与围岩相互作用;矿化产生在岩浆运移通道中或附近,主要定位于岩浆通道突然变宽或变缓的部位。但是,这几个特征并不是必须完全都满足才能形成世界级的镍铜硫化物矿床。
研究表明,高Mg的岩浆在离开地幔时S都是不饱和的(Keays,1995),并且需要较高程度的部分熔融,所以其可以携带大量成矿元素上升到地壳。但是,要形成岩浆Cu-Ni硫化物矿床,原始岩浆必须发生硫化物的熔离,而引起硫化物熔体熔离的机制主要包括:岩浆(富Fe矿物)的分异,可导致S溶解度的降低,使其含量饱和(Haughton et al., 1974);不同成分的S不饱和岩浆的混合导致S的饱和(Li et al., 2001);围岩混染,可以导致外来S的加入,而使S饱和(Ripley,1981;Lesher et al., 1993);也可能是围岩Si的加入,降低岩浆硫的溶解度而使其饱和(Irvine,1975;张招崇等,2003)。许多地壳混染证据已在诺里尔斯克、肖德伯里、金川等地区得到了广泛的同位素、稀土元素、痕量元素等资料的证实(Naldrett,1999;张招崇等,2003)。
第二组研究样品的Th/Ta和La/Sm值显示其经历了比较强烈的地壳物质的混染,具有形成Cu-Ni硫化物矿床的条件。在超基性岩浆分异时,Ni和Mg往往以类质同象的形式进入硅酸盐矿物结晶相,因此Mg含量的高低通常可以指示熔体中成矿元素Ni含量的高低。孙赫等(2006)对东天山图拉尔根Cu-Ni硫化物矿床的研究显示,与成矿有关的超基性岩中,含有较高的FeO代表了低的氧逸度环境,有利于铜镍硫化物的富集。此次研究的第二组样品相对于第一组样品虽然具有更高的MgO含量和Ni含量(平均为1809×10-6),但FeO含量较低,以Fe2O3为主,其高氧逸度的环境不利于铜镍硫化物的富集。
戈德列夫斯基(1982)按照侵入岩中MgO的含量把超基性岩浆及其结晶产物分为3类:(1)无硫化物的镁铁质岩石(≤8%);(2)含铜镍中等镁铁质岩石(8%~30%);(3)无硫化物的超镁铁质岩石(>30%)。孙小攀等(2018)对柴达木西北缘大通沟南山基性—超基性岩的研究也证实了第二类超基性岩浆具有一定的含矿性,而无硫化物的第一类和第三类岩浆铜镍矿化很弱甚至无矿化。此次研究的第一组样品为第一类,第二组样品为第三类,都属于无硫化物的超基性岩,限制了其Cu-Ni硫化物矿床的成矿潜力。
此次研究第一组样品的MgO含量为4.15%~ 13.01%,平均值为8.35%,应属于无硫化物的镁铁质岩石,m/f值为0.51~1.85,平均值为1.13,属于无矿的富铁质超基性岩(表 5),因此第一组样品不具有CuNi成矿潜力(图 10)。第二组超基性岩样品MgO含量为37.09%~46.56%,平均值为42.60%,应属于无硫化物的超镁铁质岩石,m/f值为3.44%~14.33%,平均值为11.80%,属于与铬铁矿有关的镁质超基性岩(表 5),说明北阿尔金超基性岩具有铬铁矿的成矿潜力,化学分析Cr的平均品位为0.273%,这与野外所观察到的超基性岩体铬铁矿化主要发育在蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩和二辉辉橄岩中相吻合。
表 5 基性-超基性岩含矿性分类Table 5. Ore-bearing potentiality of the ultrabasic rocks
Ni、Cu和PGE具有不同于其他微量元素的特殊的地球化学性质,在S不饱和的条件下,Ni、Os、Ir和Ru具有相容元素的特性,而Cu和Pd是强不相容元素,因此,它们在玄武岩浆分离结晶过程中常常发生分异。一旦体系达到S饱和,由于PGE具有极高的硫化物熔浆/硅酸盐熔浆分配系数,这些元素则会强烈地进入硫化物熔浆,极微量的硫化物熔离便可导致残余岩浆中PGE的显著亏损,因此,PGE是玄武岩浆硫化物熔离作用最敏感的示踪元素。PGE的这种特殊性质可用来探讨岩浆硫化物成矿的关键控制因素。Ni、Cu和PGE具有不同的单硫化物固溶体/硫化物熔浆分配系数,因此,它们也是硫化物熔浆结晶分异的重要示踪元素(宋谢炎等,2009)。
国内一些大型的铜镍矿床镁铁质岩石的PGE含量总体并不一定很高。一般认为,从硅酸盐岩浆中熔离出来的硫化物中PGE、Ni、Cu的含量最初由它们在硅酸盐岩浆中的浓度和硅酸盐熔体与硫化物熔体的比值决定(Campbell and Naldrettt, 1979)。PGE、Ni、Cu在硫化物中的含量也可能因为与新鲜补给的岩浆发生反应以及硫化物熔体分异而改变,或者因为后期热液作用而改变(Ebel and Naldrett, 1996)。
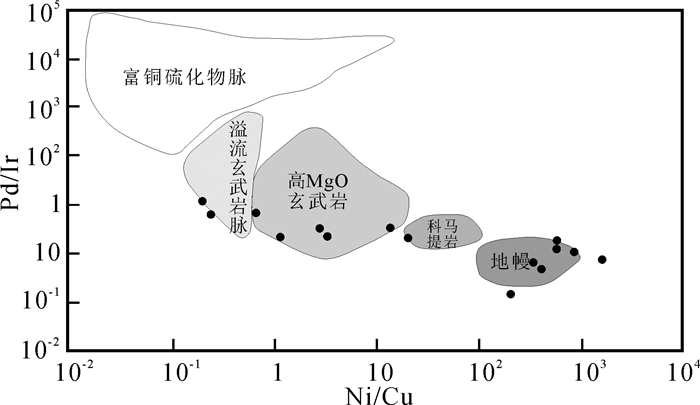
Pd和Ir是PGE元素中地球化学性质差异最大的元素,常用Pd/Ir值表征铂族元素的总体分异特征,原始地幔的Pd/Ir值为1.22,而不同成因的硫化物矿床具有不同的Pd/Ir值分布范围。研究的超基性岩的Pd/Ir值大部分小于10,说明研究区超基性岩PGE特征主要为岩浆作用的结果,受热液交代作用的硫化物和岩体的Pd/Ir值一般高于100。此次研究的样品Pd/Ir值最大为12,出现在红柳沟超基性岩中,说明其在所有样品中PGE分异程度最高,其他超基性岩PGE分异程度差别不大。一般来说,部分熔融程度越大,岩浆中的Pd/Ir值越小,Ni/Cu值越大。除红柳沟超基性岩外,其他岩体Pd/Ir值为0.16~12,平均值为2.77,Ni/Cu值变化范围较大,为0.21~1658。第一组样品为0.21~21.24,平均值为4.98,低于原始地幔值(71.4),变化范围包括了超镁铁质岩浆(>7)和镁铁质岩浆(< 2)形成的硫化物矿床的Ni/Cu值,说明该组样品母岩浆可能为玄武质岩浆和超镁铁质岩浆混合的结果。第二组样品Pd/Ir值为208~1658,其Ni含量一般大于1000×10-6,最大为2577×10-6,该组样品的另一个特征为PGE含量较高,在Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir图解上,第一组样品主要落在高MgO玄武岩和溢流玄武岩区域,个别样品位于科马提岩区域的边缘(图 11),研究认为,形成高Mg玄武质岩浆的地幔部分熔融程度应该≥10%,高镁玄武质岩浆和科马提岩浆在形成之初为硫化物不饱和岩浆。第二组样品主要落在了地幔区域内,说明其岩浆来源于地幔。
![]() 图 11 北阿尔金地区超基性岩Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir图解(不同源区范围据Barnes et al., 1988)Figure 11. Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area(outlined areas after Barnes et al., 1988)
图 11 北阿尔金地区超基性岩Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir图解(不同源区范围据Barnes et al., 1988)Figure 11. Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area(outlined areas after Barnes et al., 1988)岩浆在演化过程中S达到饱和发生硫化物熔离时,残余岩浆中的PGE较Cu、Ni、Ti大大亏损,Ni和Cu只发生微弱的降低。因此,残余岩浆具有比原始地幔高得多的Cu/Pd值(6500)和Ti/Pd值(3000),并且早期形成的硫化物较晚期形成的硫化物PGE富集。第一组样品的Cu/Pd和Ti/Pd值明显高于第二组,分别为13~585(平均146)和1573~28787(平均为12333),Cu/Pd值小于原始地幔,Ti/Pd值大于原始地幔值,表明这些岩体发生过少量的硫化物熔离作用。第二组样品的Cu/Pd和Ti/Pd值分别为0.49~ 3.6和14~53,未发生硫化物的熔离作用。同时,区内超基性岩基性程度不够高,成矿元素以分散状态为主,其中贝克滩东超基性岩最为典型,全岩都有较高的Cu、Ni含量,但是大多数达不到矿化标准,镍含量最高为0.26%,铜含量仅有个别达到0.5%,成矿潜力有限。
综上,认为阿尔金地区超基性岩体具有两种不同的岩浆源区和成因,虽然经历了不同的演化过程,但总的经历的硫化物熔离作用有限,具有一定的铬铁矿的成矿潜力,但形成岩浆型铜镍硫化物矿床潜力不大。
6. 结论
(1)北阿尔金地区发育两种不同类型的超基性岩,它们具有两种不同的构造环境和岩浆源区特征,其中第一类样品显示出大陆裂谷构造环境,其源区没有受到明显的地壳物质的混染,可能形成于新元古代阿尔金洋(祁连洋)裂解阶段;第二类样品地球化学特征显示出明显的地壳混染,源区受到强烈的俯冲板片来源的流体或/和熔体交代作用,结合区域上基性—超基性岩年代学研究结果,认为其可能形成于早古生代发生的阿尔金洋(祁连洋)洋盆的俯冲消减过程。
(2)研究区超基性岩都属于无低硫(无硫)的超基性岩,未经历或经历的硫化物熔离作用有限,限制了其Cu-Ni硫化物矿床的成矿潜力,但第二类样品具有铬铁矿的成矿潜力。
-
图 1 北阿尔金地区地质构造简图(a)及研究区地质图(b)
1—中生代—新生代沉积岩;2—早中生代岩体;3—古生代侵入岩;4—侏罗系;5—古—新元古界;6—太古宇—古元古界;7—北阿尔金构造杂岩带;8—早古生代高压变质岩;9—基性岩;10—超基性岩;11—断裂;12—走滑断裂;13—韧性剪切带;14—正断层;15—逆断层;16—压性断层;17—性质不明断层
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the North Altun area (a) and geological map of the study area (b)
1- Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary rock; 2- Early Mesozoic intrusions; 3- Paleozoic intrusions; 4- Jurassic strata; 5- Paleocene-Neoproterozoic strata; 6- Paleocean-Paleocene strata; 7- North Altun tectonic complex zone; 8- Early Paleozoic high-pressure metamorphic rock; 9- Basic rocks; 10- Ultrabasic rocks; 11- Fracture; 12- Strike-slip fault; 13- Ductile shear zone; 14- Normal fault; 15 - Reverse fault; 16- Compressive fault; 17- Unknown fault
图 2 北阿尔金地区主要超基性岩体
a—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的二辉橄榄岩;b—恰什坎萨依沟北侧的混杂岩带中的橄榄岩;c—红柳沟产于基性火山岩中的超基性岩透镜体;d—恰什坎萨依沟北侧产于复理石沉积岩中的超基性岩;e—蛇纹石化的超基性岩
Figure 2. Main ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area
a- Lherzolite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; b- Peridotite in the melange belt on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; c- Ultrabasic rocks lens body produced in basic volcanic rocks on Hongliu ditch; d- Ultrabasic rocks produced in falsite sedimentary rocks on the north side of Qiashikansayi ditch; e- Serpentinized ultrabasic rocks
图 4 北阿尔金地区超基性岩显微镜下照片
a—蛇纹石化橄榄石;b—二辉橄榄岩矿物组成;c—橄榄岩矿物组成;Ol—橄榄石; Cpx—单斜辉石; Opx—斜方辉石; Srp—蛇纹石; Spl—尖晶石
Figure 4. Micrographs of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area
a- Serpentinized olivine; b- Mineral composition of lherzolite; c- Mineral composition of Peridotite; Cpx- Clinopyxene; Opx- Orthopyroxene; Srp-Serpentine; Spl-Spinel
图 5 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TAS和AFM图解
Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性;1—橄榄辉长岩;2a—碱性辉长岩;2b—亚碱性辉长岩;TH—拉斑系列;CA—钙碱性系列
Figure 5. TAS (a) and AFM diagrams (b) for the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area
Ir-Irvine boundary, The upper area is alkaline and the lower area is subalkaline; 1-Olivine gabbro; 2a-Basic gabbro; 2b-Subalkaline gabbro; THTholeiite series; CA-Calcium alkaline series
图 7 北阿尔金地区超基性岩铂族元素原始地幔标准化图解
(铂族元素原始地幔丰度数据引自Taylor and Mc Lennan,1985;Barnes and Maier, 1999)
Figure 7. Primitive mantle- normalized PGE diagrams of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun
(abundance of PGE in mantle after Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1985; Barnes and Maier, 1999)
图 8 北阿尔金地区超基性岩TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5
OIT—大洋岛屿拉斑玄武岩;OIA—大洋岛屿碱性玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩
Figure 8. TiO2/10-MnO-P2O5 diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area
OIT—Oceanic island tholeiite basalt; OIA- Oceanic island alkalibasalt; MORB- Mid- oceanic ridge basalt; IAT- Island arc tholeiite basalt; CAB-Calc-alkaline basalt
图 11 北阿尔金地区超基性岩Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir图解(不同源区范围据Barnes et al., 1988)
Figure 11. Ni/Cu-Pd/Ir diagram of the ultrabasic rocks in the North Altun area(outlined areas after Barnes et al., 1988)
表 1 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 1 Major element analytical results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun Area (%)

表 2 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩微量和稀土元素分析结果(10-6)
Table 2 Trace and rare earth elements analytical results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Alun area (10-6)

表 3 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩地球化学特征与各类玄武岩对比
Table 3 Comparison of geochemical characteristics of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun area with various types of basalt

表 4 北阿尔金地区超基性侵入岩铂族元素分析结果(10-9)
Table 4 Platinum group element analysis results of ultrabasic intrusive rocks in the North Altun area (10-9)

表 5 基性-超基性岩含矿性分类
Table 5 Ore-bearing potentiality of the ultrabasic rocks

-
Barnes S J, Boyd R, Korneliussen A, Nilsson L P, Often M, Pedersen R B, Robins B. 1988. The use of mantle normalization and metal ratios in discriminating between the effects of partial melting, crystallization fractionation and sulfide segregation on platinum group elements, gold, nickel and copper: Examples from Norway[C]//Prichard H M, Potts P J, Bowles J F W, Cribb S J(eds.). Geo-platinum 87: London and New York, Elsevier: 113-143.
Barnes S J, Maier W D. 1999. The fractionation of Ni, Cu and the noble metals in silicate and sulfide liquids[C]//Geological Society Canada Mineralogical Society Canada.
Barnes S J, Naldrett A J, Gorton M P. 1985. The origin of the fractionation of platinum-group elements in terrestrial magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 53(3/4):303-323.
Campbell I H, Naldrett A J. 1979. The influence of silicate:Sulfide ratios on the geochemistry of magmatic sulfides[J]. Economic Geology, 74:1503-1506. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247862145_The_influence_of_silicatesulfide_ratios_on_the_geochemistry_of_magmatic_sulfides
Chai Fengmei, Zhang Zhaochong, Dong Lianhui, Zhang Zuoheng, Wu Hua, Li Jun. 2007. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Baishiquan Cu-Ni sulfide-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the Central Tianshan, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10):2366-2378 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200710005
Chen Bailin, Cui Lingling, Bai Yanfei, Wang Shixin, Chen Zhengle, Li Xuezhi, Qi Wanxiu, Liu Rong. 2010. A determining on the displacement of the Altun Tagh sinistral strike-slip fault, NW China:New evidence from the tectonic metallogenetic belt in the eastern part of Altun Tagh Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(11):3387-3396 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201011020.htm
Chen Bailin, Jiang Rongbao, Li Li, Chen Zhengle, Qi Wanxiu, Liu Rong, Cui Lingling, Wang Shixin. 2009. Discovery of iron ore zones in the Kaladawan area within the eastern part of the Altun Mountains and its significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 30(2):143-154 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200902002
Chen Bailin, Meng Lingtong. 2018. Characteristics of folds in the Kaladawan iron orefield, Altun Mountains, Northwestern China and its prospecting implication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 42(1):32-49(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201801003
Chen Bailin, Wang Yong, Chen Zhengle, Li Songbin, Jiang Rongbao, Han Fengbin, Cui Lingling, Li Li, Zhao Shuming, Qi Wanxiu, Yang Yi, Wang Shixin, Zhou Yonggui, Hao Ruixiang. 2015. A study of the structural system of ore-forming and ore-controlling in Kaladawan ore clustering area, Altun Tagh Mountains, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(4):67-77(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201504008
Chen Bailin, Zhao Hengle, Ma Yuzhou, Yang Feng, Wang Shixin, Chen Zhengle, Qi Wanxiu, Liu Rong, Jiang Rongbao, Li Li. 2012. A preliminary discussion on genesis and structural control of Abei silver-lead deposit in eastern Altun Mountains[J]. Mineral Deposits, 31(1):13-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201201002
Chen Xuanhua, Gehrels G E, Wang Xiaofeng, Yang Feng, Chen Zhengle. 2003. Granite from north Altyn Tagh, NW China:U-Pb geochronology and tectonic setting[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 22(4):294-298 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KYDH200304002.htm
Chen Zhengle, Gong Hongliang, Li Li, Wang Xiaofeng, Chen Bailin, Chen Xuanhua. 2006. Cenozoic uplifing and exhumation process of the Altyn Tagh Mountains[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4):91-102 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY200604007.htm
Condie K C. 1997. Plate Tectonic and Crustal Evolution[M]. Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann, 1-288.
Cui Junwen, Tang Zhemin, Deng Jinfu, Yue Yongjun, Meng Lingshun, Yu Qingfan. 1999. Altyn Tagh Faults system[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-249(in Chinese).
Dong Lianhui, Zhu Zhixin, Qu Xun, Wang Kezhuo, Zhao Tongyang. 2010. Spatial distribution, geological features and latest research progress of the main ophiolite zones in Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10):2894-2904 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201010002
Dong Shunli, Li Zhong, Gao Jiam, Zhu Lian. 2013. Progress of studies on early Paleozoic tectonic framework and crystalline rock geochronology in Altun-Qilian-Kunlun orogen[J]. Geological Review, 59(4):731-746 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201304016.htm
Du Yuansheng, Zhu Jie, Han Xin, Gu Songzhu. 2004. From the back-arc basin to foreland basin-Ordovician-Devonian sedimentary basin and tectonic evolution in the North Qilian orogenic belt[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9/10):911-917(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200409013
Ebel D S, Naldrett A J. 1996. Fractional crystallization of sulfide ore liquids at high temperature[J]. Economic Geology, 191:607-637. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/240301483_Fractional_crystallization_of_sulfide_ore_liquids_at_high_temperature
Gao X F, Xiao P X, Guo L, Dong Z C, Xi R G. 2011. Opening of an early Paleozoic limited oceanic basin in the northern Altyn area:Constraints from plagiogranites in the Hongliugou-Lapeiquan ophiolitic mélange[J]. Science China (Earth Science), 54:1871-1879.
Ge Xiaohong, Liu Yongjiang, Ren Shoumai. 2002. Uplift dynamics of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau and Altun fault[J]. Geology in China, 29(4):346-350(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200204002
Godlevski M H. 1982. Formation conditions and evolution of ore-bearing ultrabasic magmas[J]. Geolgical Science and Technology Information, 1(11):62-67(in Chinese).
Guo Shaojie, Zhang Zhicheng, Ren Shoumai. 1998. Formation and evolution of the Xorkol Basin and its relation to the Altun Tagh fault[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 43(18):1981-1984 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800156130
Han Fengbin, Chen Bailin, Cui Lingling, Wang Shixin, Chen Zhengle, Jiang Rongbao, Li Li, Qi Wanxiu. 2012. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Kaladawan area, eastern Altun Mountains, NW China, and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(7):2277-2291 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201207027
Hao Ruixiang, Chen Bailin, Chen Zhengle, Wang Yong, Li Songbin, Han Fengbin, Zhou Yonggui. 2013. Geochemical characteristics of basalts from Kaladawan in East Altun Mountains of Xinjiang and their implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(3):307-317 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201303008
Haughlon D R, Roeder P L, Skinner B J. 1974. Solubility of sulfur in mafic magmas[J]. Economic Geology, 69(4):451-467.
He Jiangtao, Chen Bailin, Wang Yong, Meng Lingtong, Wu Yu, Han Meimei, Wang Bin. 2016. Rock deformation mechanism of Northern Altun margin-Evidence from X-ray fabric analysis[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(1):123-129 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/301557532_Rock_deformation_mechanism_of_northern_Altun_margin-Evidence_from_X-ray_fabric_analysis
Huang Ligong, Zhong Jianhua, Guo Zeqing, Liu Yuntian, Jiang Bo, Guan Quanjun, Liu Zuhan, Zhang Yuezhong, Zhang Yongshu, Li Yong. 2004. Evolution of the Altun orogenic belt in the mesozoic and Cenozoic[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(3):287-294 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200403002
Irvine T N. 1975. Crystallization sequences in the Muskox intrusion and other layered intrusions-Ⅱ. Origin of chromitite layers and similar deposits of other magmatic ores[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimfica Aeta, 39(6/7):991-l008.
Keays. 1995. The role of komatiitic and picritic magmatism and Ssaturation in the formation of ore deposits[J]. Lithos, 34, 1-18. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0024493795900039
Lassiter J, Depaolo D L. 1997. Plume/lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalt: Chemical and isotope constraints[C]//Mahoney J(ed.). Large Igneous Provinces: Continental, oceanic, and planetary flood Volcanism. Geophysical Monography 100, Amercian Geophysical Union, 335-355.
Lesher C M, Campbell I H. 1993. Geochemical and fluid dynamic modeling of compositional variations in Archaean komatiite-hosted nickel sulfide ores in Western Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 88:804-816. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247862936_Geochemical_and_fluid_dynamic_modeling_of_compositional_variations_in_Archean_komatiite-hosted_nickel_sulfide_ores_in_Western_Australia
Li C, Maier W D, de Waal S A. 2001. The role of magma mixing in the genesis of PGE mineralization in the Bushveld Complex:Thermodynamic calculations and new interpretations[J]. Economic Geology, 96:653-662.
Li Haibing, Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Qi Xuexiang, Tapponnier P. 2007. The maximum cumulative strike-slip displacement of the Altyn Tagh fault-900 km?[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(10):1288-1298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Songbin, Chen Bailin, Chen Zhengle, Hao Ruixiang, Zhou Yonggui, Han Fengbin. 2013. Geochemistry and tectonic implications of the Early Paleozoic felsic to intermediate volcanic rocks from Kaladawan area, North Altyn[J]. Geological Review, 59(3):423-436(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201303003
Li Wenyuan, Zhang Zhaowei, Gao Yongbao, Tan Wenjuan, Jiang Hanbin, Guo Zhouping. 2011. Important metallogenic events and tectonic response of Qinling, Qilian and Kunlun orogenic belts[J]. Geology in China, 38(5):1135-1149(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201105002
Li Yuechen, Chen Bailin, Chen Zhengle, Xia Bin. 2007. Sulfur isotope features of Cu-Au polymetallic deposits in the Hongliugou-Lapeiquan area on the Northern Margin of the Altyn Tagh Mountains and their relation to the tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 13(2):131-140 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200702006
Liu Han, Wang Guocan, Cao Shuzhao, Luo Yanjun, Gao Rui, Huang Wenxing. 2012. Discovery of Nanhuaian bimodal volcanics in Northern Altyn Tagh and it's tectonic significance[J]. Earth Science, 37(5):917-928(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201205007.htm
Liu Han, Wang Guocan, Yang Zijiang, Luo Yanjun, Gao Rui, Huang Wenxing. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Qiashikansayi basalt and its constraint on the closure progress of the North Altyn Ocean[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(1):38-54(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201301005
Liu L, Cao Y T, Chen D L, Zhang L C, Yang W Q, Kang L, Liao X Y. 2013. New progresses on the HP-UHP metamorphism in the South Altyn Tagh and the North Qinling[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(22):2113-2123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201322002
Liu Liang, Che Zicheng, Wang Yan, Luo Jinhai, Chen Danling. 1999. The petrological characters and geotectonic setting of high-pressure metamorphic rock belts in Altun Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(1):57-64 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98199901006
Liu Xiaohuang, Deng Jun, Sun Xingli, Liu Jiufen, Sun Bainian, Kang Hongjie. 2010. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of lavas from Shijihe area in western North Qilian Mountains[J]. Earth Science, 35(6):959-968 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201006007
Liu Y J, Neubauer F, Genser J, Ge X H, Takasu A, Yuan S H, Chang L H, Li W M. 2007. Geochronology of the initiation and displacement of the Altyn Strike-Slip Fault, western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(2/3):243-252. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912006000745
Liu Yongjiang, Neubauer F, Ge Xiaohong, Genser J, Yuan Sihua, Li Weimin, Gong Qinglin, Chen Yuanzhong. 2007. Geochronology of the Altun Fault zone and rising of the Altun Mountains[J]. Scientia Geologia Sinica, 42(1):134-146(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200701012
Lu S N, Li H K, Zhang C L, Niu G H. 2008. Geological and geochronological evidence for the Precambrian evolution of the Tarim Craton and surrounding continental fragments[J]. Precambrian Research, 160:94-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=92cbf7cde9189410a5bd41a8161f2517
Lu Songnian, Li Hiaokun, Wang Huichu, Chen Zhihong, Zheng Jiankang, Xiao Zhenqun. 2009. Detrital zircon population of Proterozoic metasedimentary trata in the Qinling-Qilian-Kunlun Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(9):2195-2208(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mao Debao, Zhong Changting, Niu Guanghua, Wang Jie, Wang Kezhuo, Wang Hongjun, Li Zhiming. 2006. Study on metallogenic characteristics and traget areas in the Altyn Tagh metallogenic zone[J]. Northwestern Geology, 39(2):114-127(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200602007
Mao J W, Pirajno F, Zhang Z H, Chai F M, Wu H, Chen S P, Chen L S, Yang J M, Zhang C Q. 2008. A review of the Cu-Ni sulphide deposits in the Chinese Tianshan and Altay orogens (Xinjiang Autonomous Region, NW China):Principal characteristics and ore forming processes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(S2/4):184-203.
Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. 1995. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 120:223-253.
McKenzie D, O'Nions R K. 1991. Partial melt distributions from inversion of Rare Earth Element concentrations[J]. Journal of Petrology, 32(5):1021-1091. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HighWire000001926167
Meng Fancong, Zhang Jianxin, Yu Shengyao, Chen Songyong. 2010. The early paleozoic pillow basalt in Northern Altyn, Western China and it tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(7):981-990(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201007004
Meng Lingtong, Chen Bailin, Luo Dike, Wang Yong, Sun Yue, Wu Yu, Zhang Hao, Wang Tong. 2015. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb geochronology of northern 4337 highland granodiorite in Kaladawan area of Northern Altun Mountains and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 45(6):1-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8751429
Naldrett A J, Hoffman E L, Green A H, Chou C L, Naldrett S R, Alcock R A. 1979. The composition of Ni-sulfide ores, with particular reference to their content of PGE and Au[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 17:403-415. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284100322_The_composition_of_Ni-sulfide_ores_with_particular_reference_to_their_content_of_PGE_and_Au
Naldrett A J. 1999. World-class Cu-Ni-PGE deposits:Key factors in their genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 34:227-240.
Pak Sang Wan, Ma Tuo, Gai Yongsheng, Kang Lei, Wang Chao, Liao Xiaoying, Liu Liang. 2019. Geochronology and Geochemical Characteristics of the Protolith Rock of Younusisayi High Pressure Granitic Gneiss:A Further Study on the Properties of Continental Crust Subduction Plate in South Altyn Tagh[J]. Northwestern Geology, 52(4):76-97(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qi Xuexiang, Wu Cailai, Li Haibin. 2005. SHRIMP U-Pb age of zircons from Kazisayi granite in the northern Alty Tagh mountains and its significations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3):859-866(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503025
Qian Zhuangzhi, Wang Jianzhong, Jiang Changyi, Jiao Jiangang, Yan Haiqing, He Ke, Sun Tao. 2009. Geochemistry characters of platinum-group elements and its significances on the process of mineralization in the Kalatongke Cu-Ni sulfide deposit, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(4):832-844 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200904009
Qin Kezhang, Fang Tonghui, Wang Shulai, Zhu Baoqing, Feng Yimin, Yu Haifeng, Xiu Qunye. 2002. Plate tectonics division, evolution and metallogenic settings in eastern Tianshan Mountains, NW China[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 20(4):302-308(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjdz200204002
Ripley E M. 1981. Sulfur isotopic studies of the Dunka Road Cu-Ni deposit, Duluth Complex, Minnesota[J]. Economic Geology, 76(3):610-620. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247862054_Sulfur_isotopic_studies_of_the_Dunka_Road_Cu-Ni_deposit_Duluth_Complex_Minnesota
Ritts B D, Biffi U. 2000. Magnitude of Post-Middle Jurassic(Bajocian) displacement on the central Altyn Tagh fault system, NorthWest China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112(1):61-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f840e7743f4c9e7095073113e763a5e6
Roex A P L, Dick H J B, Erlank A J, Reid A M, Frey F A, Hart S R. 1983. Geochemistry, mineralogy and petrogenesis of lavas erupted along the southwest Indian Ridge between the Bouvet triple junction and 11 degrees east[J]. Journal of Petrology, 24(3):267-318. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HighWire000001963565
San Jinzhu, Qin Kezhang, Tang Zhongli, Tang Dongmei, Su Benxun, Sun He, Xiao Qinghua, Liu Pingping. 2010. Precise zircon U-Pb age dating of two mafic-ultramafic complexes at Tulargen large Cu-Ni district and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10):3027-3035(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201010014
Seghedi I. Downes H Vaselli O. Szakacs A. Balogh K, Pecskay Z. 2004. Post-collisional Tertiary Quaternary mafic alkalic magmatism in the Carpathian Pannonian region:A review[J]. Tectonophysics, 393:43-62. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195104002525
Song X Y, Li X R. 2009. Geochemistry of the Kalatongke Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit. NW China:Implications for the formation of magmatic sulfide mineralization in a post-collisional environment[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 44(3):303-327.
Song Xieyan, Hu Ruizhong, Chen Liemeng. 2009. Geochemical natures of copper, nickel and PGE and their significance for the study of origin and evolution of mantle-derived magmas and magmatic sulfide deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(4):287-305(in Chinese with English abstract).
Stolz A J, Jochum K P, Hofmann A W. 1996. Fluid-and melt-related enrichment in the subarc mantle:Evidence from Nb/Ta variations in island-arc basats[J]. Geology, 24:587-590.
Sun He, Qin Kezhang, Li Jinxiang, Tang Dongmei, Fan Xin, Xiao Qinghua. 2008. Constraint of mantle partial melting on PGE mineralization of mafic-ultramafic intrusions in Eastern Tianshan:Case study on Tulargen and Xiangshan Cu-Ni deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(5):1079-1086.
Sun He, Qin Kezhang, Li Jinxiang, Xu Xingwang, San Jinzhu, Ding Kuishou, Hui Weidong, Xu Yingxia. 2006. Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of the Tulargen Cu-Ni-Co sulfide deposit, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, and its tectonic setting[J]. Geology in China, 33(3):606-617(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200603018
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1):313-345.
Sun Xiaopan, Yang Chunlei, Qi Yaohui, Gao Yi, Ma Wenping, Li Shulei, Zhang Ke.2018.Geochemistry and Prospecting Potential of Datonggou South Mountain Basic-ultrabasic Rocks in Northwest Qaidam Basin[J].Northwestern Geology, 51(3):53-66(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201803006
Tang D M, Qin K Z, Li C S, Qi L, Su B X, Qu W J. 2011. Zircon dating, Hf-Sr-Nd-Os isotopes and PGE geochemistry of the Tianyu sulfide-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, NW China[J]. Lithos, 126(S1/2):84-98.
Tang D M, Qin K Z, Su B X, Sakyi P A, Mao Y J, Xue S C. 2014. Petrogenesis and mineralization of the Hulu Ni-Cu sulphide deposit in Xinjiang, NW China:constraints from Sr-Nd isotopic and PGE compositions[J]. International Geology Review, 56(6):711-733.
Tang D M, Qin K Z, Sun H, Su B X, Xiao Q H. 2012. The role of crustal contamination in the formation of Ni-Cu sulfide deposits in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang, Northwest China:Evidence from trace element geochemistry, Re-Os, Sr-Nd, zircon Hf-O, and sulfur isotopes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 49(3):145-160.
Tang Zhongli, Li Wenyuan. 1995. Mineralization Model and Geological Correlation of Jinchuan Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposit(PGE)[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-209(in Chinese).
Taylor S R, Mc Lennan S M. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications: 312.
Wang Lishe, Zhang Wei, Duan Xingxing, Long Xiaoping, Ma Zhongping, Song Zhongbao, Sun Jiming. 2015. Isotopic age and genesis of the monzogranitic gneiss at the Huanxingshan in middle Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):119-132(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201501009
Wang Shengwei, Sun Xiaoming, Shi Guiyong, Xiong Dexin, Zhai Wei. 2006. Platinum group Elements(PGE) geochemistry of Baimazhai Ni-Cu sulfide deposit and its constraints on the ore genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9):1474-1486(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200609021
Wu C, Yang J, Robinson P T, Wood J L, Mazdab F K, Gao Y, Wu S, Chen Q. 2009. Geochemistry, age and tectonic significance of granitic rocks in North Altun, Northwest China[J]. Lithos, 113(3/4):423-436.
Wu Cailai, Yang Jingsui, Yao Shangzhi, Zeng Lingsen, Chen Yongsong, Li Haibin, Qi Xuexiang, Wooden J L, Mazdab F K. 2005. Characteristics of the granitoid complex and its zircon SHRIMP dating at the south margin of the Bashikaogong Basin, North Alton, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3):846-858(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Cailai, Yao Shangzhi, Zeng Lingsen, Yang Jingsui, Wooden J L, Chen Yongsong, Mazdab F K. 2007. Zircon SHRIMP dating and the characteristic of the granitic complex in Bashikaogong-Simierbulake area, Northern Altun Tagh[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 37(1):10-26(in Chinese).
Wu Jun, Lan Chaolan, Li Jiliang, Yu Liangjun. 2002. Geochemical evidence of MORB and OIB combination in Hongliugou ophiolite melanges, Altun fault belt[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 21(1):24-30(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200201003
Wu Lei, Gong Qinglin, Qin Suhua. 2013. When did Cenozoic left-slip along the Altyn Tagh Fault initiate? A comprehensive approach[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(8):2837-2850(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Liren. 1963. Metallogenic specialization of basic-ultrabasic rocks in China[J]. Scientia Geologia Sinica, (1):29-41(in Chinese). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292225527_Metallogenetic_specialization_of_basic-ultrabasic_rocks_China
Wu Yu, Chen Zhengle, Chen Bailin, Wang Yong, Meng Lingtong, He Jiangtao, Han Meimei, Wang Bin. 2016. Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the deformed diorite from the North Altyn brittle-ductile shear zone and its constraint on the Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(2):555-570(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201602019
Wu Yu, Chen Zhengle, Chen Bailin, Wang Yong, Meng Lingtong, Sun Yue, He Jiangtao, Wang Bin, Zhang Wengao. 2019. Early Paleozoic tectonic deformation in Qiashenkansayigou area, North Altun, and implication for tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25 (3):301-312(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201903001
Wu Yu. 2016. Compositions, Dtructural Deformation and Geodynamics of the Early Paleozoic Mélange Belt in North Altyn Tagh[D]. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-164(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Yuezhong, Zhao Xiaojian, Qiao Gengbiao, Wang Xing'an, Chen Denghui, Yang Hequn. 2007. Ascription and metallogenic characteristics of Altyn orogenic belt[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(4):689-697(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201704006
Xia Linqin, Xia Zuchun, Xu Xueyi, Li Xiangmin, Ma Zhongping. 2007. The discrimination between continental basalt and island arc basalt based on geochemical method[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 26(1):77-89(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200701011
Xiu Qunye, Yu Haifeng, Liu Yongshun, Lu Songnian, Mao Debao, Li Huimin, Li Quan. 2007. Geology and Zircon U-Pb Age of Pillow Basalt at Qiashikansoy in Northern Altun Tagh, W China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(6):787-794(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200706006
Xu Zhiqin, Yang Jingsui, Zhang Jianxin, Jiang Mei, Li Haibin, Cui Junwen. 1999. A comparison belween the tectonic units on the two sides of the Altun Sinistral Strike-slip fault and the mechanism of lithospheric shearing[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 73(13):193-205(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jingsui, Shi Rendeng, Wu Cailai, Su Dechen, Chen Yongsong, Wang Xibin, Wooden J. 2008. Petrology and SHRIMP age of the Hongliugou ophiolite at Milan, north Altun, at the northern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Acla Petrologica Sinica, 24(7):1567-1584(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200807013
Yang Jingsui, Zhang Jianxin, Meng Fancong, Shi Rendeng, Wu Cailai, Xu Zhiqin, Li Haibin, Chen Yongsong. 2003. Ultrahigh pressure eclogites of the North Qaidam and Altun Mountains, NW China and their protoliths[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3):291-314(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200303026
Yang Wanzhi, Zhou Jun, Zhuang Daoze, Ren Yan. 2013. A Progress of region geochemical exploration of metallogenic belt from West Kunlun to Altun Ranges in Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 46(1):110-118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201301015.htm
Yang Zijiang, Ma Huadong, Wang Zongxiu, Xiao Weifeng. 2012. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of gabbro from the Binggou ophiolite mélange in the Northern Altyn, and geological implication[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(7):2269-2276(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201207026
Yue Y J, Ritts B D, Graham S A. 2001. Initiation and long-term slip history of the Altyn Tagh fault[J]. International Geological Review, 43(12):1087-1093. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/244466727_Initiation_and_Long-Term_Slip_History_of_the_Altyn_Tagh_Fault
Zang Jianyuan, Yang Hongyi, Wan Yusheng, Liu Dunyi, Wen Daren, Lin Zongqi, Dong Guoàn. 2006. Neoproterozoic(~775Ma) magmatism found in metamorphic complex:Evidence from SHRIMP zircon dating, North Qilian Mountains[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(5):575-581(in Chinese).
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Mattinson C G, Xu Z Q, Meng F C, Shi R D. 2005. Two contrasting eclogite cooling histories, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China:Petrological and isotopic constraints[J]. Lithos, 84(1/2):51-76. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493705000423
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Meng F C, Wan Y, Li H, Wu C. 2006. U-Pb isotopic studies of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam Mountains, western China:New evidence for an early Paleozoic HP-UHP metamorphic belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(s2-3):143-150.
Zhang Jianxin, Meng Fancong, Yu Shengyao, Chen Wen, Chen Yongsong. 2007.39Ar-40Ar geochronology of high-pressure/low-temperature blueschist and eclogite in the North Altyn Tagh and their tectonic implications[J]. Geology in China, 34(4):558-564(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200704002
Zhang Jianxin, Yu Shengyao, Li Yunshuai, Yu Xingxing, Lin Yihui, Mao Xiaohong. 2015. Subduction, accretion and closure of Proto-Tethyan Ocean:Early Paleozoic accretion/collision orogeny in the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam orogenic system[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(12):3531-3554(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201512003.htm
Zhang Qi, Qian Qing, Wang Yan. 1999. Geochemical study on igneous rocks of orogenic belts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(3):113-120(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY199903015.htm
Zhang Zhanwu, Huang Gang, Li Huimin, Zhang Wenfeng. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of gabbro and diorite from Qilesayi pluton in Lapeiquan area of northern Altun Mountains and their tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(1):13-27(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201201002
Zhang Zhaochong, Wang Fusheng. 2003. A method for identifying primary magma examples from picrite and alkali basalts[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 33(2):130-134(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200302003
Zhang Zhicheng, Guo Zhaojie, Song Biao. 2009. SHRIMP zircon dating of gabbro from the ophiolite mélange in the northern Altyn Tagh and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(3):568-576(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200903010.htm
Zhu Wenbin, Ge Rongfeng, Wu Hailin. 2018. Paleoproterozoic ca. 2.0Ga magmatic-metamorphic event in the northern Altyn Tagh area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(4):1175-1190(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201804017
柴凤梅, 张招崇, 董连慧, 张作衡, 吴华, 李军. 2007.新疆中天山白石泉含铜镍矿镁铁-超镁铁岩体地球化学特征与岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 23(10):2366-2378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200710005 陈柏林, 崔玲玲, 白彦飞, 王世新, 陈正乐, 李学智, 祁万修, 刘荣. 2010.阿尔金断裂走滑位移的确定——来自阿尔金山东段构造成矿带的新证据[J].岩石学报, 26(4):3387-3396. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201011019 陈柏林, 蒋荣宝, 李丽, 陈正乐, 祁万修, 刘荣, 崔玲玲, 王世新. 2009.阿尔金山东段喀腊大湾地区铁矿带的发现及其意义[J].地球学报, 30(2):143-154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200902002 陈柏林, 孟令通. 2018.阿尔金喀腊大湾铁矿田褶皱构造特征及找矿意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 42(1):32-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201801003 陈柏林, 王永, 陈正乐, 李松彬, 蒋荣宝, 韩凤彬, 崔玲玲, 李丽, 赵树铭, 祁万修, 杨屹, 王世新, 周永贵, 郝瑞祥. 2015.阿尔金山喀腊大湾地区控矿构造系统研究[J].地学前缘, 22(4):67-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201504008 陈柏林, 赵恒乐, 马玉周, 杨风, 王世新, 陈正乐, 祁万修, 刘荣, 蒋荣宝, 李丽. 2012.阿尔金山阿北银铅矿控矿构造特征与矿床成因初探[J].矿床地质, 31(1):13-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201201002 陈宣华, Gehrels G E, 王小凤, 杨风, 陈正乐. 2003.阿尔金山北缘花岗岩的形成时代及其构造环境探讨[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 22(4):294-298. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200304002 陈正乐, 宫红良, 李丽, 王小凤, 陈柏林, 陈宣华. 2006.阿尔金山脉新生代隆升-剥露过程[J].地学前缘, 13(4):91-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200604008 崔军文, 唐哲民, 邓晋福, 岳永君, 孟令顺, 余钦范. 1999.阿尔金断裂系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-249. 董连慧, 朱志新, 屈迅, 王克卓, 赵同阳. 2010.新疆蛇绿岩带的分布、特征及研究新进展[J].岩石学报, 26(10):2894-2904. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201010002 董顺利, 李忠, 高剑, 朱炼. 2013.阿尔金-祁连-昆仑造山带早古生代构造格架及结晶岩年代学研究进展[J].地质论评, 59(4):731-746. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HYC201405070000001439 杜远生, 朱杰, 韩欣, 顾松竹. 2004.从弧后盆地到前陆盆地-北祁连造山带奥陶纪-泥盆纪的沉积盆地与构造演化[J].地质通报, 23(9/10):911-917. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200409013 戈德列夫斯基 M H. 1982.含矿超基性岩浆的形成条件及演化[J].地质科技情报, 1(11):62-67. 葛肖虹, 刘永江, 任收麦. 2002.青藏高原隆升动力学与阿尔金断裂[J].中国地质, 29(4):346-350. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020402&flag=1 郭召杰, 张志诚, 王建军. 1998.阿尔金北缘蛇绿岩的Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其大地构造意义[J].科学通报, 43(18):1981-1984. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb199818018 韩风彬, 陈柏林, 崔玲玲, 王世新, 陈正乐, 蒋荣宝, 李丽, 祁万修. 2012.阿尔金山喀腊大湾地区中酸性侵入岩SHRIMP年龄及其意义[J].岩石学报, 28(7):2271-2281. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201207027 郝瑞祥, 陈柏林, 陈正乐, 王永, 李松彬, 韩凤彬, 周永贵. 2013.新疆阿尔金喀腊大湾地区玄武岩的地球化学特征及地质意义[J].地球学报, 34(3):307-317. 何江涛, 陈柏林, 王永, 孟令通, 吴玉, 韩梅梅, 王斌. 2016.阿尔金北缘岩石变形机制——来自X光组构分析的证据[J].地质通报, 35(1):123-129. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201601011 黄立功, 钟建华, 郭泽清, 刘云田, 江波, 管全俊, 柳祖汉, 张跃中, 张永庶, 李勇. 2004.阿尔金造山带中、新生代的演化[J].地球学报, 25(3):287-294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200403002 李海兵, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 戚学祥, Tapponnier P. 2007.阿尔金断裂带最大累积走滑位移量-900km?[J].地质通报, 26(10):1288-1298. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD200710009.htm 李松彬, 陈柏林, 陈正乐, 郝瑞祥, 周永贵, 韩凤彬. 2013.阿尔金北缘喀腊大湾地区早古生代中酸性火山熔岩岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境[J].地质论评, 59(3):423-436. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201303003 李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 谭文娟, 姜寒冰, 郭周平. 2011.秦祁昆造山带重要成矿事件与构造响应[J].中国地质, 38(5):1135-1149. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110502&flag=1 李月臣, 陈柏林, 陈正乐, 夏斌. 2007.阿尔金北缘红柳沟-拉配泉一带铜金矿床硫同位素特征及其意义[J].地质力学学报, 13(2):131-140. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200702006 刘函, 王国灿, 曹树钊, 罗彦军, 高睿, 黄文星. 2012.北阿尔金南华纪双峰式火山岩的发现及构造意义[J].地球科学, 37(5):917-928. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201205005 刘函, 王国灿, 杨子江, 罗彦军, 高睿, 黄文星. 2013.恰什坎萨伊沟玄武岩年代学、地球化学特征及其对北阿尔金洋盆闭合过程的制约[J].地质学报, 87(1):38-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201301005 刘良, 车自成, 王焰, 罗金海, 陈丹玲. 1999.阿尔金高压变质岩带的特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 15(1):57-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98199901006 刘晓煌, 邓军, 孙兴丽, 刘玖芬, 孙柏年, 康洪杰. 2010.北祁连西段石鸡河地区火山岩地球化学特征及其动力学意义[J].地球科学, 35(6):959-968. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201006007 刘永江, Neubauer F, 葛肖虹, Genser J, 袁四化, 李伟民, 巩庆林, 陈元忠. 2007.阿尔金断裂带年代学和阿尔金山隆升[J].地质科学, 42(1):134-146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200701012 陆松年, 李怀坤, 王惠初, 陈志宏, 郑健康, 相振群. 2009.秦-祁-昆造山带元古宙副变质岩层碎屑锆石年龄谱研究[J].岩石学报, 25(9):2195-2208. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200909013 毛德宝, 钟长汀, 牛广华, 王杰, 王克卓, 王宏君, 李智明. 2006.阿尔金成矿带成矿规律与找矿预测[J].西北地质, 39(2):114-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200602007 孟繁聪, 张建新, 于胜尧, 陈松永. 2010.北阿尔金红柳泉早古生代枕状玄武岩及其大地构造意义[J].地质学报, 84(7):981-990. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201007004 孟令通, 陈柏林, 罗迪柯, 王永, 孙岳, 吴玉, 张昊, 王铜. 2015.北阿尔金喀腊大湾地区4337高地北花岗闪长岩SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45(6):1757-1771. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=67676890504849534854484954 Pak Sang Wan, 马拓, 盖永升, 康磊, 王超, 廖小莹, 刘良. 2019.南阿尔金尤努斯萨依高压花岗质片麻岩原岩的形成时代与地球化学特征:对南阿尔金陆壳深俯冲板片属性的进一步限定[J].西北地质, 52(4):76-97. 戚学祥, 吴才来, 李海兵. 2005.北阿尔金喀孜萨依花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 21(3):859-866. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503025 钱壮志, 王建中, 姜常义, 焦建刚, 闫海卿, 何克, 孙涛. 2009.喀拉通克铜镍矿床铂族元素地球化学特征及其成矿作用意义[J].岩石学报, 25(4):832-844. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200904009 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 朱宝清, 冯益民, 于海峰, 修群业. 2002.东天山板块构造分区、演化与成矿地质背景研究[J].新疆地质, 20(4):302-308. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjdz200204002 三金柱, 秦克章, 汤中立, 唐冬梅, 苏本勋, 孙赫, 肖庆华, 刘平平. 2010.东天山图拉尔根大型铜镍矿区两个镁铁-超镁铁岩体的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 26(10):3027-3035. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201010014 宋谢炎, 胡瑞忠, 陈列锰, . 2009.铜、镍、铂族元素地球化学性质及其在幔源岩浆起源、演化和岩浆硫化物矿床研究中的意义[J].地学前缘, 16(4):287-305. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY200904033.htm 孙赫, 秦克章, 李金祥, 徐兴旺, 三金柱, 丁奎首, 惠卫东, 许英霞. 2006.东天山图拉尔根铜镍钴硫化物矿床岩相、岩石地球化学特征及其形成的构造背景[J].中国地质, 33(3):606-617. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060318&flag=1 孙赫, 秦克章, 李金样, 唐冬梅, 范新, 肖庆华. 2008.地幔部分熔融程度对东天山镁铁质-超镁铁质岩铂族元素矿化的约束:以图拉尔根和香山铜镍矿为例[J].岩石学报, 24(5):1079-1086. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200805015.htm 孙小攀, 杨春雷, 齐耀辉, 高毅, 马文平, 李树雷, 张轲.2018.柴达木西北缘大通沟南山基性-超基性岩地球化学特征及找矿前景分析[J].西北地质, 51(3):53-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201803006 汤中立, 李文渊. 1995.金川铜镍硫化物(含铂)矿床成矿模式及地质对比[M].北京:地质出版社, 1-209. 王立社, 张巍, 段星星, 龙晓平, 马中平, 宋忠宝, 孙吉明. 2015.阿尔金环形山花岗片麻岩同位素年龄及成因研究[J].岩石学报, 31(1):119-132. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201501009 王生伟, 孙晓明, 石贵勇, 熊德信, 翟伟. 2006.云南白马寨铜镍硫化物矿床铂族元素地球化学及其对矿床成因的制约[J].地质学报, 80(9):1474-1486. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200609021 吴才来, 杨经绥, 姚尚志, 曾令森, 陈永松, 李海兵, 戚学祥, Wooden J L, Mazdab F K. 2005.北阿尔金巴什考供盆地南缘花岗杂岩特征及锆石SHRIMP定年[J].岩石学报, 21(3):846-858. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503024 吴才来, 姚尚志, 曾令森, 杨经绥, Wooden J L, 陈永松, Mazdab F K. 2007.北阿尔金巴什考供-斯米尔布拉克花岗杂岩特征及锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J].中国科学(D辑), 37(1):10-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200701002 吴峻, 兰朝利, 李继亮, 俞良军. 2002.阿尔金红柳沟蛇绿混杂岩中MORB与OIB组合的地球化学证据[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 21(1):24-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200201003 吴磊, 巩庆霖, 覃素华. 2013.阿尔金断裂新生代大规模走滑起始时间的厘定[J].岩石学报, 29(8):2837-2850. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201308019 吴利仁. 1963.论中国基性岩、超基性岩的成矿专属性[J].地质科学, (1):29-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX196301003.htm 吴玉, 陈正乐, 陈柏林, 王永, 孟令通, 何江涛, 韩梅梅, 王斌. 2016.阿尔金北缘脆-韧性剪切带内变形闪长岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其对北阿尔金早古生代构造演化的指示[J].岩石学报, 32(2):555-570. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201602019 吴玉, 陈正乐, 陈柏林, 王永, 孟令通, 孙岳, 何江涛, 王斌, 张文高. 2019.北阿尔金恰什坎萨依沟地区早古生代构造变形特征及构造演化启示[J].地质力学学报, 25(3):301-312. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201903001 吴玉. 2016.北阿尔金早古生代混杂带的组成、构造变形特征与演化[D].中国地质科学院, 1-164. 伍跃中, 赵晓健, 乔耿彪, 王兴安, 陈登辉, 杨合群. 2007.阿尔金成矿带的归属及成矿特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 41(4):689-697. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201704006 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 李向民, 马中平. 2007.利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 26(1):77-89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200701011 修群业, 于海峰, 刘永顺, 陆松年, 毛德宝, 李惠民, 李铨. 2007.阿尔金北缘枕状玄武岩的地质特征及其锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质学报, 81(6):787-794. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200706006 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 姜枚, 李海兵, 崔军文. 1999.阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J].地质学报, 73(13):193-205. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900084695 杨经绥, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 苏德辰, 陈永松, 王希斌, Wooden J L. 2008.北阿尔金地区米兰红柳沟蛇绿岩的岩石学特征和SHRIMP定年[J].岩石学报, 24(7):1567-1584. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200807013 杨经绥, 张建新, 孟繁聪, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 许志琴, 李海兵, 陈松永. 2003.中国西部柴北缘-阿尔金的超高压变质榴辉岩及其原岩性质探讨[J].地学前缘, 10(3):291-314. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200303026 杨万志, 周军, 庄道泽, 任燕. 2013.新疆西昆仑-阿尔金成矿带区域地球化学勘查进展[J].西北地质, 46(1):110-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201301011 杨子江, 马华东, 王宗秀, 肖伟峰. 2012.阿尔金山北缘冰沟蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 28(7):2269-2276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201207027.htm 曾建元, 杨宏仪, 万渝生, 刘敦一, 温大任, 林宗祺, 董国安. 2006.北祁连山变质杂岩中新元古代(~775Ma)岩浆活动纪录的发现:来自SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年的证据[J].科学通报, 51(5):575-581. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB200605011.htm 张建新, 孟繁聪, 于胜尧, 陈文, 陈永松. 2007.北阿尔金HP/LT蓝片岩和榴辉岩的Ar-Ar年代学及其区域构造意[J].中国地质, 34(4):558-564. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070402&flag=1 张建新, 于胜尧, 李云帅, 喻星星, 林宜慧, 毛小红. 2015.原特提斯洋的俯冲、增生及闭合:阿尔金-祁连-柴北缘造山系早古生代增生/碰撞造山作用[J].岩石学报, 31(12):3531-3554. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201512003.htm 张旗, 钱青, 王焰. 1999.造山带火成岩地球化学研究[J].地学前缘, 6(3):113-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy199903011 张占武, 黄岗, 李怀敏, 张文峰. 2012.北阿尔金拉配泉地区齐勒萨依岩体的年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 31(1):13-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201201002 张招崇, 王福生. 2003.一种判别原始岩浆的方法——以苦橄岩和碱性玄武岩为例[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 33(2):130-134. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200302003 张志诚, 郭召杰, 宋彪. 2009.阿尔金山北缘蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 25(3):568-676. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200903010.htm 朱文斌, 葛荣峰, 吴海林. 2017.北阿尔金地区古元古代ca. 2.0 Ga岩浆-变质事件[J].岩石学报, 34(4):1175-1190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201804017 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 王成,杨子江,马华东,娜迪艳·克力木江,吕宁,张雅芳. 阿尔金山冰沟一带花岗岩地球化学特征及对大地构造的演化启示. 新疆地质. 2024(01): 41-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王宗斌,陈建中,杨文臣,任伟. 阿尔金北缘塔东南坳陷一带深部卤水钾盐矿地质特征与成矿规律浅析. 新疆地质. 2024(02): 219-223 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈柏林,李松彬,王永,陈正乐,周永贵,郝瑞祥,刘牧. 阿尔金山喀腊大湾地区堆晶辉长岩地球化学、年代学:洋壳演化证据. 中国地质. 2023(05): 1557-1572 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 董洪凯,薛鹏远,刘广,刘思林,于龙. 内蒙古北山地区芨芨台子-小黄山蛇绿岩构造属性及与成矿关系:来自阿民乌素地幔橄榄岩印证. 地质与勘探. 2022(04): 767-777 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高栋,吴才来,郜源红,吴迪,郑坤,徐楠,陈红杰. 南阿尔金玉苏普阿勒克塔格花岗岩体成因及其对区域早古生代构造演化的启示. 中国地质. 2022(05): 1636-1655 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 冯怀伟,许淑梅,崔红庄,侯旭波,王金铎. 甘肃敦煌盆地侏罗纪原型盆地性质与沉积环境演化. 地质论评. 2021(03): 640-654 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 代堰锫,李同柱,张惠华. 扬子陆块西缘江浪穹窿超基性岩的成因:锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素. 沉积与特提斯地质. 2021(04): 573-584 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: