2. 西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710069;
3. 中国石油长庆油田分公司陇东页岩油开发项目部,甘肃 庆阳 745000;
4. 延长油田股份有限公司靖边采油厂,陕西 榆林 719000
2. State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, Xi 'an 710069, Shaanxi, China;
3. Longdong Shale Oil Development Project Department, Petrochina Changqing Oilfield Company, Qingyang 745000, Gansu, China;
4. Jingbian Oil Production Plant, Yanchang Oilfield Company, Yulin 719000, Shaanxi, China
[Objective] The oil and gas resources of Yan'an Formation in Wuqi area of Ordos Basin are widely distributed and have great exploration potential. The systematic study on the accumulation time and stages of Yan10 reservoir of Yan 'an Formation in Wuqi area is beneficial to the fine oil and gas exploration and development process, and provides a basis for understanding and perfecting the nature of Jurassic hydrocarbon accumulation in the whole basin. [Methods] In this paper, the characteristics of reservoir fluid inclusions in the study area were analyzed by means of microscopic observation and indirect projection dating of fluid inclusions homogenization temperature and burial history, so as to further determine the hydrocarbon accumulation period. [Results] The early and late inclusions exist in Yan10 reservoir of Jurassic Yan 'an Formation in Wuqi area of Yishan slope, Ordos Basin. The early fluid inclusions are mainly distributed in dissolution cracks and quartz secondary enlarging edges on the surface of quartz grains; The late fluid inclusions are mainly distributed in the fractures and the surface of quartz particles, while they are distributed sporadically in the late siliceous cements and calcite cements. The peak homogenization temperature of early inclusions is 80-90℃. The peak of homogenization temperature of late inclusions is 100-110℃, and the homogenization temperature of the two phases is continuously distributed. [Conclusions] There are two consecutive hydrocarbon charging periods in Yan10 reservoir of Yan 'an Formation in Wuqi area of Yishan slope, Ordos Basin: the first oil and gas charging period corresponds to 112-106 Ma. The corresponding time of the second oil and gas charging is about 102-97 Ma. Two oil and gas charging shows that the oil and gas accumulation period in the study area is 112-97 Ma ago, which is the end of the Early Cretaceous.
流体包裹体是流体在矿物形成过程中,被矿物圈闭而保存于晶格缺陷或穴窝中,没有内外物质的交换,介质的原始物理属性不发生变化,这种独立的封闭体系就是流体包裹体(吕晓兰,2019)。因而地质学者将其逐步应用于石油勘探和油气成藏期次的研究,成为油气勘探中重要的一环,对解决理论和实际问题具有重要现实意义(庞雄奇,2010;周小栋等,2013;赵玉涛等,2017;辛存林等,2019)。
研究区处于伊陕斜坡的中西部,鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系延安组在油气勘探的众多层系中占有重要地位,具有分布广,埋藏浅,油藏多的特点。截至2017年7月底,研究区探明含油面积60 km2,探明地质储量1792×104 t,动用含油面积48.78 km2,动用地质储量1457.55×104 t,勘探潜力巨大。前人对鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区油气成藏特征、油气运移及沉积微相进行了较深的研究,但针对鄂尔多斯盆地中部的延10油层组的成藏时间、成藏期次缺少明确的研究,不利于研究区的油气精细勘探开发进程。油气成藏期次分析成为油气勘探中的一个重点关注问题,对油气成藏期次的准确分析不仅有助于研究油气藏的形成与分布规律,而且对勘探目标的选取和对油气储层开展系统的分期配套研究有重要价值(赵靖舟,2002;张君峰等,2018;薛楠等,2020)。对简单发育的盆地而言,油气藏的形成过程简单,成藏期次容易确定,对于构造复杂、沉积时期长的含油气盆地,具有多期成藏的特点,因此对成藏期次的确定至关重要(Schubert et al., 2007;Fu et al., 2020;薛楠等,2020;陈睿倩等,2022)。因此,笔者选取鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区延安组延10油层四口井中的砂岩储层共5块流体包裹体样品,进行了流体包裹体的类型、形态、大小、荧光观察及均一温度、盐度、密度测试,对研究区侏罗系延安组延10油层组油气成藏期次进行深入研究,以期为认识和完善全盆地侏罗系油气成藏规律提供依据。
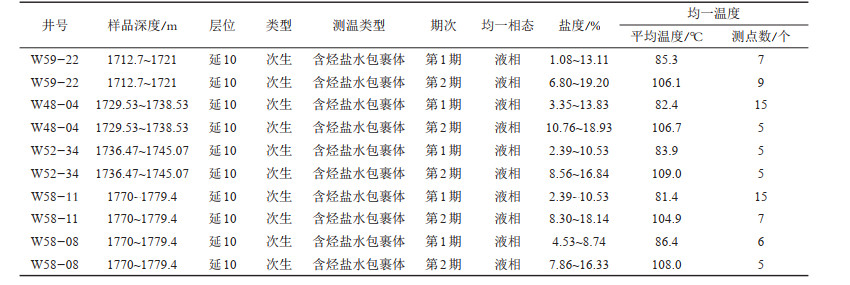
2 地质概况鄂尔多斯盆地属于中国大型沉积盆地,地处华北地台的西部,是大型陆内克拉通盆地。依据地处的构造格局,将鄂尔多斯盆地划分为伊陕斜坡带等6个一级构造单元(杨智等,2017)。研究发现鄂尔多斯盆地内部地区构造发育简单,地层平缓,很少见到发育大幅度的背斜构造,周缘地区断裂较为发育,不发育二级构造带(王平,1997)。
吴起地区总面积约7650 km2,地理范围为北起巴老毫德,南抵王洼子,西至靖边—吴起,东到马路海子,东西宽约85 km,南北长约90 km(刘犟,2012),是盆地重要的产油气区,先后发现一系列油气田。研究区处于鄂尔多斯盆地中部,位于伊陕斜坡吴起县西北部,王洼子地区沿河以西(图 1),侏罗系延安组在该研究区发育较好。
|
图 1 研究区构造位置(a)及延安组地层柱状图(b) Fig. 1 Tectonic location (a) and stratigraphic histogram (b) of Yan 'an Formation in the study area |
沉积物沉积、成岩演化过程中形成的矿物、石英次生加大边、碎屑矿物裂隙及穴窝等,由于各种因素的影响,捕获沉积、成岩环境中的介质流体形成各种包裹体,这些储层成岩矿物之间的相互包裹及先后穿插关系和油气包裹体形态、分布、均一温度和荧光特征等均记载了地质演化的历程信息(陶士振,2006;陈刚等,2013;昌婷等,2019;Song et al., 2019;邵晓州等,2020;吴小力等,2022)。本次研究选取研究区4口井的12个岩心样品进行实验,样品为来自侏罗系延安组延10油层组的砂岩(表 1,图 2),取样深度大致为1712.7~1779.4 m。
|
|
表 1 流体包裹体来源 Table 1 Sources of fluid inclusions |

|
图 2 研究区延10储层砂岩样品图 a—W59井灰色油迹细砂岩;b—W58井深灰色油迹细砂岩;c—W48井灰色细砂岩;d—W58井灰白色细砂岩;e—W48井灰色油迹细砂岩;f—W52井灰色细砂岩 Fig. 2 Sandstone sample map of Yan10 reservoir in the study area a-Well W59 grey oil-stained fine sandstone; b-Well W58 dark grey oil-stained fine sandstone; c-Well W48 grey fine sandstone; d-Well W58 grey fine sandstone; e-Well W48 grey oil trace fine sandstone; f-Well W52 grey fine sandstone |
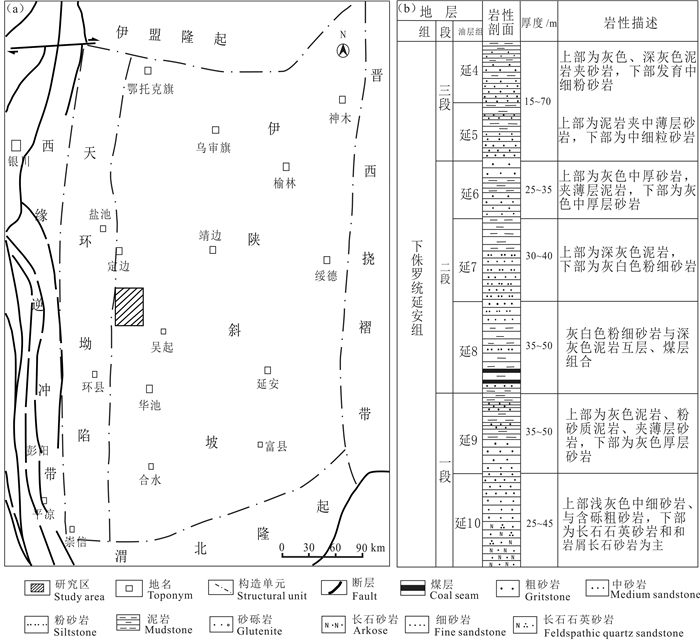
首先将砂岩样品挑样并制作成包裹体薄片,在显微镜下对薄片进行成岩作用分析,接着对薄片进行镜下包裹体识别,确定不同时期油气包裹体大小、形态、荧光特征等,再利用测温仪器进行均一温度实验,记录均一温度和冰点温度,计算出包裹体盐度和密度,最后根据伊陕斜坡吴起地区沉积埋藏史与古地温场演化史图,确定油气成藏期次。包裹体均一温度在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室流体包裹体实验室完成,测试仪器为英国Linkam科学仪器公司生产的THMS600型冷热台进行测试,测定误差为±0.1 ℃,在室温为20 ℃、湿度为30%的条件下进行测温实验。根据薄片观察和统计,研究区延安组延10储层岩性以浅灰、灰色长石石英砂岩和长石砂岩为主(图 3),颗粒以细粒为主,主要粒径为0.06~0.26 mm。延10储层分选性好为主,磨圆度以次棱角状为主,次圆状次之,孔隙式胶结。延10砂岩中石英平均含量49.9%,长石平均含量为29.2%,岩屑平均含量为8%,黑云母平均含量为7%。
|
图 3 伊陕斜坡吴起地区延10砂岩分类三角图(底图据任大忠等,2016) Fig. 3 Triangulation of sandstone classification of Yan10 in Wuqi area of Yishan Slope (base picture after Ren Dazhong et al., 2016) |
伊陕斜坡吴起地区侏罗系延安组延10油层组经历了多期成岩作用,根据镜下对包裹体薄片观察,碎屑颗粒之间紧密接触、定向排列,压实作用较强烈,除此之外还能观察到石英压溶现象和颗粒之间的凹凸接触(图 4a)。硅质胶结在本区普遍发育,易观察到石英次生加大现象(图 4b、c),石英碎屑颗粒通常被等厚环状的石英次生加大边包裹,大多数呈连续状生长。还可以观察到生长于粒间或溶蚀孔内的自生石英,沿孔壁生长形成细小的自形微晶。

|
图 4 伊陕斜坡吴起地区延10储层流体包裹体形态与分布特征 a—石英颗粒紧密排列,碎屑物质充填石英颗粒间隙,W48井,1729.53~1738.53m,单偏光;b—石英颗粒次生加大边中见气液包体,W52井,1736.47~1745.07 m,单偏光;c—与b同视域石英颗粒次生加大边中见发黄绿色荧光气液两相油包裹体,紫外光激发;d—早期裂隙充填的串珠状有机包裹体,W59井,1712.7~1721 m,单偏光;e—切穿石英颗粒表气液两相包裹体,W48井,1729.53~1738.53 m,单偏光;f—分布在长石解理缝中的油气包裹体,W59井,1712.7~1721 m,单偏光;g—石英粒表气液两相烃类包裹体,W52井,1736.47~1745.07 m,单偏光;h—石英早期裂隙中的气液两箱包体,W58井,1770~1779.4 m,单偏光;i—晚期方解石胶结物内零星分布浅褐色油包裹体,W52井,1736.47~1745.07 m,单偏光;j—与i同视域紫外光激发下晚期方解石胶结物内零星分布浅褐色油包裹体发黄绿色荧光;k—石英表面溶蚀孔中的气液二相包体,W58井,1770~1779.4 m,单偏光;l—盐水包裹体,W48井,1729.53~1738.53 m,单偏光 Fig. 4 Fluid inclusion morphology and distribution characteristics of Yan10 reservoir in Wuqi area of Yishan slope a-Quartz grains are closely arranged and quartz grains are filled by clastic materials. Well W48, 1729.53-1738.53 m, single polarized light; b-Gas-liquid inclusions found in the secondary enlarging edge of quartz particles, Well W52, 1736.47-1745.07 m, single polarized light; c-Yellow-green fluorescent gas-liquid two-phase oil inclusions were found in the secondary enlarging edge of quartz particles in the same view field as b, which was excited by UV light; d-Beaded organic inclusions from early fracture filling, well W59, 1712.7-1721 m, single polarized; e-Cut through quartz grain surface gas-liquid two-phase inclusion, Well W48, 1729.53-1738.53 m, single polarized light; f-Hydrocarbon inclusions distributed in feldspar cleavage fractures, Well W59, 1712.7-1721 m, single polarized light; g-Quartz grain surface gas-liquid two-phase hydrocarbon inclusions, Well W52, 1736.47-1745.07 m, single polarized light; h-Gas-liquid inclusions in early quartz fractures, Well W58, 1770-1779.4 m, single polarized light; i-Sporadic distribution of light brown oil inclusions in late calcite cements, Well W52, 1736.47-1745.07 m, single polarized light; j-Light brown oil inclusions with yellowish-green fluorescence were scattered in late calcite cement under UV excitation in the same field of view as i; k-Gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in dissolution pores on quartz surface, Well W58, 1770-1779.4 m, single polarization; l-Saline inclusion, Well W48, 1729.53-1738.53 m, single polarized |
依据油气包裹体分布、形态、物理相态、颜色及成岩作用分析,可以将鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区侏罗系延安组延10油层组成岩序列概括为:压实作用→石英、长石次生加大→伊利石、高岭石沉淀→长石、岩屑溶蚀→高岭石胶结、自形石英微晶→铁方解石、铁白云石胶结(叶博等,2018;邵晓州等,2020)。
4.2 流体包裹体特征 4.2.1 包裹体类型通过对延安组成岩作用序列分析及薄片镜下观察,识别出伊陕斜坡吴起地区延安组延10油层存有早、晚两期流体包裹体,说明研究区发生过两次油气运移和成藏事件。
早期包裹体形成时间较早,单偏光下颜色为褐色,在荧光下的特征为淡黄色荧光(图 4c),这类包裹体主要分布在石英颗粒表面的溶蚀裂缝中(唐建云等,2019)(图 4d、h)和石英次生加大边(图 4b)。其物理相态主要有气态烃+液态烃+少量盐水、气态烃+液态烃和纯液态烃3种(刘犟,2012;时保宏等,2012;赵彦德等,2016;Jiang et al., 2021)。气态烃和液态烃占比较大,颜色主要为黑褐色;气态烃处于包裹体中部,颜色为灰色;液态烃为黄褐色;盐水无色透明,分布在包裹体边缘。早期包裹体形态大多数为椭圆形和不规则形,形状小且密集,呈串珠状形态分布在早期裂缝中(图 4d),是流体通过早期裂缝被圈闭形成的(赵彦德等,2016;邵晓州等,2020;沈健,2020)。
晚期流体包裹体主要形成于晚期构造活动,常见于晚成岩阶段的晚期裂隙,通过镜下观察,在晚期硅质胶结物和晚期方解石胶结物中零星分布(图 4i、j),单偏光下为浅褐色,紫外光下的荧光特征为黄绿色荧光(赵彦德等,2016;刘润川等,2019)。这类包裹体主要分布在切穿石英颗粒裂缝和石英颗粒表面,包裹体较大,以气态烃和气液两相烃为主,形态不一,以椭圆或不规则状为主(张亚超等,2020)(图 4e、g)。通过荧光观察延10油层组流体包裹体荧光颜色较浅,说明包裹体中含有的烃类较少,油气发生了二次运移,这是晚期构造抬升导致的结果,所以其荧光颜色比较浅。
4.2.2 均一温度、盐度、密度特征流体包裹体均一温度是室温下呈两相或多相的包裹体,通过人工加热,使其变成均匀单一相流体时的瞬时温度,一般选取与烃类伴生的同期盐水包裹体进行均一温度测定,大致可代表储层中烃类包裹体的形成温度(陈刚等, 2012, 2013;罗枭等,2015;李伟等,2020)。
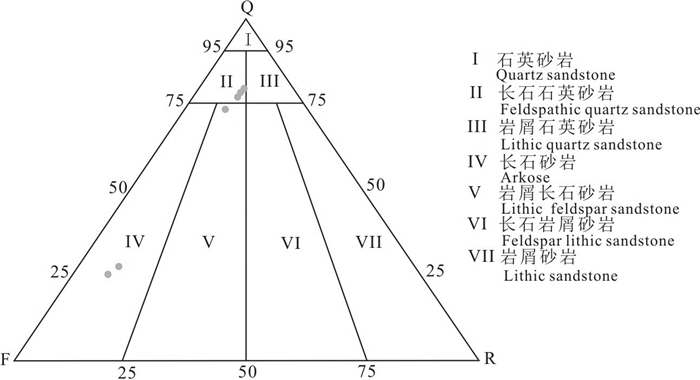
对鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区5块样品79个测点进行了流体包裹体测温研究,包裹体主要分布于石英微裂隙、次生加大边及方解石胶结物中,具体测试数据如表 2所示。分别统计与不同期次油气包裹体相伴生的盐水包裹体及含烃盐水包裹体的均一温度数据(Goldstein,2001),制作成直方图。包裹体均一温度结果(图 5)表明,研究区砂岩样品包裹体均一温度从66.4~129.5℃连续分布,说明研究区油气成藏是一个连续的过程。并在80~90℃和100~110℃两个区间内出现峰值,说明研究区延10储层主要有两期烃类充注,并且是一个由强到弱,再由弱到强的充注过程。
|
|
表 2 研究区延10储层包裹体均一温度与盐度测试统计 Table 2 Test statistics of homogenization temperature and salinity of reservoir inclusion in Yan10 in the study area |
|
图 5 伊陕斜坡吴起地区延安组储层包裹体均一温度分布 Fig. 5 Homogenization temperature distribution of reservoir inclusions in Yan 'an Formation in Wuqi area of Yishan oblique slope |
流体包裹体盐度是反映介质流体物理属性的一个参数,可以指示油气成藏流体的物理化学性质和流体来源,能够近似代表矿物孔隙中溶液的盐度(田亚铭等,2011;卢焕章,2014;罗春艳等,2014;Jiang et al., 2021;郭飞飞,2022)。盐度的大小是通过测得的流体包裹体的冰点温度进一步计算得出的,一般选取镜下清晰,形态好,稳定跳动的两相盐水包裹体进行冰点温度测试,测量精度为0.1℃。通过实验得到研究区包裹体的冰点温度主要分布在-7.2~-1.8℃和-8.7~-4.1℃两个温度范围内。
本文所采用Hall et al.(1988)提出的H2O-NaCl体系盐度-冰点经验公式对包裹体盐度进行计算处理,并制作成盐度-均一温度关系图(图 6)。研究结果表明,两期包裹体的盐度主要处于2.39%~19.20%,其中第一期流体包裹体的盐度为2.39%~13.83%,第二期流体包裹体盐度主要为6.80%~19.20%。
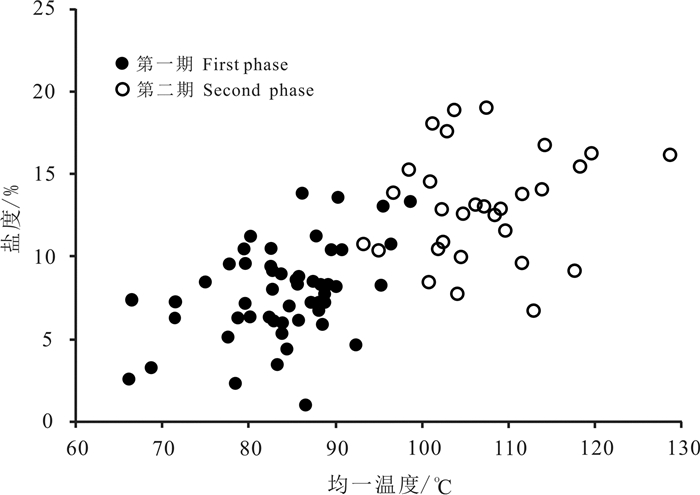
|
图 6 伊陕斜坡吴起地区延10储层包裹体盐度分布 Fig. 6 Salinity distribution of Yan10 reservoir in Wuqi area of Yishan oblique slope |
流体包裹体的密度计算根据刘斌和段光贤(1987)提出的公式,将测得的均一温度和含盐度代入公式,计算得到包裹体密度。根据实验数据处理计算可得流体包裹体密度变化范围主要为0.95~1.13 g/cm3(图 7)。综上包裹体盐度、密度分析可知,早期包裹体对应低盐度、高密度流体,晚期包裹体对应高盐度、低密度流体,体现出一期两幕的成藏模式。
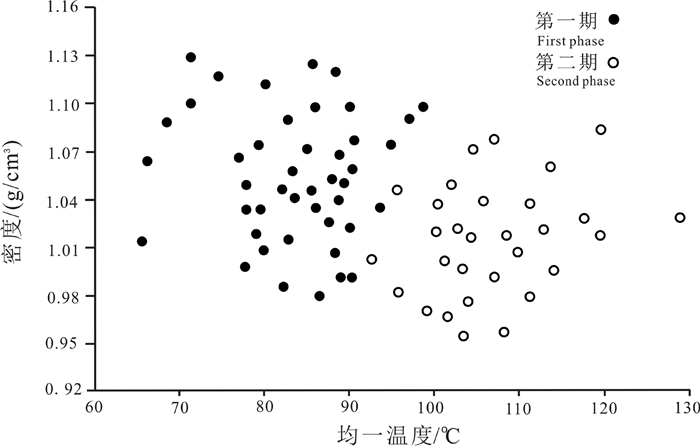
|
图 7 油气包裹体均一温度与密度关系图 Fig. 7 Relationship between homogenization temperature and density of hydrocarbon inclusions |
通过分析均一温度-盐度关系图,得出流体包裹体的盐度与和均一温度呈正相关关系。根据石油充注与流体性质的变化关系,随着烃源岩的成熟度提高,油气充注程度也随之提高,成岩环境由相对开放到相对封闭,溶解于地层水中的烃类和有机酸含量升高(李艳霞等,2003)。导致孔隙水酸性增强,溶解周缘各类岩石,使得K+、Na+、Ca2+等离子迁移释放进入孔隙水中,加之随着温度不断升高,成岩环境由相对开放到相对封闭,其他流体的交换作用逐渐下降,导致地层中流体的盐度升高。
4.3 成藏期次与充注时间目前确定油气成藏时期的主要方法是流体包裹体均一温度法,通过实验测得的流体包裹体均一温度,确定油气发生充注时的古地温,根据古地温梯度进一步确定包裹体的形成深度,再根据研究区的沉积埋藏史图和热演化史图来确定包裹体的形成时间,通过投影确定达到相应温度的地质历史时间,从而判断油气充注时间(Hu et al., 2010;Guo et al., 2012;石刚等,2014;Chen et al., 2017;赵桂萍,2017;吕晓兰,2019;李伟等,2020)。油气成藏的多期次性往往受控于地层埋藏史及其地层温度的演化史,故盆地热演化史恢复是提高成藏期次研究准确性的关键(任战利等,2008)。本次研究将测得的两期包裹体均一温度峰值投影到研究区埋藏史图(W58井)(图 8),通过对比得出如下结论:

|
图 8 伊陕斜坡吴起地区埋藏史图(W58井) Fig. 8 Burial history map of Wuqi Area in Yishan Slope (Well W58) |
第一期油气包裹体形成时间较早,烃源岩成熟度低,油气充注程度相对低,油气充注期次对应于距今112~106 Ma;将第二期油气包裹体相伴生的盐水包裹体均一温度与储层埋藏史、古地温史相结合,说明对应时间距今约102~97 Ma。通过包裹体特征研究,并结合盆地热史等方法,确定了鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡吴起地区延10储层油气成藏时间距今112~97 Ma,为早白垩世末期。本次研究成果与前人的研究成果具有较好的一致性,赵彦德等(2016)对侏罗系延安组油层段砂岩样品进行了伊利石K-Ar同位素定年测试,结果显示鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系油气成藏时期为早白垩世。黄志龙等(2009)对侏罗系延安组延9段砂岩样品进行了研究,结合G71井埋藏史图和K-Ar同位素年龄为105 Ma左右,认为侏罗系油气充注发生在早白垩世末期的构造运动之后。
5 结论(1) 鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡吴起地区侏罗系延安组延10储层主要存在早、晚两期流体包裹体,早期包裹体主要分布在石英次生加大边以及石英颗粒表面的溶蚀裂缝;晚期流体包裹体主要分布在切穿石英颗粒裂缝和石英颗粒表面,同时在晚期硅质胶结物和方解石胶结物中零星分布。
(2) 包裹体均一温度主要集中在70~120℃,早期包裹体均一温度主峰为80~90℃,盐度为2.39%~13.83%,密度为0.98~1.13 g/cm3;晚期包裹体均一温度主峰为100~110℃,盐度为6.80%~19.20%,密度为0.96~1.08 g/cm3。两期包裹体均一温度分布连续,结合两期包裹体盐度、密度特征,体现了研究区一期两幕的成藏模式。
(3) 通过包裹体测温,并结合研究区埋藏史图,确定鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡吴起地区延安组延10储层存在两次连续性油气充注:第一次油气充注期次对应于距今112~106 Ma;第二次油气充注对应时间距今约102~97 Ma。两次油气充注表明研究区油气成藏时期距今112~97 Ma,为早白垩世末期。
Chang Ting, Xu Hao, Zhou Haiyan, Bian Congsheng, Wang Lan, Wang Liang, Guo Jingzhen. 2019. Characteristics of the fluid inclusion and classification of the hydrocarbon accumulation period in Member Qing 2-3 of Taikang Uplift Belt in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 38(2): 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Chen Gang, Ding Chao, Xu liming, Zhang Huiruo, Li Nan, Li Yan, Hu Yanxu, Huang Deshun. 2012. Indirect dating of multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulations by fluid inclusion data: A case study of the Permian hydrocarbon accumulation in the northeast Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(6): 1003-1011 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Chen Gang, Li Shuheng, Zhang Huiruo, Ding Chao, Yang Fu. 2013. Timing and stages of the Permian oil-gas accumulations in northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1453-1465 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.010 |
Chen Ruiqian, Liu Guangdi, Sun Mingliang, Cao Yushun, Liu Xiangbai, Li Qiang. 2022. Study on fluid inclusions and oil and gas accumulation stages in the Middle Proterozoic in the northern Hebei depression[J]. Journal of Geology of Higher Education, 28(1): 64-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Fu S, Liao Z, Chen A, Chen H. 2020. Reservoir characteristics and multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the southwestern Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 38(2): 348-371. |
Goldstein R H. 2001. Fluid inclusions in sedimentary and diagenetic systems[J]. Lithos, 55(1): 159-193. |
Guo X, Liu K, Sheng H, Song G, Wang Y, Hao X, Wang B. 2012. Petroleum generation and charge history of the northern Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Insight from integrated fluid inclusion analysis and basin modelling[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 32(1): 21-35. |
Guo Feifei. 2022. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and reservoir formation stages in the third member of the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in the Nanyang Sag of the Nanxiang Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 33(7): 1049-1059 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. 1988. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H[J]. Economic Geology, 83(1): 197-202. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197 |
Hu G, Jin L, Shan X, Han Z. 2010. The origin of natural gas and the hydrocarbon charging history of the Yulin gas field in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 81(4): 381-391. DOI:10.1016/j.coal.2009.07.016 |
Huang Zhilong, Jiang Qingchun, Xi Shengli, Zhang Caili, Zhang Juhong. 2009. Study on oil and gas accumulation period of Yanchang Formation of Triassic and Jurassic in North Shaanxi slope zone, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 24(1): 21-24, 109 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Jiang Wenqi, Zhang Yunlong, Jiang Li. 2021. Fluid inclusions in buried quartz of the Yanchang sandstone in the Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin, China: Implications for basin evolution and petroleum accumulation[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 39(1): 201-203. |
Jing Chen, Wang Zhaobing, Zhang Delong. 2018. Research progress on fluid inclusion applied to the determination of hydrocarbon accumulation period[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 23(11): 48-54. |
Li Wei, Jiang Bin, Liu Miao, Chen Jingsheng, Li Bin, Yang Fan, Zhang Yujin, Liu Shifeng, Cai Nao. 2020. A study of the fluid inclusions and chronology of the Shanwanzi gold deposit in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 47(2): 394-405 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Li Yanxia, Liu Hongjun, Yuan Dongshan, Zhang Zhihuan, Zhu Youmin, Zhong Dakang. 2003. Effect of oil charging on reservoirs diagenetic mineral evolution[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, (3): 274-280, 295 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.03.017 |
Liu Bin, Duan Guangxian. 1987. The density and isochoric formulae for NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions (salinity≤25 wt%) and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 7(4): 345-352 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1987.04.010 |
Liu Jiang. 2012. Research on Reservoir Characteristics of Fuxian Formation and Yan-10 Oil Reservoir Set in Wuqi Area in Ordos Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1-78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
Liu Runchuan, Ren Zhanli, Ma Kan, Zhang Yuanyuan, Qi Kai, Yu Chunyong, Ren Wenbo, Yang Yan. 2019. Classification of hydrocarbon accumulation phases of Yanchang Formation in Southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 33(6): 1263-1274 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Lu Huanzhang. 2014. Fluid inclusion petrography: A discussion[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 20(2): 177-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.002 |
Luo Chunyan, Luo Jinglan, Luo Xiaorong, Bai Xuejian, Lei Yuhong, Cheng Ming. 2014. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and its application in analysis of hydrocarbon accumulation stages from the Chang 8 sandstone in the Middle West Area of Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 20(4): 623-634 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.04.014 |
Luo Xiao, Jiang Zhenxue, Li Zhuo, Li Feng, Liu Jianliang, Gao Tian, Feng Jie. 2015. The properties of petroleum inclusions and stages of hydrocarbon accumulation in Mesozoic-Cenozoic reservoirs in Yingmaili area of Tabei uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(1): 60-66 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Lü Xiaolan. 2019. Application of fluid inclusions in hydrocarbon accumulation research[J]. China Petroleum & Chemical Standards & Quality, 39(2): 103-105 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2019.02.049 |
Pang xiongqi. 2010. Key challenges and research methods of petroleum exploration in the deep of superimposed basins in western China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 31(5): 517-534, 541 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Ren Dazhong, Sun Wei, Huang Hai, Liu Dengke, Qu Xuefeng, Lei Qihong. 2016. Genetic mechanism of Chang 6 tight sandstone reservoir in Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Sciences, 41(10): 1735-1744 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Ren Zhanli, Liu Li, Cui Junping, Xiao Hui, Gao Shengli. 2008. Application of tectonic-thermal evolution history to hydrocarbon accumulation timing in sedimentary basins[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 29(4): 502-506 (in Chinese with English abstract). DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.04.013 |
Schubert F, Diamond L W, Toth TM. 2007. Fluid-inclusion evidence of petroleum migration through a buried metamorphic dome in the Pannonian Basin, Hungary[J]. Chemical Geology, 244(3/4): 357-381. |
Shao Xiaozhou, Li Yong, Zhang Wenxuan, Guo Yixuan, Zhao Yande,
Zhang Xiaolei, Qi Yalin, Chu Meijuan. 2020. The fluid inclusion
characteristics and petroleum accumulation of Chang 8 tight
sandstone in northern Shaanxi, Ordos Basin[J/OL]. Geology in
China, 1-15 http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200623.1304.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
Shen Jian. 2020. Carbonate cementation characteristics and genetic mechanism of tight sandstone reservoirs in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 32(2): 24-32 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Shi Baohong, Zhang Yan, Zhang Lei, Yang Yajuan, Li Hui. 2012. Hydrocarbon accumulation dating by fluid inclusion characteristics in Chang 7 tight sandstone reservoirs of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 34(6): 599-603 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Shi Gang, Zhang Jinchuan, Tang Xuan, Jing Tieya, Bian Ruikang. 2014. Timing and stages of oil and gas accumulation in western Tanhai[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 21(3): 41-44, 152 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Song Tushun, Liu Li, LI Fulai, Liu Na, Zhou Bing. 2015. The study of the tight sandstone reservoir's characteristics and the fluid inclusions in Fuyu oil layer, Daqing Placanticline[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 89(S1): 79-80. DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.12302_34 |
Tang Jianyun, Zhang Gang, Shi Zheng, Zhang Xing, Chen Yubao. 2019. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and hydrocarbon accumulation stages of Yanchang Formation in Fengfuchuan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 31(3): 20-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Tao Shizhen. 2006. Sequence of diagenetic authigenic mineral: The basis of timing the inclusions formation in sedimentary rocks[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, (2): 154-160 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Tian Yaming, Shi Zejin, Song Jianghai, Qi Yalin, Gao Xiang, Zou Yongdong. 2011. Fluid Inclusion Characteristics of Chang 6-Chang 8 Reservoirs in the Triassic Yanchang Formation of the Yichuan-Xunyi Area[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 30(1): 80-87 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Wang Ping. 1997. Mineral Resources of Fuxian county[M]. Xi 'an: Northwest University Press, 1-125 (in Chinese).
|
Wu Xiaoli, Xu Wanglin, Li Rongxi, Li Ningxi, Liu Qi, Zhao Di, Zhao Bangsheng, Qin Xiaoli, Bai Ying. 2022. Origin of hydrogen sulfide in the Majiagou Formation of the Ordovician in the central and eastern Ordos Basin: Evidence from fluid inclusions[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 43(2): 250-261 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Xin Cunlin, Xu Mingru, An Guobao, Hu Juying, Yang Tao, Dong Kai. 2019. Deposit geology, fluid inclusion characteristics and ore genesis of the Matoushan Cu-Au deposit in Southwest Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 46(6): 1556-1572 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Xue Nan, Zhu Guangyou, Lv Xiuxiang, He Tao, Wu Zhenghui. 2020. Advances in geochronology of hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 31(12): 1733-1748 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Yang Zhi, Fu Jinhua, Guo Qiulin, Lin Senhu, Chen Ningsheng, Pan Songqi, Li Shixiang. 2017. Discovery, characteristics and resource potential of continental tight oil in Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 22(6): 9-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Ye Bo, Liang Xiaowei, Song Juan, Cao Runrong, Mao Zhenhua, Hao Bingying. 2018. Reservoir accumulation characteristics of Jurassic Yan'an Formation in Yanwu area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 30(4): 65-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhang Junfeng, Xu Hao, Zhao Junlong, Ren Pengfei. 2018. Geological characteristics and exploratial of oil and gas in the northeast area of China[J]. Geology in China, 45(2): 260-273 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhang Yachao, Li Xianqing, Wei Qiang, Sun Kexin, Xie Zengye, Xiao Zhongyao. 2020. Characteristics of paleo-fluid and hydrocarbon charge history of Jurassic reservoir in Dibei gas field, Kuqa depression[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 5(4): 353-363 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Guiping. 2017. Characterization of fluid inclusions and timing of gas accumulation in Upper Paleozoic reservoirs of Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 38(5): 905-912 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Jingzhou. 2002. Geochronology of petroleum accumulation: New advances and the future trend[J]. Advances in Earth Science, (3): 378-383 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Yande, Qi Yalin, Luo Anxiang, Cheng Dangxing, Li Jihong, Huang Jinxiu. 2016. Application of fluid inclusion and authigenic illite dating to reconstruct the hydrocarbon charging history of Jurassic reservoirs in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 46(6): 1637-1648 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhao Yutao, Shao mingli, Jia Kexin, Lin Shuang, Tang Min. 2017. Hydrocarbon accumulation stages of deep reservoir in Huajia tectonic zone of Dehui depression of Songliao basin based on evidence of fluid inclusions[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 41(1): 73-81, 139-140 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
Zhou Xiaodong, Guo Kunyi, Chen Guoguang, Zeng Yong, Song Shiming. 2013. Geological and ore-forming fluid characteristics of vein type copper deposits in northern Ningwu area[J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1622-1633 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
昌婷, 许浩, 周海燕, 卞从胜, 王岚, 王亮, 郭景震. 2019. 松辽盆地泰康隆起带青二、三段储层流体包裹体特征与成藏期次[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 38(2): 8-15. |
陈刚, 丁超, 徐黎明, 章辉若, 李楠, 李岩, 胡延旭, 黄得顺. 2012. 多期次油气成藏流体包裹体间接定年——以鄂尔多斯盆地东北部二叠系油气藏为例[J]. 石油学报, 33(6): 1003-1011. |
陈刚, 李书恒, 章辉若, 丁超, 杨甫, 雷盼盼. 2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部二叠系油气成藏的时间和期次[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1453-1465. |
陈睿倩, 柳广弟, 孙明亮, 曹玉顺, 刘祥柏, 李强. 2022. 冀北坳陷中元古界流体包裹体与油气成藏期次研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 28(1): 64-72. |
郭飞飞. 2022. 南襄盆地南阳凹陷古近系核桃园组三段储层流体包裹体特征与成藏期次[J]. 天然气地球科学, 33(7): 1049-1059. |
黄志龙, 江青春, 席胜利, 张才利, 张菊红. 2009. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北斜坡带三叠系延长组和侏罗系油气成藏期研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 24(1): 21-24, 109. |
李伟, 江斌, 刘淼, 陈井胜, 李斌, 杨帆, 张渝金, 刘世峰, 蔡闹. 2020. 内蒙古赤峰山湾子金矿流体包裹体和年代学研究[J]. 中国地质, 47(2): 394-405. |
李艳霞, 刘洪军, 袁东山, 张枝焕, 朱筱敏, 钟大康. 2003. 石油充注对储层成岩矿物演化的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, (3): 274-280, 295. |
刘斌, 段光贤. 1987. NaCl-H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报, 7(4): 345-352. |
刘犟. 2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区侏罗系富县组—延10油层组储层特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 1-78.
|
刘润川, 任战利, 马侃, 张园园, 祁凯, 于春勇, 任文波, 杨燕. 2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组油气成藏期次研究[J]. 现代地质, 33(6): 1263-1274. |
卢焕章. 2014. 流体包裹体岩相学的一些问题探讨[J]. 高校地质学报, 20(2): 177-184. |
罗春艳, 罗静兰, 罗晓容, 白雪见, 雷裕红, 程明. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地中西部长8砂岩的流体包裹体特征与油气成藏期次分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 20(4): 623-634. |
罗枭, 姜振学, 李卓, 李峰, 刘建良, 高甜, 冯洁. 2015. 英买力地区中生界—新生界油气藏石油包裹体特征及成藏期次[J]. 石油学报, 36(1): 60-66. |
吕晓兰. 2019. 流体包裹体在油气成藏研究中的应用[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 39(2): 103. |
庞雄奇. 2010. 中国西部叠合盆地深部油气勘探面临的重大挑战及其研究方法与意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 31(5): 517-534, 541. |
任大忠, 孙卫, 黄海, 刘登科, 屈雪峰, 雷启鸿. 2016. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油田长6致密砂岩储层成因机理[J]. 地球科学, 41(10): 1735-1744. |
任战利, 刘丽, 崔军平, 肖晖, 高胜利. 2008. 盆地构造热演化史在油气成藏期次研究中的应用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 29(4): 502-506. |
邵晓州, 李勇, 张文选, 郭懿萱, 赵彦德, 张晓磊, 齐亚林, 楚美娟. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北地区长8致密砂岩流体包裹体特征与石油成藏[J/OL]. 中国地质, 1-15. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200623.1304.004.html.
|
沈健. 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区致密砂岩储层碳酸盐胶结物特征及成因机理[J]. 岩性油气藏, 32(2): 24-32. |
石刚, 张金川, 唐玄, 荆铁亚, 边瑞康. 2014. 辽河滩海西部地区油气成藏时间和成藏期次[J]. 特种油气藏, 21(3): 41-44, 152. |
时保宏, 张艳, 张雷, 杨亚娟, 李慧. 2012. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7致密储层流体包裹体特征与成藏期次[J]. 石油实验地质, 34(6): 599-603. |
唐建云, 张刚, 史政, 章星, 陈玉宝. 2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地丰富川地区延长组流体包裹体特征及油气成藏期次[J]. 岩性油气藏, 31(3): 20-26. |
陶士振. 2006. 自生矿物序次是确定包裹体期次的根本依据[J]. 石油勘探与开发, (2): 154-160. |
田亚铭, 施泽进, 宋江海, 齐亚林, 吴晓明, 高翔, 邹永东. 2011. 宜川—旬邑地区长6~长8储层流体包裹体特征及意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 30(1): 80-87. |
王平. 1997. 富县的矿产资源[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1-125.
|
吴小力, 徐旺林, 李荣西, 李宁熙, 刘齐, 赵迪, 赵帮胜, 覃小丽, 白莹. 2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部奥陶系马家沟组硫化氢成因——来自流体包裹体的证据[J]. 石油学报, 43(2): 250-261. |
辛存林, 徐明儒, 安国堡, 胡菊英, 杨涛, 董凯. 2019. 川西南马头山铜金矿床地质和流体包裹体特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 46(6): 1556-1572. |
薛楠, 朱光有, 吕修祥, 贺涛, 吴郑辉. 2020. 油气成藏年代学研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 31(12): 1733-1748. |
杨智, 付金华, 郭秋麟, 林森虎, 陈宁生, 潘松圻, 李士祥. 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组陆相致密油发现、特征及潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 22(6): 9-15. |
叶博, 梁晓伟, 宋娟, 曹润荣, 毛振华, 郝炳英. 2018. 鄂尔多斯盆地演武地区侏罗系延安组油藏成藏特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 30(4): 65-73. |
张君峰, 许浩, 赵俊龙, 任鹏飞. 2018. 中国东北地区油气地质特征与勘探潜力展望[J]. 中国地质, 45(2): 260-273. |
张亚超, 李贤庆, 魏强, 孙可欣, 谢增业, 肖中尧. 2020. 库车坳陷迪北气藏侏罗系储层古流体特征与油气充注史[J]. 矿业科学学报, 5(4): 353-363. |
赵桂萍. 2017. 鄂尔多斯杭锦旗地区上古生界储层流体包裹体特征与天然气成藏时期[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 38(5): 905-912. |
赵靖舟. 2002. 油气成藏年代学研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, (3): 378-383. |
赵彦德, 齐亚林, 罗安湘, 程党性, 李继宏, 黄锦绣. 2016. 应用流体包裹体和自生伊利石测年重构鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系油藏烃类充注史[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(6): 1637-1648. |
赵玉涛, 邵明礼, 贾可心, 林爽, 唐敏. 2017. 松辽盆地德惠断陷华家构造带深层储层油气成藏期次—来自流体包裹体证据[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 41(1): 73-81, 139-140. |
周小栋, 郭坤一, 陈国光, 曾勇, 宋世明, 申金超. 2013. 宁芜北部脉状铜矿床地质与成矿流体特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1622-1633. |